5.3.3: Quadratic Formula and Complex Sums
- Page ID
- 4161
Solve quadratic equations with complex roots, and add and subtract complex numbers.
Complex Roots of Quadratic Functions
The quadratic function \(y=x^2−2x+3\) (shown below) does not intersect the x-axis and therefore has no real roots. What are the complex roots of the function?
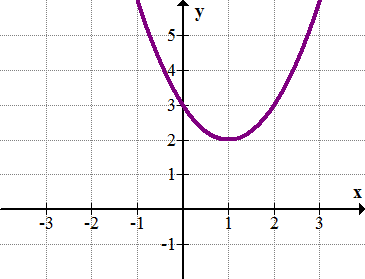
Complex Roots of Quadratic Functions
Recall that the imaginary number, \(i\), is a number whose square is –1:
\(\textcolor{red}{i^2=−1}\) and \(\textcolor{red}{i=\sqrt{−1}}\)
The sum of a real number and an imaginary number is called a complex number. Examples of complex numbers are \(5+4i\) and \(3−2i\). All complex numbers can be written in the form a+bi where a and b are real numbers. Two important points:
- The set of real numbers is a subset of the set of complex numbers where \(b=0\). Examples of real numbers are 2,7,12,−4.2.
- The set of imaginary numbers is a subset of the set of complex numbers where a=0. Examples of imaginary numbers are \(i\), \(−4i\), \(\sqrt{2}i\).
This means that the set of complex numbers includes real numbers, imaginary numbers, and combinations of real and imaginary numbers.
When a quadratic function does not intersect the x-axis, it has complex roots. When solving for the roots of a function algebraically using the quadratic formula, you will end up with a negative under the square root symbol. With your knowledge of complex numbers, you can still state the complex roots of a function just like you would state the real roots of a function.
Let's solve the quadratic equation: \(m^2−2m+5=0\)
You can use the quadratic formula to solve. For this quadratic equation, \(a=1\), \(b=−2\), \(c=5\).
\(\begin{array}{l}
m=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
m=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{-2}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{-2})^{2}-4(\textcolor{red}{1})(\textcolor{red}{5})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{1})} \\
m=\dfrac{2 \pm \sqrt{4-20}}{2} \\
m=\dfrac{2 \pm \sqrt{-16}}{2} \quad \sqrt{-16}=\sqrt{16} \times i=4 i \\
m=\dfrac{2 \pm 4 i}{2} \\
m=1 \pm 2 i \\
m=1+2 i \text { or } m=1-2 i
\end{array}\)
There are no real solutions to the equation. The solutions to the quadratic equation are \(1+2i\) and \(1−2i\).
Now, let's solve the following equation by rewriting it as a quadratic and using the quadratic formula:
\(\dfrac{3}{e+3}−\dfrac{2}{e+2}=1\)
To rewrite as a quadratic equation, multiply each term by \((e+3)(e+2)\).
\(\begin{aligned} \dfrac{3}{e+3} \textcolor{red}{(e+3)(e+2)}−2e+2\textcolor{red}{(e+3)(e+2)}=1\textcolor{red}{(e+3)(e+2)} \\ 3(e+2)−2(e+3)=(e+3)(e+2) \end{aligned}\)
Expand and simplify.
\(\begin{aligned} 3e+6−2e−6=e^2+2e+3e+6 \\ e^2+4e+6=0 \end{aligned}\)
Solve using the quadratic formula. For this quadratic equation, a=1,b=4,c=6.
\(\begin{array}{l}
e=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
e=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{4}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{4})^{2}-4(\textcolor{red}{1})(\textcolor{red}{6})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{1})} \\
e=\dfrac{-4 \pm \sqrt{16-24}}{2} \\
e=\dfrac{-4 \pm \sqrt{-8}}{2} \quad \sqrt{-8}=\sqrt{8} \times i=\sqrt{4 \cdot 2} \times i=2 i \sqrt{2} \\
e=\dfrac{-4 \pm 2 i \sqrt{2}}{2} \\
e=-2 \pm i \sqrt{2} \\
e=-2+i \sqrt{2} \text { or } e=-2-i \sqrt{2}
\end{array}\)
There are no real solutions to the equation. The solutions to the equation are −2+i\sqrt{2} and −2−i\sqrt{2}
Finally, let's sketch the graph of the following quadratic function. What are the roots of this function?
\(y=x^2−4x+5\)
Use your calculator or a table to make a sketch of the function. You should get the following:
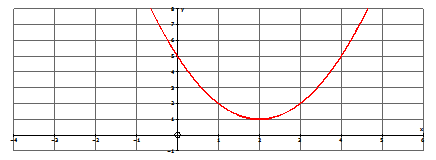
As you can see, the quadratic function has no x-intercepts; therefore, the function has no real roots. To find the roots (which will be complex), you must use the quadratic formula.
For this quadratic function, \(a=1\), \(b=−4\), \(c=5\).
\(\begin{array}{l}
x=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
x=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{-4}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{-4})^{2}-4\textcolor{red}{1})(\textcolor{red}{5})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{1})} \\
x=\dfrac{4 \pm \sqrt{16-20}}{2} \\
x=\dfrac{4 \pm \sqrt{-4}}{2} \quad \sqrt{-4}=\sqrt{4} \times i=2 i \\
x=\dfrac{4 \pm 2 i}{2} \\
x=2 \pm i \\
x=2+i \text { or } x=2-i
\end{array}\)
The complex roots of the quadratic function are 2+i and 2−i.
Earlier, you were asked to find the complex roots of \(y=x^2−2x+3\).
Solution
To find the complex roots of the function \(y=x^2−2x+3\), you must use the quadratic formula.
For this quadratic function, \(a=1\), \(b=−2\), \(c=3\).
\(\begin{array}{l}
x=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
x=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{-2}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{-2})^{2}-4(\textcolor{red}{1})(\textcolor{red}{3})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{1})} \\
x=\dfrac{2 \pm \sqrt{4-12}}{2} \\
x=\dfrac{2 \pm \sqrt{-8}}{2} \quad \sqrt{-8}=\sqrt{8} \times i=2 \sqrt{2} i \\
x=\dfrac{2 \pm 2 \sqrt{2} i}{2} \\
x=1 \pm \sqrt{2} i
\end{array}\)
Solve the following quadratic equation. Express all solutions in simplest radical form.
\(2n^2+n=−4\)
Solution
\(2n^2+n=−4\)
Set the equation equal to zero.
\(2n^2+n+4=0\)
Solve using the quadratic formula.
\(\begin{array}{l}
x=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
n=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{1}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{1})^{2}-4(\textcolor{red}{2})(\textcolor{red}{4})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{2})} \\
n=\dfrac{-1 \pm \sqrt{1-32}}{4} \\
n=\dfrac{-1 \pm \sqrt{-31}}{4} \\
n=\dfrac{-1 \pm i \sqrt{31}}{4}
\end{array}\)
Solve the following quadratic equation. Express all solutions in simplest radical form.
\(m^2+(m+1)^2+(m+2)^2=−1\)
Solution
\(m^2+(m+1)^2+(m+2)^2=−1\)
Expand and simplify.
\(\begin{aligned} m^2+(m+1)(m+1)+(m+2)(m+2)&=−1 \\ m^2+m^2+m+m+1+m^2+2m+2m+4&=−1 \\ 3m^2+6m+5&=−1 \end{aligned}\)
Write the equation in general form.
\(3m^2+6m+6=0\)
Divide by 3 to simplify the equation.
\(\begin{aligned} \dfrac{3m^2}{\textcolor{red}{3}}+\dfrac{6m}{\textcolor{red}{3}}+\dfrac{6}{\textcolor{red}{3}}&=\dfrac{0}{\textcolor{red}{3}} \\ m^2+2m+2&=0 \end{aligned}\)
Solve using the quadratic formula:
\(\begin{array}{l}
m=\dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a} \\
m=\dfrac{-(\textcolor{red}{2}) \pm \sqrt{(\textcolor{red}{2})^{2}-4(\textcolor{red}{1})(\textcolor{red}{2})}}{2(\textcolor{red}{1})} \\
m=\dfrac{-2 \pm \sqrt{4-8}}{2} \\
m=\dfrac{-2 \pm \sqrt{-4}}{2} \\
m=\dfrac{-2 \pm 2 i}{2} \\
m=-1 \pm i
\end{array}\)
Is it possible for a quadratic function to have exactly one complex root?
Solution
No, even in higher degree polynomials, complex roots will always come in pairs. Consider when you use the quadratic formula-- if you have a negative under the square root symbol, both the + version and the - version of the two answers will end up being complex.
Review
- If a quadratic function has 2 x-intercepts, how many complex roots does it have? Explain.
- If a quadratic function has no x-intercepts, how many complex roots does it have? Explain.
- If a quadratic function has 1 x-intercept, how many complex roots does it have? Explain.
- If you want to know whether a function has complex roots, which part of the quadratic formula is it important to focus on?
- You solve a quadratic equation and get 2 complex solutions. How can you check your solutions?
- In general, you can attempt to solve a quadratic equation by graphing, factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. If a quadratic equation has complex solutions, what methods do you have for solving the equation?
Solve the following quadratic equations. Express all solutions in simplest radical form.
- \(x^2+x+1=0\)
- \(5y^2−8y=−6\)
- \(2m^2−12m+19=0\)
- \(−3x^2−2x=2\)
- \(2x^2+4x=−11\)
- \(−x^2+x−23=0\)
- \(−3x^2+2x=14\)
- \(x^2+5=−x\)
- \(\dfrac{1}{2}d^2+4d=−12\)
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 9.7.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| complex number | A complex number is the sum of a real number and an imaginary number, written in the form \(a+bi\). |
| complex root | A complex root is a complex number that, when used as an input (\(x\)) value of a function, results in an output (\(y\)) value of zero. |
| Imaginary Numbers | An imaginary number is a number that can be written as the product of a real number and i. |
| Quadratic Formula | The quadratic formula states that for any quadratic equation in the form \(ax^2+bx+c=0\), \(x=\dfrac{−b\pm \sqrt{b^2−4ac}}{2a}\). |
| Real Number | A real number is a number that can be plotted on a number line. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers. |
Additional Resources
Video: Using the Quadratic Formula
Practice: Quadratic Formula and Complex Sums

