19.8: Life and the Geologic Time Scale
- Page ID
- 6054
Does this look more like geologic time?
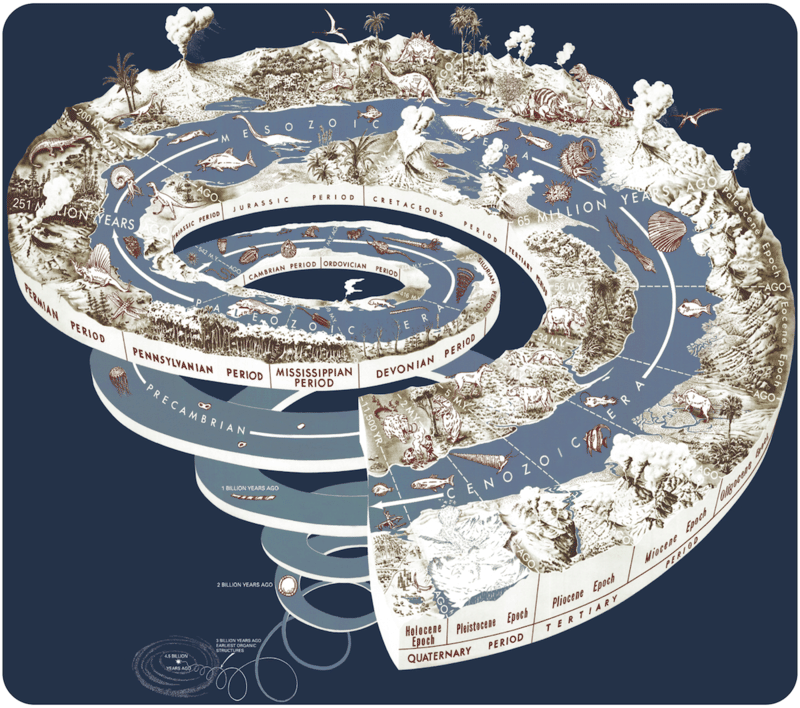
This image gives some sense of what life forms appeared when. Take a good look. It's pretty amazing!
Life and the Geologic Time Scale
The geologic time scale may include illustrations of how life on Earth has changed. Major events on Earth may also be shown. These include the formation of the major mountains or the extinction of the dinosaurs. The figure above is a different kind of the geologic time scale. It shows how Earth’s environment and life forms have changed.
Your Place in Geologic Time
We now live in the Phanerozoic Eon, the Cenozoic Era, the Quarternary Period, and the Holocene Epoch. Phanerozoic means visible life. During this eon, rocks contain visible fossils. Before the Phanerozoic, life was microscopic. The Cenozoic Era means new life. It encompasses the most recent forms of life on Earth. The Cenozoic is sometimes called the Age of Mammals. Before the Cenozoic came the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Mesozoic means middle life. This is the age of reptiles, when dinosaurs were abundant. The Paleozoic is old life. Organisms like invertebrates and fish were the most common lifeforms.
The Quaternary Period is the time since the beginning of the ice ages. The climate has been cooler than it was earlier in the Cenozoic. Since the end of the Pleistocene ice ages, which are probably not entirely over, we have been in the Holocene Epoch. The Holocene is also called the Recent.
Summary
- Complex life forms evolved relatively late in geologic time.
- The Holocene is a teeny part of Earth history. Humans evolved very recently.
- The last 540 million years has seen an incredible amount of biodiversity.
Review
- Why do we not know exactly when life first evolved on Earth?
- When did life become abundant?
- Where do humans appear in this graphic? Is that where you would expect them to be?