20.8: Petroleum Power
- Page ID
- 6077
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)What is this unusual sight?
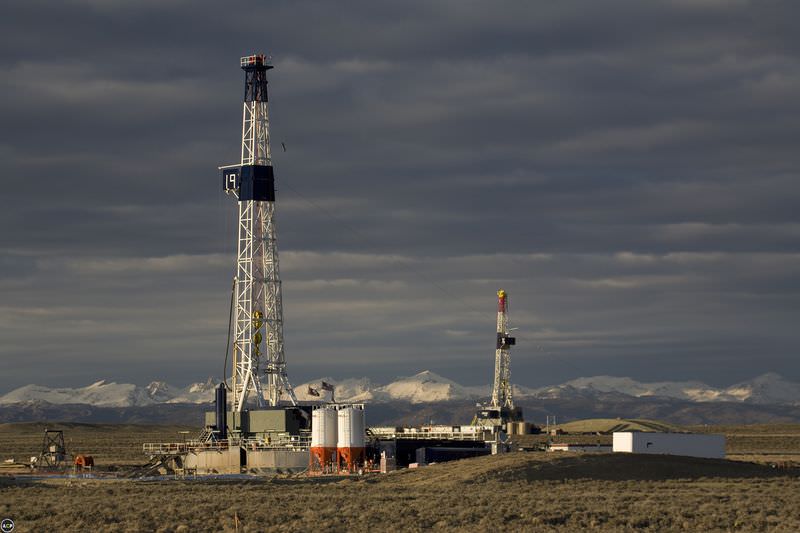
There's oil beneath this land. These drill rigs are pumping it to the surface. Drill rigs can be small and closely spaced. They can be large and solitary. This is true, especially when they are in deep water offshore.
Oil
Oil is a thick, dark brown or black liquid. It is found in rock layers of Earth's crust. Oil is currently the most commonly used source of energy in the world.
How Oil Forms
The way oil forms is similar, in many ways, to coal. Tiny organisms like plankton and algae die and settle to the bottom of the sea. Sediments settle over the organic material. Oxygen is kept away by the sediments. When the material is buried deep enough, it is exposed to high heat and pressure. Over millions of years, the organic material transforms into liquid oil.
Mining Oil
The United States produces only about one-quarter as much oil as it uses. The main oil producing regions in the U.S. are the Gulf of Mexico, Texas, Alaska, and California.
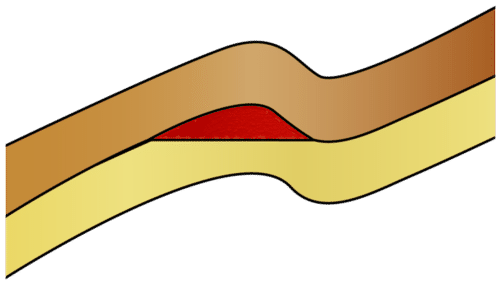
Geologists look for oil in folded layers of rock called anticlines (Figure below). Oil moves through permeable rock and is trapped by the impermeable cap rock.
Oil (red) is found in the porous rock layer (yellow) and trapped by the impermeable layer (brown). The folded structure has allowed the oil to pool so a well can be drilled into the reservoir.
Types of Oil
Oil comes out of the ground as crude oil. Crude oil is a mixture of many different hydrocarbons. Oil is separated into different compounds at an oil refinery. This is done by heating the oil. Each hydrocarbon compound in crude oil boils at a different temperature. We get gasoline, diesel, heating oil, waxes, plastics, and fertilizers from crude oil.
These fuels are rich sources of energy. Since they are mostly liquids, they can be easily transported. These fuels provide about 90% of the energy used for transportation around the world.
Gasoline
Gasoline is a concentrated resource. It contains a large amount of energy for its weight. This is important because the more something weighs, the more energy is needed to move it. If gasoline could provide only a little energy, a car would have to carry a lot of it to be able to travel very far, or the car would need to be filled up frequently. So a highly concentrated energy resource is a practical fuel to power cars and other forms of transportation.
Let's consider how gasoline powers a car. As gasoline burns, it releases most of its energy as heat. It also releases carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. The heat makes the gases expand. This forces the pistons inside the engine to move. The engine makes enough power to move the car.
Using Oil
Using gasoline to power automobiles affects the environment. The exhaust fumes from burning gasoline cause air pollution. These pollutants include smog and ground-level ozone. Air pollution is a big problem for cities where large numbers of people drive every day. Burning gasoline also produces carbon dioxide. This is a greenhouse gas and is a cause of global warming. Similar pollutants come from other forms of oil.
Summary
- Petroleum is a liquid fossil fuel. Petroleum is useful for vehicles because it is easily stored and transported.
- Petroleum is also used to make waxes, plastics, fertilizers, and other products.
- Using petroleum causes smog and global warming.
Review
- What makes petroleum unique among fossil fuels? Why is this unique property extremely important?
- Besides powering your car, what is petroleum used for?
- How does crude oil form?
Explore More
Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
- What produced the fossil fuels?
- What role does sediment play in petroleum formation?
- What is kerogen?
- How does oil get trapped so that we can drill to it?
- How do we find oil?
- How do we get the oil out of the ground?
- Why is drilling mud pumped down the pipe?
- What are cuttings?
- What does the pumping unit do?
- What happens at the refinery? What does fractional distillation produce?
- What are petrochemicals used for?
- What other products are made from oil?