2.7: Importance of International Trade
- Page ID
- 1692
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Importance of International Trade
The international market is important not just in terms of the goods and services it provides to a country, but as a market for that country’s goods and services. Because foreign demand for U.S. exports is almost as large as investment and government purchases as a component of aggregate demand, it can be very important in terms of growth.
Universal Generalizations
- Trade affects neither the economy's natural level of employment nor its real wage in the long run; those are determined by the demand for and the supply curve of labor.
- Growth in international trade has outpaced growth in world output over the past five decades.
- The chief determinants of net exports are domestic and foreign incomes, relative price levels, exchange rates, domestic and foreign trade policies, and preferences and technology.
- A change in the price level causes a change in net exports that moves the economy along its aggregate demand curve. This is the international trade effect.
- A change in net exports produced by one of the other determinants of net exports will shift the aggregate demand curve by an amount equal to the initial change net exports times the multiplier.
Guiding Questions
- How does specialization facilitate trade between individuals and nations?
- How does importing and exporting affect the economy of the United States and the trading partners of the United States?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of having trade barriers?
- How do changes made to the exchange rate impact imports and exports?
Video: Imports, Exports, and Exchange Rates
The Case for Trade
International trade increases the quantity of goods and services available to the world’s consumers. By allocating resources according to the principle of comparative advantage, trade allows nations to consume combinations of goods and services they would be unable to produce on their own, combinations that lie outside each country’s production possibilities curve.
When an economy or individual can produce more of any good per unit of labor than another country or individual, that country or person is said to have an absolute advantage. A country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good if it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost than can other countries. If each country specializes in the production of goods in which it has a comparative advantage and trades those goods for things in which other countries have a comparative advantage, global production of all goods and services will be increased. The result can be higher levels of consumption for all.
If international trade allows expanded world production of goods and services, it follows that restrictions on trade will reduce world production. That is the economic case for free trade. It suggests that restrictions on trade, such as a tariff, a tax imposed on imported goods and services, or a quota, a ceiling on the quantity of specific goods and services that can be imported, reduce world living standards.
The conceptual argument for free trade is a compelling one; virtually all economists support policies that reduce barriers to trade. Economists were among the most outspoken advocates for the 1993 ratification of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which virtually eliminated trade restrictions between Mexico, the United States, and Canada, and the 2004 Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA), which did the same for trade between the United States, Central America, and the Dominican Republic. Most economists have also been strong supporters of worldwide reductions in trade barriers, including the 1994 ratification of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), a pact slashing tariffs and easing quotas among 117 nations, including the United States, and the Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations, named after the site of the first meeting in Doha, Qatar, in 2001 and still continuing. In Europe, member nations of the European Union (EU) have virtually eliminated trade barriers among themselves, and 15 EU nations now have a common currency, the euro, and a single central bank, the European Central Bank, established in 1999. Trade barriers have also been slashed among the economies of Latin America and of Southeast Asia. A treaty has been signed that calls for elimination of trade barriers among the developed nations of the Pacific Rim (including the United States and Japan) by 2010 and among all Pacific Rim nations by 2020.
The global embrace of the idea of free trade demonstrates the triumph of economic ideas over powerful forces that oppose free trade. One source of opposition to free trade comes from the owners of factors of production used in industries in which a nation lacks a comparative advantage.
A related argument against free trade is that it not only reduces employment in some sectors but also reduces employment in the economy as a whole. In the long run, this argument is clearly wrong. The economy’s natural level of employment is determined by forces unrelated to trade policy, and employment moves to its natural level in the long run.
Further, trade has no effect on real wage levels for the economy as a whole. The equilibrium real wage depends on the economy’s demand for and supply curve of labor. Trade affects neither.
In the short run, trade does affect aggregate demand. Net exports are one component of aggregate demand; a change in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve and affects real GDP in the short run. All other things unchanged, a reduction in net exports reduces aggregate demand, and an increase in net exports increases it.
Protectionist sentiment always rises during recessions. The recession that began in the United States in 2007 is no exception. The stimulus bill contained a provision ordering U.S. government agencies and contractors to purchase goods and services produced in the United States in preference to goods and services from other countries. Our trading partners have already begun threatening a trade war as a result of this provision. The stimulus bill does say that the “buy America first” provision should be “consistent with international obligations.” As yet, it is not clear how significant this provision would become.
Videos: Comparative Advantage and Comparative Advantage Practice
View the video below for a lesson on comparative advantage. The second video provides practice with the concept of comparative advantage.
The Case for Trade
International trade increases the quantity of goods and services available to the world’s consumers. By allocating resources according to the principle of comparative advantage, trade allows nations to consume combinations of goods and services they would be unable to produce on their own, combinations that lie outside each country’s production possibilities curve.
When an economy or individual can produce more of any good per unit of labor than another country or individual, that country or person is said to have an absolute advantage. A country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good if it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost than can other countries. If each country specializes in the production of goods in which it has a comparative advantage and trades those goods for things in which other countries have a comparative advantage, global production of all goods and services will be increased. The result can be higher levels of consumption for all.
If international trade allows expanded world production of goods and services, it follows that restrictions on trade will reduce world production. That is the economic case for free trade. It suggests that restrictions on trade, such as a tariff, a tax imposed on imported goods and services, or a quota, a ceiling on the quantity of specific goods and services that can be imported, reduce world living standards.
The conceptual argument for free trade is a compelling one; virtually all economists support policies that reduce barriers to trade. Economists were among the most outspoken advocates for the 1993 ratification of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which virtually eliminated trade restrictions between Mexico, the United States, and Canada, and the 2004 Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA), which did the same for trade between the United States, Central America, and the Dominican Republic. Most economists have also been strong supporters of worldwide reductions in trade barriers, including the 1994 ratification of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), a pact slashing tariffs and easing quotas among 117 nations, including the United States, and the Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations, named after the site of the first meeting in Doha, Qatar, in 2001 and still continuing. In Europe, member nations of the European Union (EU) have virtually eliminated trade barriers among themselves, and 15 EU nations now have a common currency, the euro, and a single central bank, the European Central Bank, established in 1999. Trade barriers have also been slashed among the economies of Latin America and of Southeast Asia. A treaty has been signed that calls for elimination of trade barriers among the developed nations of the Pacific Rim (including the United States and Japan) by 2010 and among all Pacific Rim nations by 2020.
The global embrace of the idea of free trade demonstrates the triumph of economic ideas over powerful forces that oppose free trade. One source of opposition to free trade comes from the owners of factors of production used in industries in which a nation lacks a comparative advantage.
A related argument against free trade is that it not only reduces employment in some sectors but also reduces employment in the economy as a whole. In the long run, this argument is clearly wrong. The economy’s natural level of employment is determined by forces unrelated to trade policy, and employment moves to its natural level in the long run.
Further, trade has no effect on real wage levels for the economy as a whole. The equilibrium real wage depends on the economy’s demand for and supply curve of labor. Trade affects neither.
In the short run, trade does affect aggregate demand. Net exports are one component of aggregate demand; a change in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve and affects real GDP in the short run. All other things unchanged, a reduction in net exports reduces aggregate demand, and an increase in net exports increases it.
Protectionist sentiment always rises during recessions. The recession that began in the United States in 2007 is no exception. The stimulus bill contained a provision ordering U.S. government agencies and contractors to purchase goods and services produced in the United States in preference to goods and services from other countries. Our trading partners have already begun threatening a trade war as a result of this provision. The stimulus bill does say that the “buy America first” provision should be “consistent with international obligations.” As yet, it is not clear how significant this provision would become.
Videos: Comparative Advantage and Comparative Advantage Practice
View the video below for a lesson on comparative advantage. The second video provides practice with the concept of comparative advantage.
The Rising Importance of International Trade
International trade is important, and its importance is increasing. From 1965 to 2007, world output rose by about 300%. The gains in total exports were even more spectacular; they soared by over 1,000%!
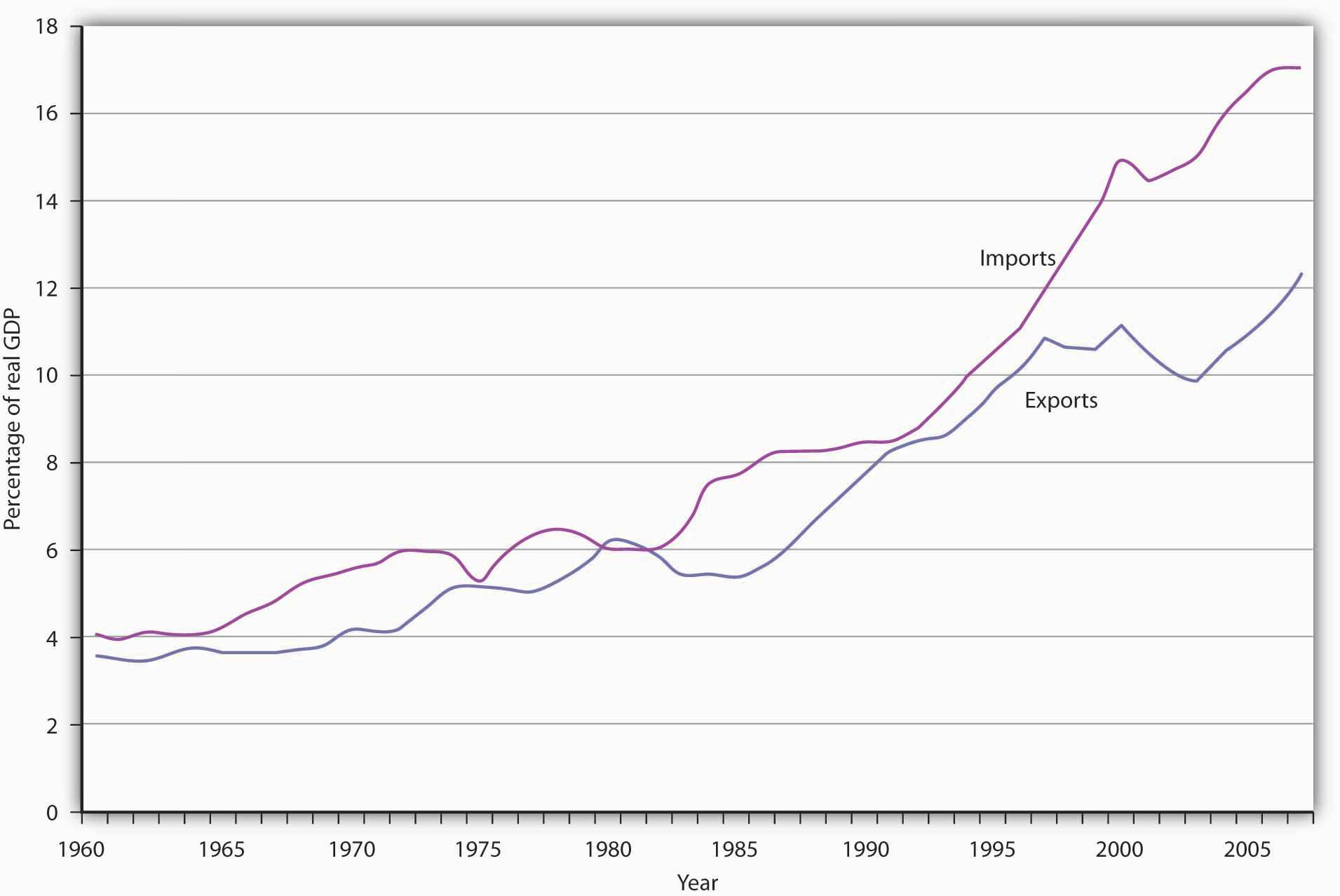
While international trade was rising around the world, it was playing a more significant role in the United States as well. In 1960, exports represented just 3.6% of real GDP; by 2007, exports accounted for 12.4% of real GDP. Figure 7.2.1 "U.S. Exports and Imports Relative to U.S. Real GDP, 1960–2007" shows the growth in exports and imports as a percentage of real GDP in the United States from 1960 to 2007.
Why has world trade risen so spectacularly? Two factors have been important. First, advances in transportation and communication have dramatically reduced the costs of moving goods around the globe. The development of shipping containerization that allows cargo to be moved seamlessly from trucks or trains to ships, which began in 1956, drastically reduced the cost of moving goods around the world, by as much as 90%. As a result, the numbers of container ships and their capacities have markedly increased. [1] Second, we have already seen that trade barriers between countries have fallen and are likely to continue to fall.
U.S. Exports and Imports Relative to U.S. Real GDP, 1960–2007
 [Figure1]
[Figure1]
The chart shows exports and imports as a percentage of real GDP from 1960 through the second quarter of 2007.
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Table 1.1.6 (Revised December 23, 2008).
Net Exports and the Economy
As trade has become more important worldwide, exports and imports have assumed increased importance in nearly every country on the planet. We have already discussed the increased shares of U.S. real GDP represented by exports and by imports. We will find in this section that the economy both influences and is influenced by, net exports. First, we will examine the determinants of net exports and then discuss the ways in which net exports affect aggregate demand.
Determinants of Net Exports
Net exports equal exports minus imports. Many of the same forces affect both exports and imports, albeit in different ways.
Income Effect
As incomes in other nations rise, the people of those nations will be able to buy more goods and services—including foreign goods and services. Any one country’s exports thus will increase as incomes rise in other countries and will fall as incomes drop in other countries.
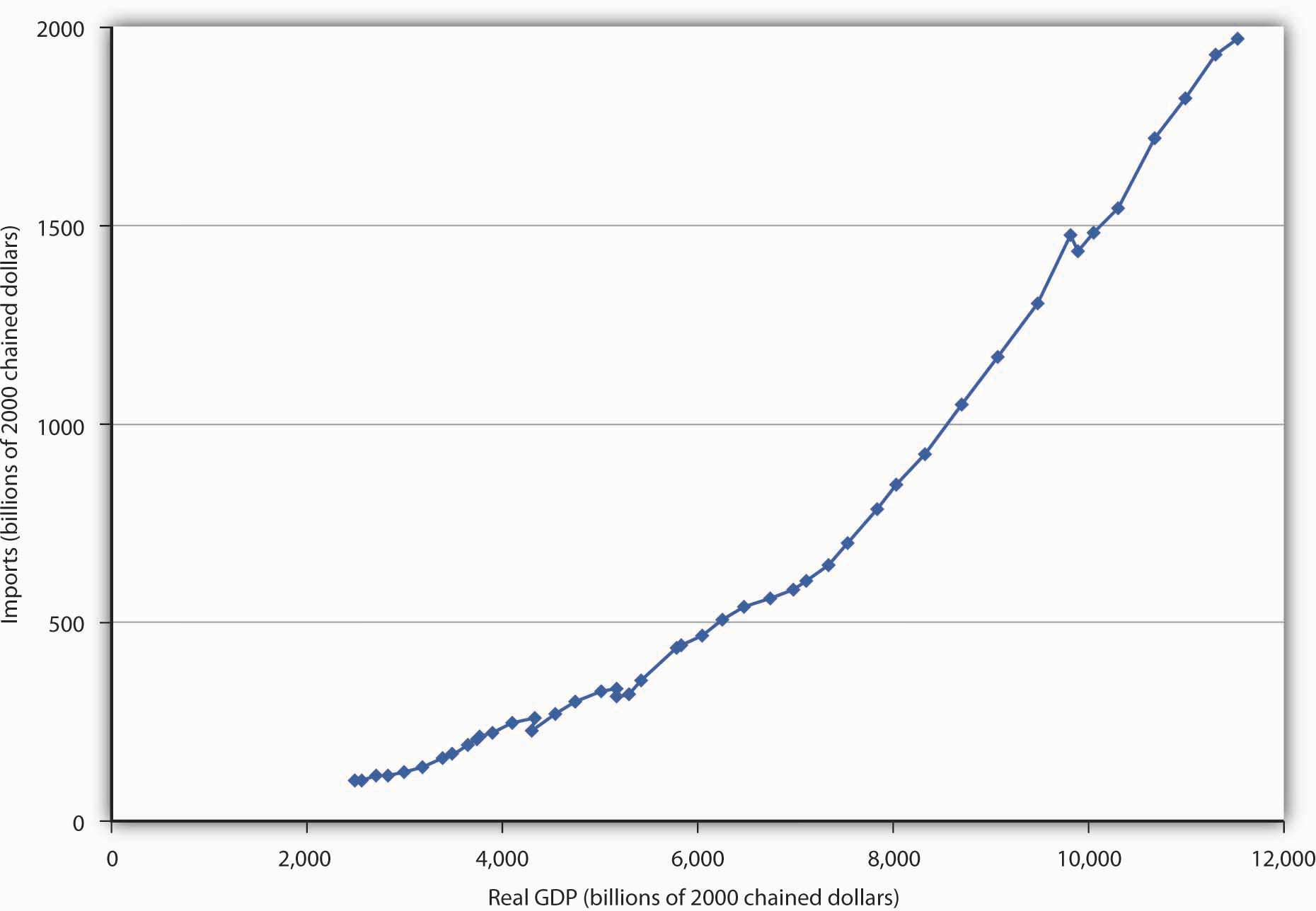
A nation’s own level of income affects its imports the same way it affects consumption. As consumers have more income, they will buy more goods and services. Because some of those goods and services are produced in other nations, imports will rise. An increase in real GDP thus boosts imports; a reduction in real GDP reduces imports. Figure 2 shows the relationship between real GDP and the real level of import spending in the United States from 1960 through 2007. Notice that the observations lie close to a straight line one could draw through them and resemble a consumption function.
U.S. Real GDP and Imports, 1960–2007
[Figure2]
The chart shows annual values of U.S. real imports and real GDP from 1960 through 2007. The observations lie quite close to a straight line.
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Table 1.1.6 (Revised December 23, 2008).
Relative Prices
A change in the price level within a nation simultaneously affects exports and imports. A higher price level in the United States, for example, makes U.S. exports more expensive for foreigners and, for this reason, tends to reduce exports. At the same time, a higher price level in the United States makes foreign goods and services relatively more attractive to U.S. buyers and thus increases imports. A higher price level therefore reduces net exports. A lower price level encourages exports and reduces imports, increasing net exports. As we saw in the chapter that introduced the aggregate demand and supply model, the negative relationship between net exports and the price level is called the international trade effect and is one reason for the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve.
The Exchange Rate
The purchase of U.S. goods and services by foreign buyers generally requires the purchase of dollars, because U.S. suppliers want to be paid in their own currency. Similarly, purchases of foreign goods and services by U.S. buyers generally require the purchase of foreign currencies, because foreign suppliers want to be paid in their own currencies. An increase in the exchange rate means foreigners must pay more for dollars, and must thus pay more for U.S. goods and services. It therefore reduces U.S. exports. At the same time, a higher exchange rate means that a dollar buys more foreign currency. That makes foreign goods and services cheaper for U.S. buyers, so imports are likely to rise. An increase in the exchange rate should thus tend to reduce net exports. A reduction in the exchange rate should increase net exports.
Trade Policies
A country’s exports depend on its own trade policies as well as the trade policies of other countries. A country may be able to increase its exports by providing some form of government assistance (such as special tax considerations for companies that export goods and services, government promotional efforts, assistance with research, or subsidies). A country’s exports are also affected by the degree to which other countries restrict or encourage imports. The United States, for example, has sought changes in Japanese policies toward products such as U.S.-grown rice. Japan banned rice imports in the past, arguing it needed to protect its own producers. That has been a costly strategy; consumers in Japan typically pay as much as 10 times the price consumers in the United States pay for rice. Japan has given in to pressure from the United States and other nations to end its ban on foreign rice as part of the GATT accord. That will increase U.S. exports and lower rice prices in Japan.
Similarly, a country’s imports are affected by its trade policies and by the policies of its trading partners. A country can limit its imports of some goods and services by imposing tariffs or quotas on them—it may even ban the importation of some items. If foreign governments subsidize the manufacture of a particular good, then domestic imports of the good might increase. For example, if the governments of countries trading with the United States were to subsidize the production of steel, then U.S. companies would find it cheaper to purchase steel from abroad than at home, increasing U.S. imports of steel.
Preferences and Technology
Consumer preferences are one determinant of the consumption of any good or service; a shift in preferences for a foreign-produced good will affect the level of imports of that good. The preference among the French for movies and music produced in the United States has boosted French imports of these services. Indeed, the shift in French preferences has been so strong that the government of France, claiming a threat to its cultural heritage, has restricted the showing of films produced in the United States. French radio stations are fined if more than 40% of the music they play is from “foreign” (in most cases, U.S.) rock groups.
Changes in technology can affect the kinds of capital firms import. Technological changes have changed production worldwide toward the application of computers to manufacturing processes, for example. This has led to increased demand for high-tech capital equipment, a sector in which the United States has a comparative advantage and tends to dominate world production. This has boosted net exports in the United States.
Net Exports and Aggregate Demand
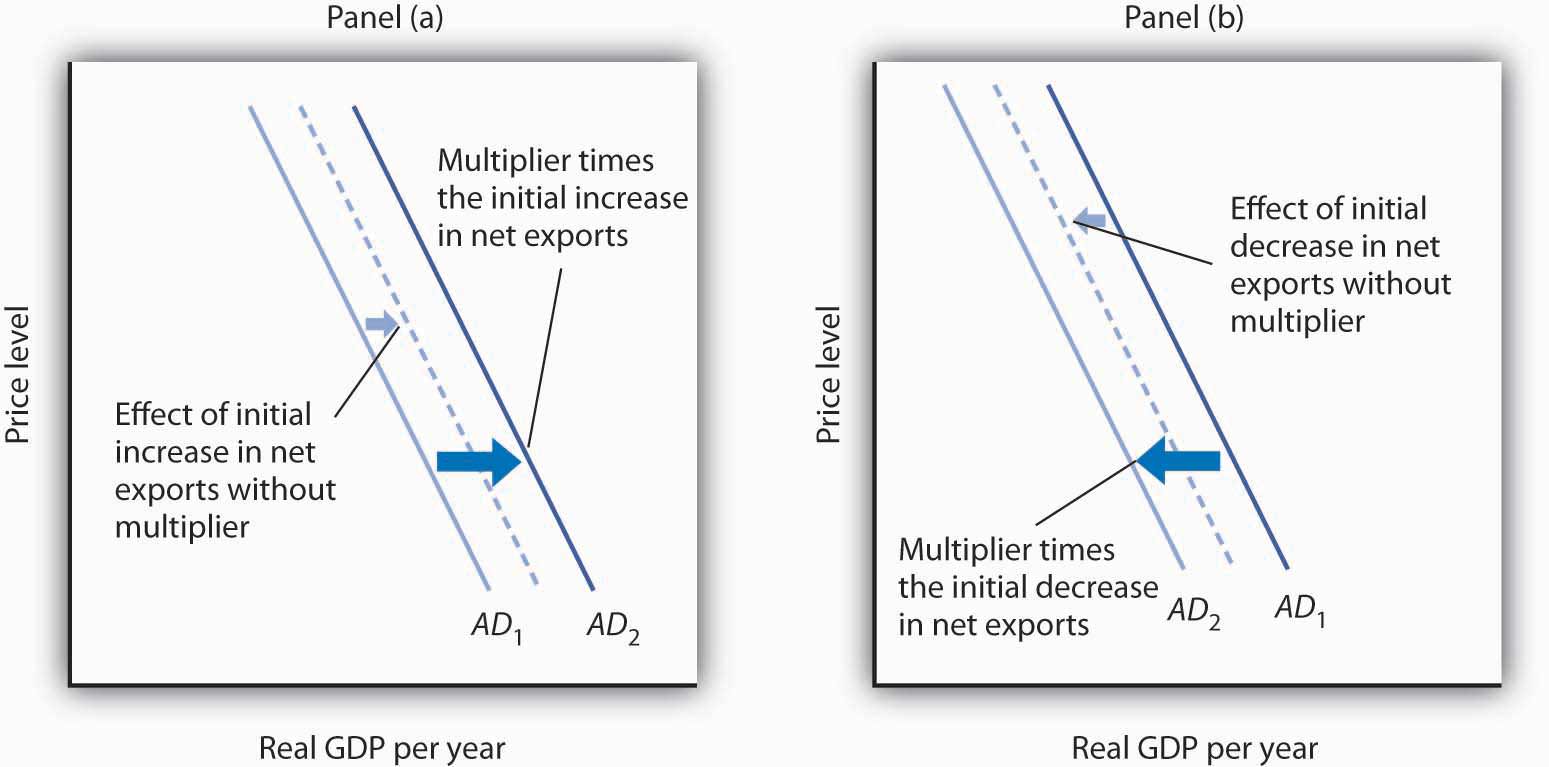
Net exports affect both the slope and the position of the aggregate demand curve. A change in the price level causes a change in net exports that moves the economy along its aggregate demand curve. This is the international trade effect. A change in net exports produced by one of the other determinants of net exports listed above (incomes and price levels in other nations, the exchange rate, trade policies, and preferences and technology) will shift the aggregate demand curve. The magnitude of this shift equals the change in net exports times the multiplier, as shown in Figure 3. Panel (a) shows an increase in net exports; Panel (b) shows a reduction. In both cases, the aggregate demand curve shifts by the multiplier times the initial change in net exports, provided there is no other change in the other components of aggregate demand.
Changes in Net Exports and Aggregate Demand
 [Figure3]
[Figure3]
In Panel (a), an increase in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by an amount equal to the multiplier times the initial change in net exports. In Panel (b), an equal reduction in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left by the same amount.
Changes in net exports that shift the aggregate demand curve can have a significant impact on the economy. The United States, for example, experienced a slowdown in the rate of increase in real GDP in the second and third quarters of 1998—virtually all of this slowing was the result of a reduction in net exports caused by recessions that staggered economies throughout Asia. The Asian slide reduced incomes there and thus reduced Asian demand for U.S. goods and services. We will see in the next section another mechanism through which difficulties in other nations can cause changes in a nation’s net exports and its level of real GDP in the short run.
 Answer the Try It! problems below to monitor your understanding of the concepts in this section.
Answer the Try It! problems below to monitor your understanding of the concepts in this section.Try It! Problems
Draw graphs showing the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves in each of four countries: Mexico, Japan, Germany, and the United States. Assume that each country is initially in equilibrium with a real GDP of Y1 and a price level of P1. Now show how each of the following four events would affect aggregate demand, the price level, and real GDP in the country indicated.
- The United States is the largest foreign purchaser of goods and services from Mexico. How does an expansion in the United States affect real GDP and the price level in Mexico?
- Japan’s exchange rate falls sharply. How does this affect the price level and real GDP in Japan?
- A wave of pro-German sentiment sweeps France, and the French sharply increase their purchases of German goods and services. How does this affect real GDP and the price level in Germany?
- Canada, the largest importer of U.S. goods and services, slips into a recession. How does this affect the price level and real GDP in the United States?
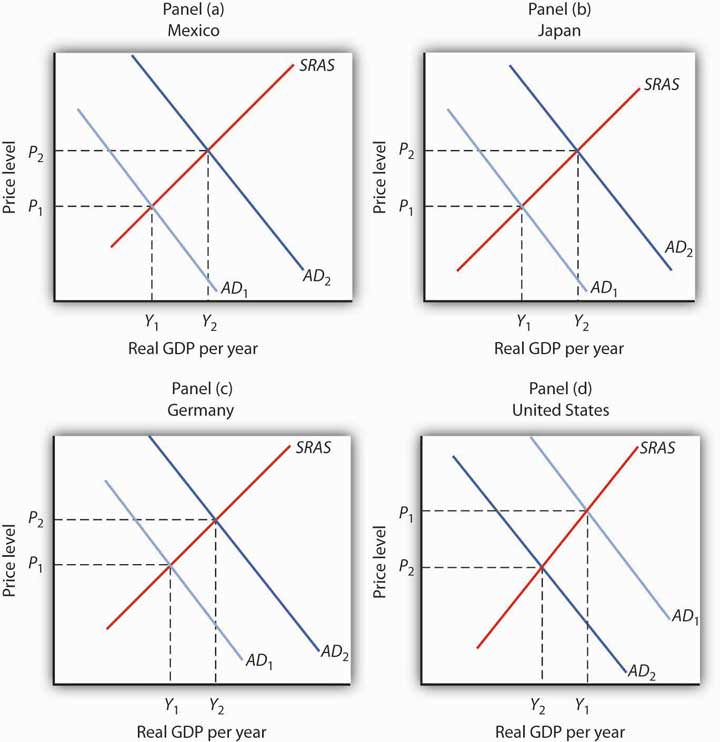 [Figure 4]
[Figure 4]- Answer
-
- Mexico’s exports increase, shifting its aggregate demand curve to the right. Mexico’s real GDP and price level rise, as shown in Panel (a).
- Japan’s net exports rise. This event shifts Japan’s aggregate demand curve to the right, increasing its real GDP and price level, as shown in Panel (b).
- Germany’s net exports increase, shifting Germany’s aggregate demand curve to the right, increasing its price level and real GDP, as shown in Panel (c).
- U.S. exports fall, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left, which will reduce the price level and real GDP, as shown in Panel (d).

