5.2: European Historical Development Patterns (2 Days)
- Page ID
- 1882
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Summarize briefly how the Roman Empire and the Viking era contributed to European development.
- Describe how European colonialism changed or influenced other countries.
- Explain the major developments that prompted the Industrial Revolution.
- Describe the impact of the rural-to-urban shift and its impact on urbanization specifically.
- Define the concept of a nation-state and explain how this applies to Europe.
- Explain how cultural forces can positively or negatively influence political units.
- List the three main language groups and the three main religious denominations of Europe.
TEKS Regional World Geography Unit 05: Chapter 5.2 European Historical Development Patterns
WG.1A Analyze the effects of physical and human geographic patterns and processes on events in the past and describe their effects on present conditions, including significant physical features and environmental conditions that influenced migration patterns in the past and shaped the distribution of culture groups today.
WG.2B Assess how people’s changing perceptions of geographic features have led to changes in human societies.
WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural characteristics.
WG.6A Locate and describe human and physical features that influence the size and distribution of settlements.
WG.16C Compare life in a variety of cities and nations in the world to evaluate the relationships involved in political, economic, social, and environmental changes.
WG.16D Compare life in a variety of urban and rural areas in the world to evaluate political, economic, social, and environmental changes.
WG.17A Describe and compare patterns of culture such as language, religion, land use, systems of education, and customs that make Europe distinctive.
WG.21A Analyze and evaluate the validity and utility of multiple sources of geographic information such as primary and secondary sources, aerial photographs and maps.
WG.21B Locate places of contemporary geopolitical significance on a map.,
WG.22A Design and draw appropriate graphics, such as maps, diagrams, tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, distributions, and relationships.
WG.22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
TEKS and ELPS for Regional World Geography Unit 05--Europe from TEKS Resource System
European Historical Development Patterns
Europe did not become a center for world economics with high standards of living by accident. Historical events in global development have favored this realm because of its physical geography and cultural factors. In southern Europe, the Greeks provided ideas, philosophy, and organization. Greek thinkers promoted the concept of democracy. The Romans carried the concept of an empire to new levels.
From about 150 B.C.E. to 475 C.E., the Romans brought many ideas together and controlled a large portion of Europe and North Africa. The Roman Empire introduced a common infrastructure to Europe. The Romans connected their world by building roads, bridges, aqueducts, and port facilities. They understood how to rule an empire. By taking advantage of the best opportunities of each region they controlled, they encouraged the best and most-skilled artisans to focus on what they did best.
The focus on encouraging the work of skilled artisans created the specialization of goods and a market economy. No longer did everyone have to make everything for themselves. They could sell in the market what they produced and purchase products made by others, which would be of higher quality than what they could make at home. Regions that specialized in certain goods due to local resources or specialty skills could transport those goods to markets long distances away. The Roman Empire connected southern Europe and North Africa.
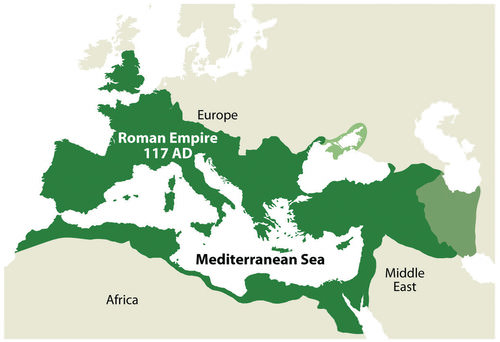
This map illustrates the extent of the Roman Empire, 117 CE.
The Vikings of Scandinavia (Norway, Sweden, and Denmark; 900–1200 C.E.) are often referred to as rogue bands of armed warriors who pillaged and plundered northern Europe. Though they were fierce warriors in battle, they were farmers, skilled craftsmen, and active traders. They developed trade routes throughout the north. Using their seafaring knowledge and skills, the Vikings used Europe’s waterways for transportation.
The Vikings were the early developers of the northern world from Russia to Iceland and even to North America. They developed colonies in Iceland, Greenland, and what is present-day Canada. Their longships were renowned for versatility and provided an advantage on the sea. The Vikings made advances deep into Europe—all the way to Constantinople. The records of history show that the Byzantine Empire employed Scandinavian Vikings as mercenaries.
In a general sense, the regions to the west of Scandinavia—such as Iceland, Scotland, Ireland, and Greenland—were targeted by the Norwegian Vikings. Southern regions such as England and France were more often destinations of the Danish Vikings. Russia and areas of Eastern Europe were standard trading grounds for the Swedish Vikings, though the different Viking groups could occasionally be found in the same destinations. The present-day Scandinavian countries were established after the main Viking period. The Vikings connected northern Europe with trade during the Dark Ages.
Colonialism
It wasn’t until after the Dark Ages of Europe ended that a rebirth of ideas, technology, and progress took hold. The Renaissance of the late 15th century prompted activity in Europe that changed the world. In 1492, Columbus and his three ships crossed the Atlantic to land on the shores of the Americas. This event symbolized the beginning of the era of European colonialism.
Colonialism’s effects remain in the colonies or protectorates that European countries still possess. Colonialism was fueled by the economic concept of mercantilism that included the drive of governments to control trade, promoting the acquisition of wealth by the quick gain of gold or silver from their colonies.
Colonialism included the development of colonies outside the home country, usually for the expansion of imperial power and the exploitation of material gain. The building of larger ships and an understanding of sea travel allowed an exchange of new goods and ideas between continents. North and South America were opened up to the European explorers for colonial expansion. European colonialism brought newfound wealth from the colonies back to Europe.
All the regions of the world outside of Europe were targeted for colonialism. Africa was divided up, Latin America was created, and Asia became a location for resources and trade. The few powerful countries along the Atlantic coast of Europe began the drive to dominate their world. If you live in the Western Hemisphere, consider the language you speak and the borders of your country. Both were most likely products of European colonialism. Most of the current political geographic boundaries were drawn up or shaped through colonial conflict or agreement

The founding of Santiago de Chile in 1541.
The Agrarian Revolution
The post-Renaissance era introduced a number of agricultural changes that impacted European food production. Before this time, most agricultural methods were primitive and labor intensive, but new technologies were introduced that greatly enhanced agricultural production. Plows, seeders, and harvesting technologies were introduced. Land reform and land ownership transitioned to adapt to the changing times.
These innovations supported the expanding port cities that created urban markets for agricultural surpluses. Colonial ships returned from the colonies with new crops such as potatoes. This era’s progress in agricultural advancements is often referred to as the agrarian revolution. The agrarian revolution led to industrial developments such as the steam tractor and steel implements that further advanced agricultural production worldwide.
The Industrial Revolution
Great Britain, being an island country, developed the world’s largest navy and took control of the seas. Their colonial reach extended from what is now Canada to Australia. The Industrial Revolution, initiated in northern England in the late 1700s, introduced an industrial period that changed how humans produced products. The shift to coal for energy, the use of the steam engine for power, the smelting of iron, and the concept of mass production changed how goods were produced.

Mass production during the Industrial Revolution prompted a rural-to-urban shift in the population. Coal for energy and steam for power energized industrial activities.
The development of the steam-powered engine provided a mobile power source. Waterwheels powered by steep-flowing rivers or streams were an early source of power. With coal for fuel and steam for power, the engines of industry were mobile and moved full speed ahead. Power looms converted textiles such as cotton and wool into cloth. Powered by a steam engine, a power loom could operate 24 hours a day and could be located anywhere. Industrialization with cheap labor and adequate raw materials brought enormous wealth to the industrial leaders and their home countries,
With the mass production of goods and advancements in technology, there was a major shift in human labor. Fewer people were needed on the farms, and more workers were needed in factories. There was a large rural-to-urban shift in the human population. Europe experienced the development of the major cities of its realm during this period. In Britain, for example, in 1800 only 9 percent of the population lived in urban areas. By 1900, about 62 percent were urban dwellers. As of 2010, it is more than 90 percent. Europe, as a whole, is about 75 percent urban. As a comparison, the population in the United States is approximately 80 percent urban.
The Industrial Revolution, which started in northern England’s Pennine mountain chain, rippled through Europe and across the Atlantic to the United States. The majority of countries in Europe are currently in stage 5 of the index of economic development. The five stages of the index of economic development illustrate a pattern of development and population dynamics for a country or region.
The model outlines how rural societies with an agrarian economy in stage 1 can make the transition to stage 5, which is the stage that indicates an urban society with a consumer economy. As a general trend, when a country’s levels of industrial activity and urban growth rise, the outcome is usually a higher standard of living and smaller family sizes. Additionally, the rural-to-urban shift takes place, driven by the pull of opportunities and advantages in the industrializing and urbanizing areas. Countries in stage 5 of the index have small families with a fertility rate below the replacement level. Their incomes, based on a consumer economy, are generally at high levels.
As Europe industrialized and progressed through the stages of the index of economic development, certain core regions reached the postindustrial stages earlier than others. Western Europe established a core industrial region with an extended periphery. The postindustrial activity in this core area continues today in four main centers of innovation:
- Stuttgart in southern Germany
- Lyon in southeastern France
- Milan in northern Italy
- Barcelona in northeastern Spain.
These four industrial centers have been referred to as the Four Motors of Europe because they promote business and industry for the European community. The European core region extends as far as Stockholm in the north to Barcelona in the south.
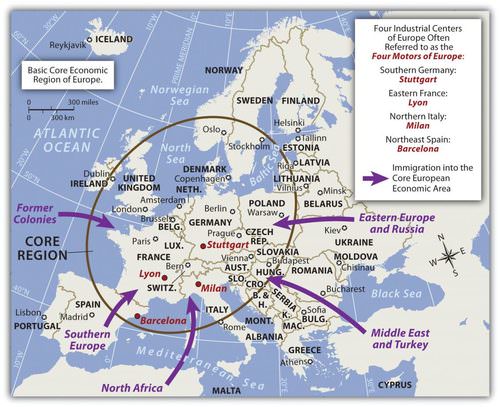
Attractive “pull” forces draw immigrants to the core economic area of Europe, seeking opportunity and advantage. “Push” forces cause people to leave an area due to negative cultural or environmental forces, and/or the lack of opportunity and advantage.
Central Business Districts and Primate Cities
European urban development centered on port cities that had industrial activity. Ships could import raw materials, the factories could manufacture the goods, and the ships could export the products. A central business district (CBD) developed around these activities. Since walking was the main transportation mode, all business activities had to be located in the same vicinity. Banks, retail shops, food markets, and residential dwellings had to be close to the factories and port facilities. Modern cities emerged from this industrialization process, and Europe is one of the more urban realms on the planet.
Many European countries have one main primary city that is more than twice as large as their second city. The term primate city indicates a city that is more than twice as large as their second city and exceptionally expressive of national feeling and heritage. One may think that the primate city is the same as the capital city of a country. However, this is not always the case.
Primate cities represent a country and are symbolic of the country’s heritage and character. Though common, not all countries of the world have a primate city. Financial and business centers in cities such as London, Rome, or Paris support the industrial activity that led to their development as primate cities. Most primate cities are ports or are located on a major river.
The Rural-to-Urban Shift and Population Growth
Consider the trend that the Industrial Revolution brought to Europe. Do you remember the population growth principle? This principle states that as countries industrialize and urbanize, family size naturally goes down and incomes traditionally go up. Integrate this with the rural-to-urban shift that occurs when countries progress through the five stages of the index of economic development. By understanding these basic trends, one can determine the average family size in Europe and why it is declining.
Because Europe is an urbanized realm, one can understand why family size in Europe is small. Various countries in Europe have negative population growth rates. Family size in Spain and Italy is around 1.2, with the average family size in all of Europe at 1.4 children. The replacement rate to maintain an even population-growth pattern would be a fertility rate of about 2.1 children.
Small families do not provide enough young people to cover the available entry-level service jobs. Europe is in stage 5 of the index of economic development and is facing low or negative population growth and a lack of a cheap labor supply. As a core economic global power, Europe has experienced an increase in immigration. With a lower fertility rate and an increase in postindustrial activity, Europe draws people from poorer peripheral countries and peripheral regions within Europe who are looking for opportunities and advantages.
With the planet’s human population increasing overall, one might think that a smaller family size is a positive trend. However, if there are fewer young people in a community—fewer children and fewer people of employment age—consider how this affects the economic situation. With a declining European population, who will apply for the entry-level jobs? Economic core areas attract immigrants seeking opportunities and advantages, and Europe follows this pattern.
There has been increasing tension between the long-standing European cultural groups and immigrants from developing countries who often speak non-European languages or follow religions other than Christianity. The main religion of immigrants from North Africa or the Middle East is Islam, which is the fastest-growing religion in Europe.
There are six main reasons for the declining family size in Europe:
- The high cost of living makes supporting a large family expensive.
- Confined living spaces in urban areas are expensive for larger families.
- Young people are naturally putting off marriage and family until they are older.
- Family planning and health care for women is available.
- More people are earning an education and putting off having children.
- More women choose professional careers and have fewer children.
The following problems arise with the decline in family size in Europe:
- Fewer children result in a shrinking workforce for entry-level jobs.
- The workforce is getting older and more professionals are retiring.
- Pension costs are increasing and there are fewer younger workers to pay for them.
- The tax burden is shifting to fewer younger professionals in the workplace.
- More revenues are needed to pay for the health care of a larger population of senior citizens.
- Immigrants seeking employment may not share the same cultural heritage or values.
Nation-States and Devolution
The agrarian revolution and the Industrial Revolution were powerful movements that altered human activity in many ways. New innovations in food production and the manufacturing of products transformed Europe, which in turn impacted the rest of the world. Even before the agrarian revolution was under way, other transitions in European political currents were undermining the established empire, such as warfare and territorial disputes.
The political revolution that transformed Europe was a result of ending continual warfare and introducing peaceful agreements that recognized the sovereignty of representative government. Various treaties and revolutions continued to shift the power from dictators and monarchs to the general population. The Treaty of Westphalia in 1648 and those that followed helped establish a sense of peace and stability for Central Europe. The French Revolution (1789–95) was an example of the political transformation taking place across Europe to establish democratic processes for governance.
The political revolution laid the groundwork for a sense of nationalism that transformed Europe into nation-states. The term nation refers to a homogeneous group of people with a common heritage, language, religion, or political ambition. The term state refers to the government. When nations and states come together, there is a true nation-state, wherein most citizens share a common heritage and a united government.
European countries are at the point where the concept of forming or remaining a nation-state is a driving force in many political sectors. Most Europeans want to be a member of a nation-state, where there is a shared culture, heritage, and government. The result of the drive for nation-states in Europe is an Italy for Italians, a united Germany for Germans, and a France for the French, for example. Though the political borders of many European countries resemble nation-states, creating a nation-state is unlikely because of the diversity.
Various ethnic populations in Europe desire their own nation-states within their countries of residence. They want to devolve or separate from the larger state. The term devolution refers to the process where regions or people within a state demand independence and autonomy at the central government’s expense. There are now a number of cases where devolution is occurring in Europe. For example, Scotland and Wales seek to devolve from the United Kingdom. The Basque region between Spain and France would like to have its own nation-state. Former Yugoslavia broke up into seven smaller nation-states. Various other minority groups in Europe seek similar arrangements. Thus, cohesive cultural forces and divisive cultural forces are active in the European community.
Centrifugal and Centripetal Forces
Cultural forces continually apply pressure on a country. Some of these cultural forces pull the nation together (centripetal forces) and others pull it apart (centrifugal forces). Primary sources of these cultural forces include religion, language, ethnicity, politics, and economic conditions.
Centrifugal Forces Divide a State
- Ethnic Conflict
- Social Injustice
- Poverty
- Dictatorial Leadership
- Religious Intolerance
- Nationalism
- Loss of Rights
- Any Other Divisive Force
Centripetal Forces Hold a State Together
- Ethnic Unity and Tolerance
- Social/Economic Equity
- Just and Fair Legal System
- Charismatic Leadership
- Religious Acceptance
- Nationalism
- Common Heritage
- Common Language
- Any Other Unifying Force
Centrifugal forces happen when there is division, conflict, or confrontation. Centripetal forces happen when there is unification, agreement, or nationalism. The sources that tie a country together can also be the sources that divide a country. Ethnic unity can be a positive force, while ethnic division and conflict can be a divisive force. If centrifugal forces become strong, the result may be war. Unity can also be evident through national struggles, such as the nationalism displayed immediately after the 9/11 terrorist attacks in the United States. After the attacks, an outpouring of goodwill and agreement strengthened the bonds within the United States.
To understand our world, it is helpful to understand the cultural forces that are active in any one location. Disagreement, inequity, or injustice related to the cultural factors of ethnicity, religion, language, and economics of a region or country is the cause of most conflicts. The strong personalities that provide leadership can similarly prove to be powerful forces that either divide or unite a nation. An example of cultural forces in conflict in Europe can be found in Northern Ireland, where political forces use religious differences as a means of social division.
Religion and Language in Europe
Europe has historically been considered a Christian realm. The three main branches of Christianity in Europe are Roman Catholic, Protestant, and Eastern Orthodox. Rome has been the geographical base for the Roman Catholic Church since the Roman Empire. Operating on the Romance language, Latin, the Catholic Church has provided southern Europe with a common religion for over 1,500 years.
The Roman Catholic Church split when Constantinople (present-day Istanbul), gained preeminence. The Eastern Orthodox Church launched itself as the primary organization in the Slavic lands of Eastern Europe and Russia. The reformation of the 14th century, led by people such as Martin Luther, brought about the Protestant Reformation and a break with the Roman Catholic Church. Protestant churches have dominated northern Europe to this day.
Three Main Language Groups
| Germanic Language Group (Found Mainly in Northern Europe) | Romance Language Group (Latin Based; Found Mainly in Southern Europe) | Slavic Language Group (Found Mainly in Eastern Europe) |
| English, Dutch, German | French, Italian, Spanish | Polish, Russian, Czech |
| Danish, Norwegian, Swedish | Portuguese, Romanian, Walloon | Ukrainian, Slovak, Slovene |
| Icelandic, Faroese, Frysian | Romancsh, Catalan, Provencal | Belarussian, Serbo-Croatian, Lusatian |
| Macedonian, Bulgarian |
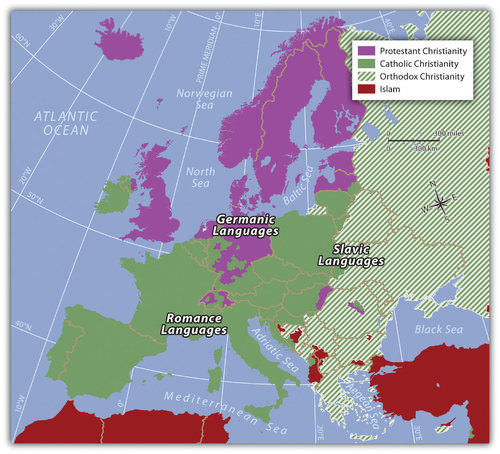
This map depicts the three dominant languages groups and the three Christian denominations of Europe.
Three main Indo-European language groups dominate Europe. Though there are additional language groups, the dominant three coincide with the three main religious divisions. In the east, where the Eastern Orthodox Church is dominant, the Slavic language group prevails. In the north, along with Protestant Christianity, one finds the Germanic language group. In southern Europe, where Roman Catholicism is dominant, the Romance languages are more commonly spoken.
- The Roman Empire connected southern Europe and created an infrastructure to help promote trade and intercultural connections.
- The Vikings connected northern Europe through trade and exploitation.
- Technological advancements helped European colonialism dominate other countries and exploit their labor and resources.
- Coastal European countries created colonies and external sources of wealth.
- The Industrial Revolution was promoted by the development of steam power with coal as a fuel source.
- The mass production of goods gave the European countries an advantage in the world marketplace.
- The Industrial Revolution prompted a shift in population from the rural agricultural regions to the urban centers.
- More people were needed in the factories and fewer workers were required on the farms because of improved agricultural methods. This shift resulted in smaller families and more women entering the workplace.
- The early empires of Europe gave way to the concept of a similar people (the nation) unifying under a common government (the state) to create nation-states.
- Divisive centrifugal cultural forces tend to divide and separate people in a state, whereas cohesive centripetal cultural forces tend to unify a state.
- The Indo-European language family has three dominant groups in Europe: Germanic in the north, Romance in the south, and Slavic in the east.
- The Christian religion has three main divisions in Europe: a Protestant north, Catholic south, and an Orthodox east.
Vocabulary Terms
| central-business-district (CBD) | The core of a city, which is almost always based on commercial activity. |
| colonialism | A system in which another country controls another area as a colony The ruling colony controls trade with its colony for its own benefit |
| devolution | To the process whereby regions or people within a state demand independence and autonomy at the central government’s expense |
| Fascism | A totalitarian form of government where one person rules |
| feudalism | A type of social system in Europe that thrived during the 9th and 15th centuries in which the holding of land was used in exchange for labor and military services |
| imperialism | When a country takes over or controls another country by domination or force |
| militarism | The belief or desire to have a strong military within one's country |
| nation-state | The name of a territory when a nation and state occupy the same territory |
| nationalism | The belief or ideology of strongly identifying with one nation |
| Germanic | One of the three major language families in Europe |
| Germanic languages | German, Dutch, Danish, Swedish, and Norwegian |
| Indo-European | The base of languages in Europe |
| Romance | One of the three major language families in Europe |
| Romance languages | Romanian, Italian, French, Spanish, and Portuguese |
| Slavic | One of the three major language families in Europe |
| Slavic languages | Russian, Ukrainian, Polish, and Czech |
Applying Knowledge
Interactive Notebook Activities
- Summarize how the Roman Empire and the Viking era contributed to European development.
- Describe how European colonialism changed or influenced other countries.
- Explain the major developments that prompted the Industrial Revolution.
- Describe the impact of the rural-to-urban shift and its impact on urbanization specifically.
- Define the concept of a nation-state and explain how this applies to Europe.
- Explain how cultural forces can positively or negatively influence political units.
- List the three main language groups and the three main religious denominations of Europe.
Discussion and Study Questions
- Why do you think the Industrial Revolution started where it did?
- How did the Industrial Revolution affect Europe’s population and employment opportunities?
- What was the relationship between industrial activity and urbanization?
- What is a CBD? Where would you find it in your closest city?
- How does Europe’s fertility rate impact employment opportunities?
- Why is family size declining in Europe?
- What are the three dominant language branches of the Indo-European language family in Europe?
- How are the three main branches of Christianity distributed in Europe?
- What are some examples of centrifugal and centripetal cultural force where you live?
- Why do people gravitate toward a nation-state structure as a political unit?
Real-World Geography Exercise
Using Google Maps, find the capital of each country below. Calculate the approximate distance from your house to each capital. Next, go to Real-Time World Air Quality Index and find out what the air pollution index is for each capital. What impact do you think the air quality has on the citizens of each capital? Be prepared to share your answers.
- Spain
- Denmark
- France
- Italy
- Norway
- Germany
- Sweden
Mapping Exercise
March of Time: In this activity students will use GIS to identify the world’s largest cities at different times during the past 2000 years. Students will look for patterns in their locations and speculate on reasons for changes in the patterns.
Videos for Geography Enrichment
Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
Canadian Encyclopedia is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
CIA World Factbook provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
Congress.gov is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
Library of Congress is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
NASA Earth Observatory (NEO) is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
National Archives is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
National Map is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
NationMaster is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
Real-Time World Air Quality Index is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
StateMaster is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
United States Census Bureau is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
United States Geological Survey (USGS) is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
Whitehouse.gov is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
World Health Organization (WHO) is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health; shapes the research agenda on health; and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
WG.1A Analyze the effects of physical and human geographic patterns and processes on events in the past and describe their effects on present conditions, including significant physical features and environmental conditions that influenced migration patterns in the past and shaped the distribution of culture groups today.
WG.2B Assess how people’s changing perceptions of geographic features have led to changes in human societies.
WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural characteristics.
WG.6A Locate and describe human and physical features that influence the size and distribution of settlements.
WG.16C Compare life in a variety of cities and nations in the world to evaluate the relationships involved in political, economic, social, and environmental changes.
WG.16D Compare life in a variety of urban and rural areas in the world to evaluate political, economic, social, and environmental changes.
WG.17A Describe and compare patterns of culture such as language, religion, land use, systems of education, and customs that make Europe distinctive.
WG.21A Analyze and evaluate the validity and utility of multiple sources of geographic information such as primary and secondary sources, aerial photographs and maps.
WG.21B Locate places of contemporary geopolitical significance on a map.,
WG.22A Design and draw appropriate graphics, such as maps, diagrams, tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, distributions, and relationships.
WG.22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
| Image | Reference | Attributions |
 |
[Figure 1] | Credit: Wikimedia Commons – public domain. Source: open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeography/wp-content/uploads/sites/181/2016/04/6320891422c8cb0c36a56e96095fc622.jpg License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |
 |
[Figure 2] | Credit: [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons Source: https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonialism#/media/File:Fundacion_de_Santiago.jpg License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |
 |
[Figure 3] | Credit: Buzrael – Old train – CC BY-NC 2.0. Source: http://open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeography/chapter/2-2-historical-development-patterns/ License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |
 |
[Figure 4] | Credit: http://open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeograp...ment-patterns/ Source: http://open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeography/chapter/2-2-historical-development-patterns/ License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |
 |
[Figure 5] | Credit: http://open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeograp...ment-patterns/ Source: open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeography/wp-content/uploads/sites/181/2016/04/99cb27833445a092a2ea4e882bbf067b.jpg License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |

