10.4: Japan, North Korea, and South Korea (2 Days)
- Page ID
- 1978
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Summarize the physical geography of the Korean peninsula.
- Understand how North Korea and South Korea developed independently.
- Outline the political structure of North Korea.
- Describe how South Korea developed a high standard of living and a prosperous economy.
- Express how the concept of regional complementarity can apply to the Koreas.
TEKS Regional Unit 10 East and Southeast Asia: Chapter 10.4 Japan, North, and South Korea
WG.1B Trace the spatial diffusion of phenomena such as the Columbian Exchange or the diffusion of American popular culture and describe the effects on regions of contact.
WG.2A Describe the human and physical characteristics of the same regions at different periods of time to evaluate relationships between past events and current conditions.
WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural elements.
WG.5B Interpret political, economic, social, and demographic indicators (gross domestic product per capita, life expectancy, literacy, and infant mortality) to determine the level of development and standard of living in nations using the terms Human Development Index, less developed, newly industrialized, and more developed.
WG.10A Describe the forces that determine the distribution of goods and services in free enterprise, socialist, and communist economic systems.
WG.10B Classify where specific countries fall along the economic spectrum between free enterprise and communism.
WG.13A Interpret maps to explain the division of land, including man-made and natural borders, into separate political units such as cities, states, or countries.
WG.14A Analyze current events to infer the physical and human processes that lead to the formation of boundaries and other political divisions.
WG.14B Compare how democracy, dictatorship, monarchy, republic, theocracy, and totalitarian systems operate in specific countries.
WG.15B Explain how citizenship practices, public policies, and decision making may be influenced by cultural beliefs, including nationalism and patriotism.
WG.17A Describe and compare patterns of culture such as language, religion, land use, education, and customs that make specific regions of the world distinctive. make specific regions of the world distinctive.
WG.18A Analyze cultural changes in specific regions caused by migration, war, trade, innovations, and diffusion.
WG.21A Locate places of contemporary geopolitical significance on a map.
WG.22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
Japan, North Korea, and South Korea
Japan
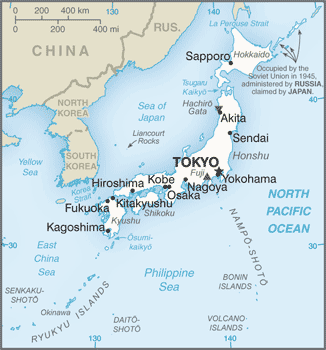 Map of Japan
Map of JapanJapan consists of islands that lie along the Pacific Rim east of China and across the Sea of Japan from the Korean Peninsula. Most of the archipelago, which has more than 3,000 islands, is just north of 30° latitude. Four islands make up most of the country: Shikoku, Kyushu, Hokkaido, and Honshu. The islands have tall mountains originating from volcanic activity. Many of the volcanoes are active, including the famous Mount Fuji.
The physical area of all Japan’s islands is equivalent to about the size of the US state of Montana. The mountainous islands of Japan extend into two climate zones. All but the northern region of Japan has a type C climate. The island of Hokkaido in northern Japan has a type D climate and receives enough snow for downhill skiing. Japan hosted the Winter Olympics in 1998. Mount Fuji, located just west of Tokyo, is a widely photographed mountain because of its symmetrical volcanic cone.
 Japan has 108 active volcanoes.
Japan has 108 active volcanoes.The largest metropolitan urban area in the world that can be verified is Tokyo, with a population of more than 38 million. The Tokyo metropolitan area is located in an extensive agricultural region called the Kanto Plain and includes the conurbation of Tokyo, Yokohama, and Kawasaki. The second-largest urban area in Japan is located in the Kansai District and includes the cities of Kobe, Osaka, and Kyoto.
Japan is a mountainous region, and most of its large cities are located in low-lying areas along the coast. Most of the population (67 percent) lives in urban areas such as Japan’s core area, an urbanized region from Tokyo to Nagasaki. According to the CIA World Factbook, the 2017 (estimate) population of Japan was more than 126 million, less than half the size of the United States.
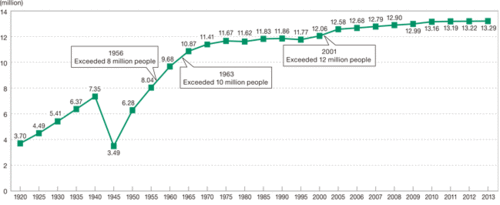 Tokyo's historical population since 1920.
Tokyo's historical population since 1920.Tokyo is located where three tectonic plates meet: the Eurasian Plate, the Philippine Plate, and the Pacific Plate. Earthquakes result when these plates shift, leading to extensive damage and destruction. In 1923, a large earthquake struck the Tokyo area and killed an estimated 143,000 people. In 1995, an earthquake near Kobe killed about 5,500 people and injured another 26,000.
.jpg?revision=1) The average elevation in Tokyo is 131 feet.
The average elevation in Tokyo is 131 feet.In March 2011, a magnitude 9.0 earthquake struck 43 miles off of the eastern coast of northern Japan. The earthquake itself caused extensive damage to the island of Honshu. A shockwave after the earthquake created a tsunami of more than 130 feet high that crashed into the eastern coast of Japan causing enormous damage to infrastructure as well as the loss of life. Hundreds of aftershocks were recorded. At least three registered over 7.0 in magnitude. This is the strongest earthquake to ever hit Japan in recorded history. It resulted in more than 15,500 deaths and wreaked serious damage across Japan in the value of billions of dollars. Thousands of additional people remain missing.
Nuclear power plants along the coast were hit hard by the tsunami, which knocked out their cooling systems and resulted in the meltdown of at least three reactors. The nuclear meltdowns created explosions that released a sizeable quantity of nuclear material into the atmosphere. This is considered the worst nuclear accident since the 1986 reactor meltdown at the Soviet plant at Chernobyl, located north of Kyiv in present-day Ukraine. The next big earthquake could happen at any time since Japan is located in an active tectonic plate zone.
Development
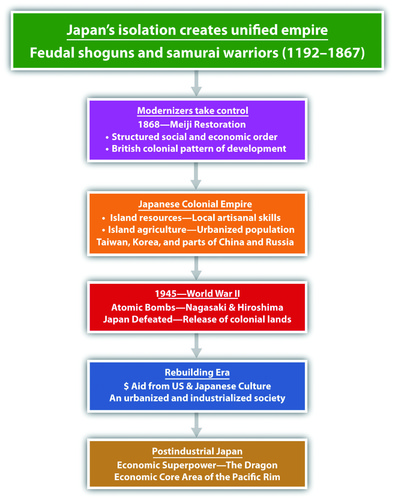
The country of Japan is an interesting study in isolation geography and economic development. For centuries, shogun lords and samurai warriors ruled Japan, and Japan’s society was highly organized and structured. Urban centers were well planned, and skilled artisans developed methods of creating high-grade metal products. While agriculture was always important, Japan always existed as a semi-urban community because the mountainous terrain forced most of the population to live along the country’s coasts.
Without a large rural population to begin with, Japan never really experienced the rural-to-urban shift common in the rest of the world. Coastal fishing, always a prominent economic activity, remains so today. The capital city of Tokyo was formerly called Edo and was a major city even before the colonial era. Japan developed its own unique type of urbanized cultural heritage.
 By the mid-18th century, Edo had a population of more than one million.
By the mid-18th century, Edo had a population of more than one million. Encounters with European colonial ships prompted Japan to industrialize. For the most part, the Japanese kept the Europeans out and only traded with select ships that were allowed to approach the shores. The fact that European ships were there at all was enough to convince the Japanese to evaluate their position in the world. During the colonial era, Britain was the most avid colonizer with the largest and best-equipped navy on the high seas.
Britain colonized parts of the Americas, the Middle East, Africa, South Asia, and Australia and was advancing in East Asia when they encountered the Japanese. Both Japan and Great Britain are island countries. Japan reasoned that if Great Britain could become so powerful, they should also have the potential to become powerful. Japan encompassed a number of islands and had more land area than Britain, but Japan did not have the coal and iron ore reserves that Britain had.
Around 1868, a group of reformers worked to bring about a change in direction for Japan. Named after the emperor, the movement was called the Meiji Restoration (the return of enlightened rule). Japanese modernizers studied the British pattern of development. The Japanese reformers were advised by the British about how to organize their industries and how to lay out transportation and delivery systems.
Today, the British influence in Japan is easily seen in that both Japanese and British drivers drive on the left side of the road. The modernizers realized that to compete on the high seas in the world community they had to move beyond samurai swords and wooden ships. Iron ore and coal would have to become the goods to fuel their own industrial revolution. Labor and resources were valuable elements of early industrialization in all areas of the world, including Asia.
Japan began to industrialize and build its economic and military power by first utilizing the few resources found in Japan. Since it was already semi-urban and had an organized social order with skilled artisan traditions, the road to industrialization moved quickly. Japan needed raw materials and expanded to take over the island of Formosa (Taiwan) and the Korean Peninsula in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Japan was on its way to becoming a colonial power in its own right. They expanded to take control of the southern part of Sakhalin Island from Russia and part of Manchuria (Northeast China) from the Chinese. Japanese industries grew quickly as they put the local people to work and extracted the raw materials they needed from their newly taken colonies.
The three-way split in China revealed that the Japanese colonizers were a major force in China even after the other European powers had halted their colonial activities. Japan’s relative location as an independent island country provided both quick access to their neighbors and also protection from them. By World War II, Japan’s economic and military power had expanded until they were dominating Asia’s Pacific Rim community.
The Japanese military believed that they could invade the western coast of North America and eventually take control of the entire United States. Their attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, in 1941, was meant to be only a beginning. The United States rallied its people and resources to fight against the Japanese in World War II. The Soviet Union also turned to fight the Japanese empire.
The end came after atomic bombs were dropped by the United States on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The terms of Japan’s surrender in 1945 stipulated that Japan had to give up claims on the Russian islands, Korea, Taiwan, China, and all the other places that they had previously controlled. Japan also lost the Kurile Islands—off its northern shores—to the Soviet Union.
The islands have never been returned. Japan offered Russia an enormous amount of cash for them but the matter remains unresolved. The Kurile Island chain continues to be controlled by Russia. Japan also agreed not to have a military for offensive purposes. Japan was decimated during World War II, its infrastructure and economy destroyed.
Economic Growth
Since 1945, Japan has risen to become Asia’s economic superpower and the economic center of one of the three core areas of the world. Japanese manufacturing has set a standard for global production. For example, think of all the automobiles that are Japanese products: Toyota, Honda, Mitsubishi, Subaru, Nissan, Isuzu, Mazda, and Suzuki. How many Russian, Brazilian, Chinese, or Indonesian autos are sold in the United States?
The term “economic tiger” is used in Asia to indicate an entity with an aggressive and fast-growing economy. Japan has surpassed this benchmark and is called the economic dragon of Asia. The four economic tigers competing with Japan are Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and South Korea. Japan came back from total devastation in 1945 to become a world economic superpower.
Japan’s recovery in the last half of the century has been remarkable. If an island nation like Japan could accomplish this rapid growth in its economy, why couldn’t other similar-sized countries accomplish the same level of growth? What was it that caused the Japanese people to not only recover so quickly but rise above the world’s standard to excel in their economic endeavors?
The answer could be related to the fact that Japan already had an industrialized and urbanized society before the war. The United States did help rebuild some of Japan’s infrastructure that had been destroyed during World War II—things like ports and transportation systems to help bring aid and provide for humanitarian support. However, the Japanese people were able to not only recover from the devastation of World War II but also rise to the level of an economic superpower to compete with the United States.
Japan used internal organization and strong centripetal dynamics to create a highly functional and cohesive society that focused on creating a manufacturing sector that catapulted the country’s economy from devastation to financial success.
The loss of colonies after World War II prompted Japan to look elsewhere for its raw materials. Extensive networks of trade were developed to provide the necessary materials for the rapidly growing manufacturing sector. The urbanized region around Tokyo, including the cities of Yokohama and Kawasaki, grew to accommodate the growth of the industry. Japan’s coastal interior has a number of large cities and urban areas that rapidly increased with the growing manufacturing sector.
The basis for Japan’s technological and economic development may be related to its geographic location and cultural development. Japan’s pattern of economic development has similarities to the patterns of other Asian entities that have created thriving economic conditions. Hong Kong and Taiwan are both small islands with few natural resources, yet they have become economic tigers.
Explaining how or why countries develop at different rates can be complex because there may be many interrelated reasons. One element might be centripetal cultural forces that hold a country together and drive it forward. The ability to manage labor and resources would be another part of the economic situation. The theory of how countries gain wealth may shed some light on this issue.
Japan used manufacturing as a major means of gaining wealth from value-added profits. This is the same method the Asian economic tigers also developed their economies. Japan developed itself into a core economic country that took advantage of the peripheral countries for labor and resources during the colonial era. Japan took advantage of every opportunity that presented itself to become a world manufacturing center.
Modern Japan
Japan is a homogeneous society. In 2010, all but 1 percent of the population was ethnically Japanese. Japan resembles a nation-state, where people of a common heritage and aspirations hold to a unified government. This provides a strong centripetal force that unites the people under one culture and one language. However, religious allegiances in Japan vary, and there are a good number of people who indicate nonreligious ideologies.
Shintoism and Buddhism are the main religious traditions. Shintoism includes a veneration of ancestors and the divine forces of nature. There is no one single written text for Shintoism. This religion is a loosely knit set of concepts based on morality, attitude, sensibility, and right practice. It is possible for a Shinto priest to conduct a wedding for a couple, whereas the funeral for either of the spouses might be conducted by a Buddhist priest.
Modernization has brought new opportunities and problems to the Japanese people. With a highly urban and industrial society, personal incomes in Japan are high and family size is quite low, at about 1.2 children. The replacement level for a given population is about 2.1 children, which means Japan has a declining population. The population is aging and there are not enough young people to take entry-level jobs.
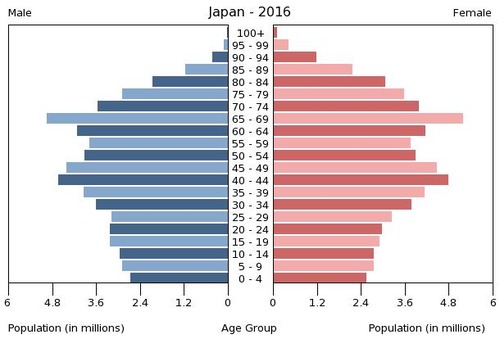 The Age Structure in Japan: 0-14 years: 12.84 percent (male 8,361,611/female 7,875,045); 15-24 years: 9.64 percent (male 6,417,085/female 5,778,904); 25-54 years: 37.5 percent (male 23,435,323/female 23,980,781); 55-64 years: 12.15 percent (male 7,692,424/female 7,665,157); 65 years and over: 27.87 percent (male 15,397,309/female 19,847,759)
The Age Structure in Japan: 0-14 years: 12.84 percent (male 8,361,611/female 7,875,045); 15-24 years: 9.64 percent (male 6,417,085/female 5,778,904); 25-54 years: 37.5 percent (male 23,435,323/female 23,980,781); 55-64 years: 12.15 percent (male 7,692,424/female 7,665,157); 65 years and over: 27.87 percent (male 15,397,309/female 19,847,759)The family has been at the center of Japanese tradition, and the elderly have been venerated and honored. As the country has become more economically developed, higher incomes for young people have prompted a shift toward convenience and consumer amenities. Consumer goods are available, but all the oil and about 60 percent of the food products have to be imported. During the offseason, fruit, for example, is expensive. Beef is at a premium price, so fish is a staple source of protein. Income levels are high, but the cost of living in places like Tokyo is also quite high.
Japan is facing a labor shortage for many low-level service jobs that had traditionally been held by young people entering the workforce. Japan is an island country that has prided itself in being 99 percent Japanese. Countries in stage 5 of the index of economic development usually enter a negative population growth pattern. According to population statistics, Japan is at the start of a serious population decline, with a negative population growth pattern.
While Western Europe and the United States also have a declining percentage of young people, in those countries the declining youth cohort has been replaced by an elevated level of immigration, both legal and illegal. Culturally, this is not an attractive option for Japan, but they are forced to address the labor shortage in any way they can. Their economy will depend on the ability to acquire cheap labor and resources to compete in the global marketplace.
As the economic dragon of Asia, Japan has had an enormous economic impact on the East Asian Community (EAC). The shortage of cheap labor has forced Japan to look elsewhere for new manufacturing ventures. China is an attractive country in this respect because of its substantial population and low standard of living for many of its citizens. Japan is looking to take advantage of its geographical location to establish a more positive trade situation with its Asian neighbors.
The dynamics of Japan's economy are uniquely similar to that of the United States and Europe. All three core economic areas are competing for inexpensive labor and resources to fuel their economies. Japan’s history as a colonizer has caused serious cultural attitudes against it from its Asian neighbors. Nevertheless, economics usually drive politics, and Japan wields enormous economic power. Japan now engages in trade with China and continues to be a core economic country in the global economy.
- Ethnic Unity and Tolerance
- Social/Economic Equity
- Just and Fair Legal System
- Charismatic Leadership
- Religious Acceptance
- Nationalism
- Common Heritage
- Common Language
- Any Other Unifying Force
Korea
The Korean Peninsula juts out into the Pacific Rim from northwestern Asia. The peninsula is bound by the Sea of Japan (the East Sea) and the Yellow Sea. North and South Korea share the peninsula. These countries have been separated by the Korean demilitarized zone (DMZ) since 1953. To the west and north is China and to the far north along the coast is Russia.
Korea is separated from China by the Yellow Sea and the Yalu and Tumen Rivers to the north. The Yalu and Tumen rivers form the actual border between North Korea and China. Japan is located just east of the Korean Peninsula across the Korea Strait. The Korean Peninsula is now split between South Korea and North Korea. The capital city of North Korea is Pyongyang, and Seoul is the capital of South Korea.
The topography of the Korean Peninsula is mountainous with arable land. Approximately 70 percent of the Korean Peninsula is mountainous. The bedrock is predominantly composed of volcanic and granitic rocks that have been severely modified by glacial processes over the 25,000 years. The highest peak in North Korea rises more than 9,000 feet. The Korean Peninsula can be thought of as four general areas:
- Western Region with an extensive coastal plain, river basins, and small foothills
- Eastern Region with high mountain ranges and a narrow coastal plain
- Southeastern Basin
- Southwestern Region of mountains and valleys
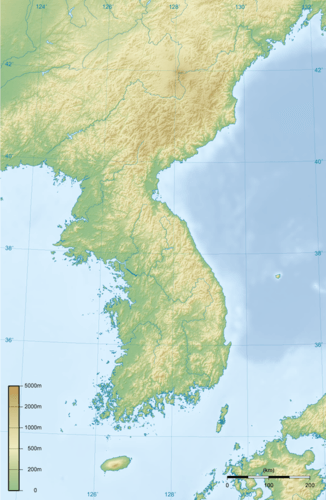 The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia.
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. Off of the southern and western coasts of the Korean Peninsula are about 3,000 small and mostly uninhabited islands, all within the territory of South Korea. South Korea’s largest island has an area of 712 square miles. It is the highest point of land in South Korea, at 6,398 feet above sea level.
North and South Korea have very different, yet related, environmental issues, primarily related to the degree of industrialization. With a low level of industrialism, North Korea has severe issues of water pollution as well as deforestation and related soil erosion and degradation. Other issues in North Korea include inadequate supplies of clean drinking water and many waterborne diseases. South Korea has water pollution associated with sewage discharge and industrial effluent from its many industrial centers. Air pollution is severe at times in the larger cities, which also contributes to higher levels of acid rain.
The physical size in square miles of North Korea (46,540 square miles) is similar to the physical area of the US state of Pennsylvania. South Korea (38,502 square miles) is similar to the physical area of Tennessee. For centuries, Korea was a unified kingdom that was often invaded by outsiders. After the fall of the Chinese Qing (Manchu) Dynasty, the Japanese took control of the Korean Peninsula (1910) and controlled it as a colony. Japanese colonial rule ended in 1945 when the United States defeated Japan, forcing it to give up its colonial possessions. The structure of modern Korea is a result of the ending of World War II.
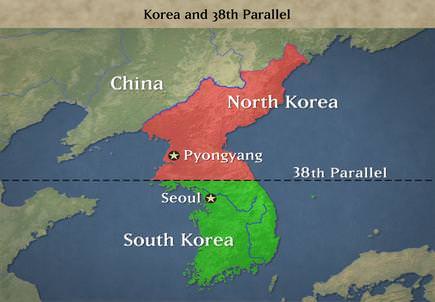 Japan had occupied the Korean peninsula between 1910 and 1945.
Japan had occupied the Korean peninsula between 1910 and 1945. United Nations Forces crossing the 38th parallel line in Korea during the Korean War
United Nations Forces crossing the 38th parallel line in Korea during the Korean WarThe conclusion of World War II was a critical period for the Korean Peninsula. The United States and the Soviet Union both fought against the Japanese in Korea. When the war was over, the Soviet Union took administrative control of the peninsula north of the 38th parallel, and the United States established administrative control over the area south of the 38th parallel.
The United States and the Soviet Union divided Korea approximately in half and eventually established governments in their respective regions that were sympathetic to each nation’s own ideology. The Soviet Union administered the northern portion; the United States administered the southern region. Politics deeply affected each of the regions. Communism dominated North Korea and capitalism dominated South Korea.
In 1950, with aid from China and the Soviet Union, the Communists from the north invaded the south. After bitter fighting, a peace agreement was reached in 1953 to officially divide the Korean Peninsula near the 38th parallel. Korea remains divided to this day. The United States has thousands of soldiers stationed along the Cease-Fire Line (or DMZ), which is the most heavily guarded border in the world.
- 1945: After the surrender of Japan, the Korean peninsula is divided between Soviet and American occupation forces at the 38th parallel.
- 1945: South Korea created a franchise to raise money and funds to recover.
- 1945: 6 September, Establishment of the Peoples Republic of Korea with Yuh Woon-Hyung, but 1946 February, US Army breaks it and Yuh Woon Hyung is murdered.
- 1946: US-USSR Joint-Commission on the formation of a Korean Government reaches an impasse. The Joint-commission is dissolved as the Cold War begins.
- 1948: 10 May. United Nations (UN) sponsored elections are held in South Korea.
- 1948: 15 August. Establishment of the Republic of Korea with Syngman Rhee as President.
- 1948: 9 September. Establishment of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea with Kim Il-sung as Premier.
- 1949: The murder of Kim Gu. Kim Gu was a Korean independence activist who believed in, and fought for, a unified Korea. He strongly objected to the formation of a separate South Korean state. He was shot in his home by a South Korean Army lieutenant.
- 1950: 25 June. The Korean War begins.
- 1950: August. UN Forces are driven back to the Southeast corner of the Korean Peninsula (The Pusan Perimeter).
- 1950: September. UN Troops make an Amphibious Landing at Inchon.
- 1950: November. Chinese Forces enter the war.
- 1953: The Korean War is halted by the Korean Armistice Agreement that has remained in force until now.
- 1960: A student uprising begins the April Revolution which overthrows the autocratic First Republic of South Korea. Syngman Rhee resigns and goes into exile.
- 1961: 16 May. Military forces, headed by General Park Chung Hee, overthrow the Second Republic of South Korea in what is known as the Military Coup d'état of 16 May.
- 1961: 12 November. Summit conference for normalization of Kor-Japanese relations.
- 1962: Start of the first Five-year plans of South Korea.
- 1964: South Korea joined the Vietnam War.
- 1965: 22 June. Signing of the Treaty on Basic Relations between Japan and the Republic of Korea. Earned both much controversy and procurement of budgets for later economic developments.
- 1967: Start of the second Five-year plans of South Korea.
- 1968: 21 January. An unsuccessful attempt of North Korean commandos to assassinate President Park Chung Hee- the Blue House Raid.
- 1968: 1 April. Establishment of the Pohang Iron and Steel Company.
- 1968: 5 December. Proclamation of the National Education Charter.
- 1970: 22 April. Start of the government-operated New Community Movement.
- 1970: Gyeongbu Expressway is completed and opened to traffic.
- 1972: Start of the third Five-year plans of South Korea.
- 1972: 12 August. The first Red Cross talks between North and South Korea are held.
- 1972: President Park Chung Hee declares Emergency Martial Law and changes the Constitution in August, which may allow him to become the permanent ruler. This is similar to Gojong of the Korean Empire stating his country's governmental system as 'autocratic' in the constitution- for greater leadership and less opposition.
- 1974: 15 August. The assassination of first lady Yuk Young-soo by self-proclaimed North Korean Mun Segwang.
- 1976: 18 August. The Axe Murder Incident in Panmunjom, Joint Security Area. Triggers former North Korean leader Kim Il-sung's first official apology to the South.
- 1976: 12 October: Discontinuation of rice imports, the accomplishment of total self-sufficiency in rice by the Unification Rice.
- 1977: Start of the fourth Five-year plans of South Korea.
- 1977: 22 December. Celebration of achievement of 10 billion dollars gained by exports.
- 1978: 26 October. Detection of the third underground tunnel. Made by North Korea to attack South Korea.
- 1978: 10 December. Achievement of US $1,117 as Gross National Product (GNP).
- 1979: American president Jimmy Carter visits Korea. Threatens Park by stating he would reduce the US forces in Korea if he does not stop the ongoing Nuclear Weapons Development project.
- 1979: 26 October, President Park Chung Hee is assassinated by the chief of KCIA, Kim Jaegyu (Assassination of Park Chung Hee).
- 1979: Coup d'état of December Twelfth, Chun Doo Hwan gets military power.
- 1980: Gwangju massacre. Martial Law is declared throughout the nation. The city of Gwangju becomes a battleground between dissenters and the Armed Forces (18–27 May). The official death toll was set at 200 people but some reports claim over 1000 casualties.
- 1987: A student uprising begins the June Democracy Movement, which overthrows the autocratic Fifth Republic of South Korea. The ruling party of Fifth Republic, Democratic Justice Party, declares democratic elections.
- 1988: 24th Olympic Games held in Seoul.
- 1990: 11 September: South Korea and the USSR established diplomatic relations.
- 1991: 17 September: North Korea (DPRK) and South Korea (ROK) join the United Nations (UN).
- 1991: 26 December: The end of the Cold War as the Soviet Union ceased to exist and North Korea loses military and economic aid.
- 1992: 11 August: South Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 is successfully launched from Guiana Space Center.
- 1992: 24 August: South Korea and the People's Republic of China (PRC) establish diplomatic relations.
- 1993: Test of Rodong-1, a single stage, mobile liquid propellant medium range ballistic missile by the DPRK.
- 1994: Kim Jong Il takes control of North Korea upon the death of his father Kim Il-Sung. Start of the Arduous March.
- 1998: Taepodong-1, a two-stage intermediate-range ballistic missile is developed and tested by the DPRK. End of the Arduous March. It is possible that up to 3.5 million people died in the march.
- 1999: The DPRK promises to freeze long-range missile tests.
- 2002: The 2002 FIFA World Cup jointly held by Korea and Japan. South Korea national football team makes it to the semi-finals for the first time in Korean football history. The DPRK pledges to extend the moratorium on missile tests beyond 2003.
- 2004: The DPRK reaffirms moratorium.
- 2005: The DPRK fires a short-range missile into the East Sea.
- 2006: Test of Taepodong-2 by DPRK, a successor of Taepodong-1.There is a nuclear test in the DPRK. US officials assert it might have been a misfire.
- 2007: The second summit between DPRK and ROK leaders is held, with Roh Moo-hyun representing the south and Kim Jong Il the north. The DPRK fires short-range missile into the East Sea.
- 2009: North Korea launches a rocket (Unha), supposedly for space exploration. This move affects relationships with Japan, the United States and South Korea. The DPRK conducts another nuclear test.
- 2010: North Korea launches missile attacks Korean Pohang class corvette, ROKS Cheonan. 46 Korean soldiers die because of the attack. At November, North Korean army rains artillery fire on Yeon-Pyeong-Do island.
- 2011: Kim Jong Il dies, Kim Jong-un takes over as the Supreme Leader of North Korea. The National Intelligence Service discovers Communist spies who have been working underground for the DPRK for almost 10 years. One of the members was a former Democratic Party representative. Their mission was to influence the party named above and extract military secret information.
- 2012: 13 April: The Kim Regime of the DPRK tested a rocket, officially called "Unha-3", an expendable launch system developed from the Soviet Scud rockets. The rocket was to send a satellite, called Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3, into orbit. The rocket failed to launch the satellite and fell into the Yellow Sea. The mission ultimately ended in complete failure.
- 2012: 12 December: DPRK has a successful launch of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 it was launched from the Sohae Satellite Launching Ground. A South Korean military official cited 3 stage success. DPRK confirmed.
- 2012: 19 December: Park Geun-Hye, a daughter of Park Chung-hee, is elected as the first female and the 11th president of South Korea.
- 2013: 8 December: Jang Song Thaek, uncle of North Korean Leader Kim Jong Un, was ousted from all-powerful posts on various charges. The official Korean Central News Agency said the political bureau of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea stripped Jang of all posts, depriving him of all titles and expelling him and removing his name from the party.
- 2013: 12 December: North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong Un, executes his Uncle, Jang Song-thaek, as a "traitor for all ages." Jang Song-thaek's execution was said to be set up by his own wife, Kim Kyong-hui, Late Supreme Leader Kim Jong Il's sister. Jang Song-Thaek was considered to be the most powerful official in the DPRK Regime.
- 2016: 9 December: The impeachment vote of President Park Geun-hye took place, whilst 234 members in the 300-member National Assembly voting in favor of the impeachment and temporary suspension of her presidential powers and duties. Hwang Kyo-ahn, then prime minister, became acting president while the Constitutional Court of Korea was due to determine whether to accept the impeachment.
- 2017: 10 March: The court upheld the impeachment in a unanimous 8–0 decision, removing Park from the office.
- 2017: 10 May: Moon Jae-in was sworn into office immediately after official votes were counted on May 10th, replacing Acting President and Prime Minister Hwang Kyo-ahn.
North Korea
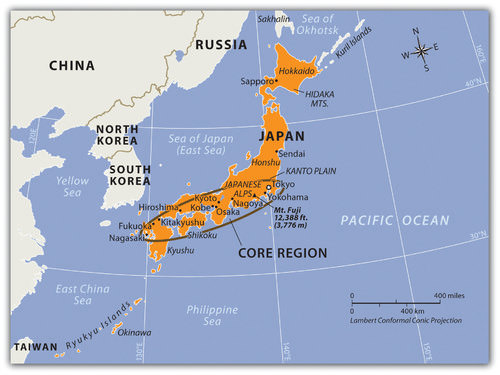
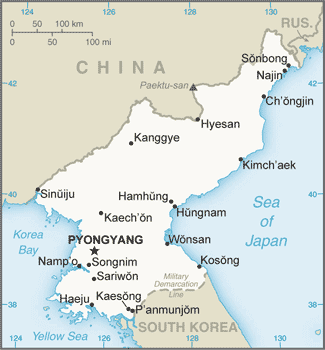 Map of North Korea
Map of North KoreaThe government of North Korea (the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, or DPRK) was formed with the leadership of Communist dictator Kim Il Sung, who shaped his country with a mix of Soviet and Chinese authoritarian rule. Having few personal freedoms, the people worked hard to rebuild a state. Using the threat of a US military invasion as a means of rallying his people, Kim Il Sung built up a military of more than one million soldiers, one of the largest in the world. People could not travel in or out of the country without strict regulation. North Korea existed without much notice until the 1990s, when things suddenly changed.
When the Soviet Union fell in 1991, North Korea lost a valued source of financial support and oil. Without fuel and funding, many of the factories closed. Unemployment rates rose significantly. Meanwhile, China adopted a more open posture and began to increase its level of trade with the West. The result was that China began to lose interest in propping up North Korea politically. North Korea was facing serious problems. Massive food shortages caused famine and starvation, and thousands of people died. Kim Il Sung died in 1994 and the country lost its leader. He had ruled the country since World War II and in the end, became a deified "Supreme Leader."
 An official portrait of Kim Il-sung, issued after his death.
An official portrait of Kim Il-sung, issued after his death.The government dictatorship continued as the Great Leader’s son, Kim Jong Il, took over the leadership role. Kim Jong Il, known as the “Dear Leader,” took repression of his people to new levels. Televisions and radios sold in North Korea can only receive government-controlled frequencies. Cell phones and the Internet are banned. The government takes a hard line against dissenters. If you are caught speaking against the state or taking any action to support dissent, you can be arrested, fined, placed in a prison camp, or executed. People are not allowed to leave or enter the country without government approval. Only a couple hundred tourists are allowed into the country per year and are closely escorted.
.jpg?revision=2) Kim Jun-un II
Kim Jun-un IIKim Jong Il has taken hard measures to stay in power and to avoid yielding to the capitalist frenzy of corporate colonialism. He has nuclear weapon capability and has used his military weapons production as a bargaining chip against the United States and other world powers. North Korea has demonized the United States as the ultimate threat and has used state-funded propaganda to indoctrinate its people. North Korea’s government continually tells its people that the United States will invade at any minute and to be prepared for the worst. Propaganda has been used to create and enforce military, economic, and political policies for an ideology that supports the unification of all of Korea under Communist control.
North Korea is mainly mountainous, and there is little quality farmland. While only 2 percent of the land is in permanent crops, about one-third of the population works in agriculture. The best farmland in North Korea is located south of the capital city of Pyongyang. The capital is a restricted area where only the most loyal to the state can live. There is a serious shortage of goods and services. Electricity is not available on a dependable basis.
 North Korea's sparse agricultural resources limit agricultural production.
North Korea's sparse agricultural resources limit agricultural production. Mansudae Assembly Hall, the seat of the Supreme People's Assembly, the North Korean parliament.
Mansudae Assembly Hall, the seat of the Supreme People's Assembly, the North Korean parliament.Massive international food aid has sustained the people of North Korea. Outside food aid is accepted even though Kim Jong Il has continued a policy of self-reliance and self-sufficiency called Juche. Juche is designed to keep Korea from becoming dependent on the outside. The policy of Juche has been quite effective in isolating the people of North Korea and keeping dictator Kim Jong Il in power. The policy of Juche also holds back the wave of corporate capitalism that seeks to exploit labor and resources in global markets for economic profit.
One way that North Koreans are finding out about the outside world is through smuggled cell phones and videos from South Korea. Popular videos include South Korean soap operas, because of the common heritage, language, and ethnicity. The North Korean government has attempted to crack down on smuggled videos by going from home to home. Electricity is turned off before entering the home. Once the electricity is turned off, videos cannot be removed from the video player. The government agents then confiscate the video.
Citizens found with smuggled videos are punished with fines or imprisonment. Desperate North Koreans have escaped across the border into northern China, where thousands of refugees have tried to find better opportunities for their future. China’s economy is growing and North Korea’s economy is stagnant, which creates strong push-pull forces on migration.
South Korea
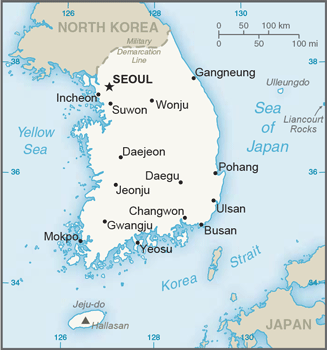 Map of South Korea
Map of South Korea In 1993, South Korea became a complete democracy with its first democratically elected president. Seoul is the capital city and is home to almost ten million people. Seoul is located south of the Cease-Fire Line, also known as the DMZ, which is commonly referred to as the 38th parallel. The United States has many military installations in this area.
South Korea manufactures automobiles, electronic goods, and textiles that are sold around the world. South Korea is a democracy that has used state capitalism to develop its economy. After the World War II era, South Korea was ruled by a military government that implemented land reform and received external economic aid. Large agricultural estates were broken up and redistributed to the people. Agricultural production increased to meet the demands of the population. South Korea has much more agricultural production than North Korea and is therefore in providing food for the high population density. A once-modest manufacturing sector has grown to become a major production center for export trade.
The 50 million people who live in South Korea have a much higher standard of living than the residents of North Korea. Personal income in the north is barely equivalent to a few dollars per day, while personal income in the south is similar to that of Western countries. The economic growth of the south was a result of state-controlled capitalism, rather than free-enterprise capitalism.
The state has controlled or owned most of the industrial operations and sold its products in the global marketplace. Giant corporations, which forced industrialization along the coastal region, have promoted South Korea as the world’s leading shipbuilding nation. South Korean corporations include Daewoo, Samsung, Kia Motors, Hyundai, and the Orion Group. As an economic tiger, South Korea continues to reform its economic system to adapt to global economic conditions.
South Korea has announced plans to conduct a comprehensive overhaul of its energy and transportation networks. Government funding will augment efforts to create more green-based initiatives. Part of this effort will focus on lower energy dependency with environmentally friendly energy developments such as wind, solar, bike lanes, and new lighting technologies. High-speed rail service and increased capacity in electronic transmissions lines are planned as part of the next generation of energy-efficient technologies that will increase economic efficiency. These policies have been enacted to update South Korea’s economy and create new products for manufacturing export.
Buddhism was introduced into the Korean Peninsula, as were many other aspects of Chinese culture that had significant effects on Korean heritage. Buddhism has been a prominent religion in Korea for centuries. The teachings of Confucius are also widely regarded. About 30 percent of the population claims Christianity as their religious background. About 20 percent of the Christians are Protestant and 10 percent are Catholic. This is the highest Christian percentage of any Asian country.
Up to one-half of the population makes no claims or professions of faith in any organized religion. Before 1948, Pyongyang was a notable Christian center. At that time, approximately 300,000 people identified as Christian. After the establishment of a Communist government in North Korea, many of the Christians fled to South Korea to avoid persecution.
| Age | Buddhism | Catholicism | Protestantism | Other religions | No affiliation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-29 | 10% | 7% | 18% | 1% | 65% |
| 30-39 | 12% | 8% | 19% | 1% | 62% |
| 40-49 | 16% | 7% | 20% | 1% | 57% |
| 50-59 | 22% | 9% | 19% | 1% | 49% |
| 60-69 | 26% | 10% | 21% | 1% | 42% |
| 70-79 | 27% | 10% | 21% | 1% | 41% |
| 80-85 | 24% | 10% | 22% | 2% | 42% |
| above 85 | 21% | 11% | 23% | 2% | 43% |
| Other religions include Won Buddhism, Confucianism, Cheondoism, Daesun Jinrihoe, Daejongism, and Jeungsanism. |
Unification of North and South
What if North Korea and South Korea would become unified again? In the field of geography, there is a concept of regional complementarity, which exists when two separate regions possess qualities that would work to complement each if unified into one unit. North and South Korea are the classic illustrations of regional complementarity. The North is mountainous and has access to minerals, coal, iron ore, and nitrates (fertilizers) that are needed in the South for industrialization and food production. The South has the most farmland and can produce large harvests of rice and other food crops. The South has industrial technology and capital needed for development in the North. If and when these two countries are reunited, they could work well as an economic unit.
The harder question is how and under what circumstances the two Koreas could ever come to terms of unification. What about the thirty-five to forty thousand US soldiers along the DMZ? What type of government would unified Korea have? There are many young people in South Korea that would like to see the US military leave Korea and the two sides united. The generation of soldiers that survived the Korean War in the 1950s understands the bitterness and difficulties caused by the division. This segment of the population is highly supportive of maintaining the presence of the US military on the border with North Korea. Unification is not likely to take place until this generation either passes away or comes to terms with unification.
The brutal dictatorship of Kim Jong Il, with his claimed nuclear capabilities, has been a main barrier to unification. This is a political division, not technically a cultural division, even though the societies are quite different at the present time. The geography of this situation is similar to that of East and West Germany after World War II and during the Cold War. Korea may have different qualities from Germany, but unification may be possible under certain conditions, foremost being different leadership in the north.
The Great Unification Buddha, called "Tongil Daebul" is a 48-foot gilt-bronze statue that weighs 108 tons. It sits on top of a 15-foot high pedestal. The total height is 62 feet, which does not include the lightning rod and nimbus. The lotus pedestal is adorned with 16 ornately engraved panels. The forehead of the statue is embedded with eight 3-inch amber stones. In the center of the amber stones is a 4-inch stone of jade.
Tongil Daebul sits with crossed legs, half-closed eyes in meditation, and a perceptible smile. He wears a robe that drapes over his torso and reveals his right shoulder. The hands of the Tongil Daebul are positioned in the mudra (a symbolic gesture), which symbolizes the "enlightened one." Within the hollow statue are the original Buddhist scriptures (Tripitaka) and three pieces of the Buddha's sari (remains collected after his creation), which were donated by the Myanmar government.
The Great Unification Buddha was a long term project completed with 4.1 million dollars in donations from people visiting the temple. Tongil Daebul represents the hope of the Korean people for the reunification of the divided country.
 Sinheungsa is a head temple of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism.
Sinheungsa is a head temple of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism.- Japan’s mountainous archipelago has provided isolation and protection for the Japanese people to maintain their unique culture and heritage. The islands were created by tectonic plate action, which continues to cause earthquakes in the region.
- Japan was a colonial power that colonized much of the Asian Pacific region. Its defeat in World War II devastated the country and liberated all its colonies. Since 1945, Japan has been developing one of the strongest economies in the world through manufacturing.
- Japan is a highly industrialized country that is in stage 5 of the index of economic development. The country’s small family size and declining population are a concern for economic growth in the future.
- The Korean Peninsula is divided in two by the DMZ. North Korea is a Communist dictatorship with a low standard of living and no civil rights. South Korea is a capitalist democracy with a high standard of living and a free-market economy.
- North Korea is more mountainous and lacks arable land to grow food. South Korea has more farmland and fewer mountains. If the two countries were to be united with a common economy, they would complement each other with a balance of natural resources.
Vocabulary Terms
|
A country with rapid economic growth due to cheap labor, high technology, and aggressive exports. (Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan.) |
|
|
The largest plain in Japan located in the Kanto Region of central Honshū |
|
|
Created by an agreement between North Korea, China and the United Nations in 1953, itis a strip of land running across the Korean Peninsula that serves as buffer soon between North and South Korea |
|
|
Japan's highest mountain |
|
|
A professional soldier in Japan who served the interests of landowners and clan chiefs |
|
|
The ethnic religion of Japan that focuses on ritual practices to be carried out diligently, to establish a connection between present-day Japan and its ancient past |
|
|
The general of the emperor's army with the powers of a military dictator, a position created by the Japanese emperor in 1192 after a struggle between two powerful clans |
|
|
A fee (tax) that a country charges on imports or exports |
|
|
The kingdoms formed in the peninsula of Korea by A.D. 300-–Koguryo in the northeast, Paekche in the southwest, and Silla in the southeast |
|
|
The capital city of Japan |
|
|
A giant ocean wave, caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption, with a great destructive power |
Applying Knowledge
Discussion and Study Questions
- What climate types are found in Japan? How does climate type correspond to the population?
- Why has Japan never experienced a strong rural-to-urban shift in its population?
- What is the ethnic makeup of Japan? Why does this pattern exist in Japan?
- Does Japan have a high or low population growth rate? What problems arise from this situation?
- How did Japan become an economic superpower after 1945?
- How would South Korean soap operas pose a serious threat to North Korea?
- How did South Korea develop such a robust economy with such a small physical area?
- Why are thousands of US soldiers positioned on the DMZ?
- How does North Korea’s policy of Juche align with the global economy?
- Explain how the concept of regional complementarity applies to the two Koreas.
Real-World Geography Exercise
Go to the Weather Channel. Find out what the current weather is for five of the locations below. How do you think the weather impacts the economy? Be prepared to share your answers.
- Edo
- Hokkaido
- Honshu
- Kansai District
- Kanto Plain
- Kawasaki
- Kobe
- Korea Strait
- Kurile Islands
- Kyoto
- Kyushu
- Mt. Fuji
- Osaka
- Pyongyang
- Sakhalin Island
- Sea of Japan
- Seoul
- Shikoku
- Yellow Sea
- Tokyo
- Yokohama
Videos for Geography Enrichment
Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
Canadian Encyclopedia is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
CIA World Factbook provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
Congress.gov is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
Library of Congress is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
NASA Earth Observatory (NEO) is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
National Archives is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
National Map is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
NationMaster is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
Real-Time World Air Quality Index is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
StateMaster is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
United States Census Bureau is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
United States Geological Survey (USGS) is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
Whitehouse.gov is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
World Health Organization (WHO) is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.

