2.4.1: Inverse Trig Functions
- Page ID
- 14469
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Solving for an angle given a trigonometric ratio.
Inverse Trig Functions and Solving Right Triangles
A right triangle has legs that measure 2 units and \(2 \sqrt{3}\) units. What are the measures of the triangle's acute angles?
Inverse of Trigonometric Functions
We have used the trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent to find the ratio of particular sides in a right triangle given an angle. In this concept we will use the inverses of these functions, \(\sin^{-1}\), \(\cos^{-1}\) and \(\tan^{-1}\), to find the angle measure when the ratio of the side lengths is known. When we type \(\sin 30^{\circ}\) into our calculator, the calculator goes to a table and finds the trig ratio associated with \(30^{\circ}\), which is 12. When we use an inverse function we tell the calculator to look up the ratio and give us the angle measure. For example: \(\sin^{-1}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=30^{\circ}\). On your calculator you would press \(2^{ND} SIN\) to get \(\sin^{-1}\) and then type in \(\dfrac{1}{2}\), close the parenthesis and press ENTER. Your calculator screen should read \(\sin^{-1}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\) when you press ENTER.
Let's find the measure of angle \(A\) associated with the following ratios and round answers to the nearest degree.
- \(\sin A=0.8336\)
- \(\tan A=1.3527\)
- \(\cos A=0.2785\)
Using the calculator we get the following:
- \(\sin^{-1}(0.8336)\approx 56^{\circ}\)
- \(\tan^{-1} (1.3527)\approx 54^{\circ}\)
- \(\cos^{-1} (0.2785)\approx 74^{\circ}\)
Now, let's find the measures of the unknown angles in the triangle shown and round answers to the nearest degree.
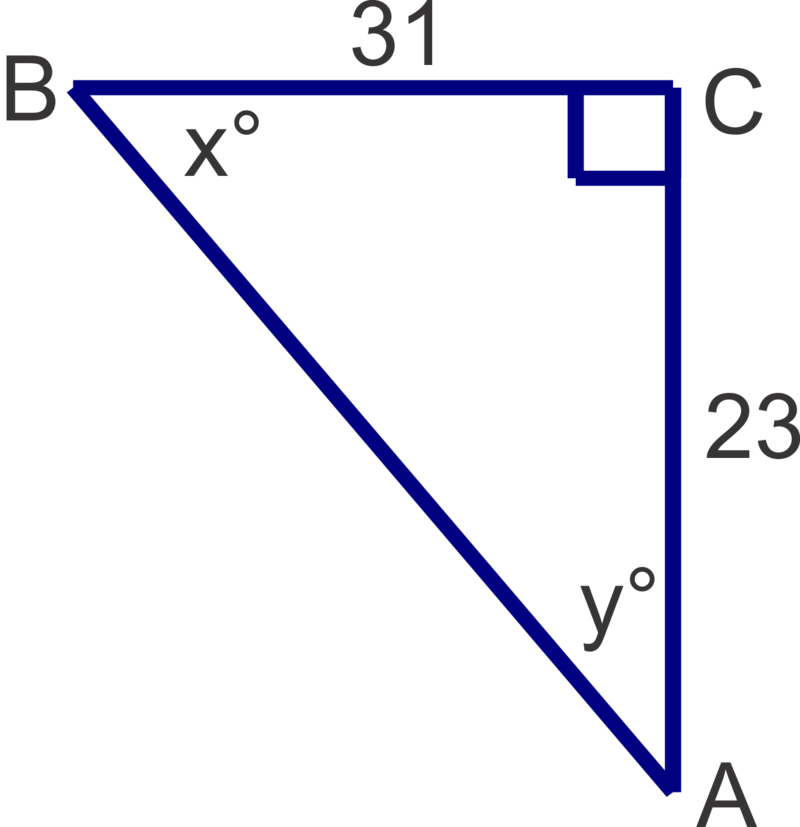
We can solve for either \(x\) or \(y\) first. If we choose to solve for \(x\) first, the 23 is opposite and 31 is adjacent so we will use the tangent ratio.
\(x=\tan^{-1} \left (\dfrac{23}{31}\right)\approx 37^{\circ}\).
Recall that in a right triangle, the acute angles are always complementary, so \(90^{\circ} −37^{\circ} =53^{\circ}\), so \(y=53^{\circ}\). We can also use the side lengths an a trig ratio to solve for y:
\(y=\tan^{-1} \left(\dfrac{31}{23}\right)\approx 53^{\circ}\).
Finally, let's solve the right triangle shown below and round all answers to the nearest tenth.
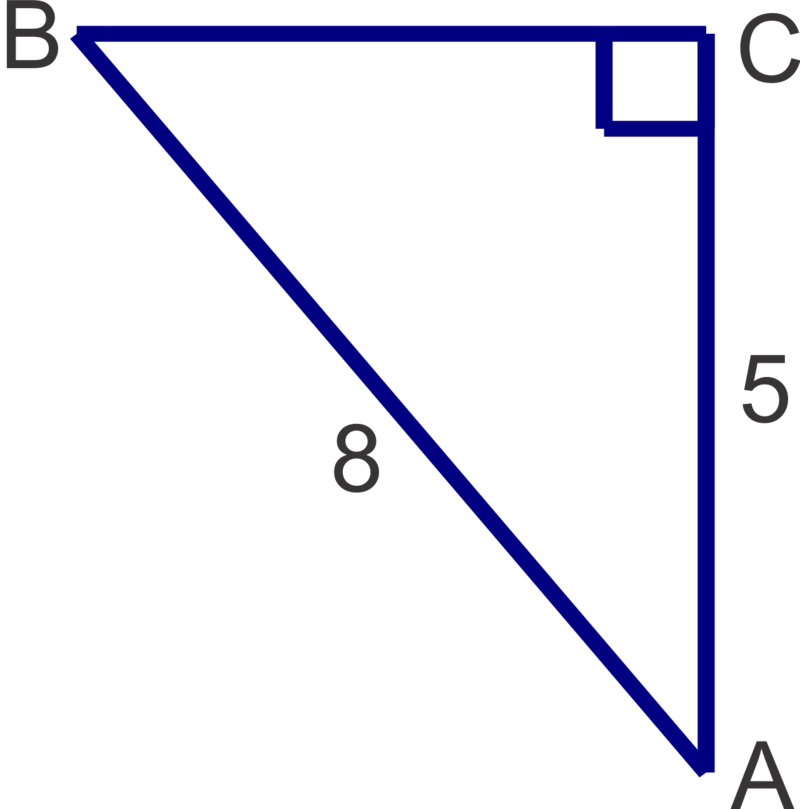
We can solve for either angle \(A\) or angle \(B\) first. If we choose to solve for angle \(B\) first, then 8 is the hypotenuse and 5 is the opposite side length so we will use the sine ratio.
\(\begin{aligned}\sin B&=\dfrac{5}{8} \\ m\angle B&=\sin^{-1} \left(\dfrac{5}{8}\right)\approx 38.7^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Now we can find A two different ways.
Method 1: We can using trigonometry and the cosine ratio:
\(\begin{aligned}\cos A&=\dfrac{5}{8} \\ m\angle A&=\cos^{-1} \left(\dfrac{5}{8}\right)\approx 51.3^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Method 2: We can subtract \(m\angle B\) from \(90^{\circ}\) : \(90^{\circ} −38.7^{\circ} =51.3^{\circ}\) since the acute angles in a right triangle are always complimentary.
Either method is valid, but be careful with Method 2 because a miscalculation of angle B would make the measure you get for angle \(A\) incorrect as well.
Earlier, you were asked to find the measures of the triangle's acute angles.
Solution
First, let's find the hypotenuse, then we can solve for either angle.
\(\begin{aligned} 2^2+(2\sqrt{3})^2 &=c^2 \\ 4+12&=c^2 \\ 16&=c^2 \\ c&=4\end{aligned}\)
One of the acute angles will have a sine of \(\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\).
\(\begin{aligned} \sin A&=\dfrac{1}{2}\\ m\angle A&=\sin^{-1} \dfrac{1}{2}=30^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Now we can find B by subtracting \(m\angle A\) from \(90^{\circ}\): \(90^{\circ} −30^{\circ} =60^{\circ}\) since the acute angles in a right triangle are always complimentary.
Find the measure of angle \(A\).
Solution
\(\begin{aligned} \sin A&=0.2894 \\ \sin^{-1}(0.2894) &\approx 17^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
Find the measure of angle \(A\).
Solution
\(\begin{aligned} \tan A&=2.1432 \\ \tan^{-1} (2.1432)&\approx 65^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
Find the measure of angle \(A\).
Solution
\(\begin{aligned} \cos A&=0.8911 \\ \cos^{-1} (0.8911) &\approx 27^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Find the measures of the unknown angles in the triangle shown. Round answers to the nearest degree.
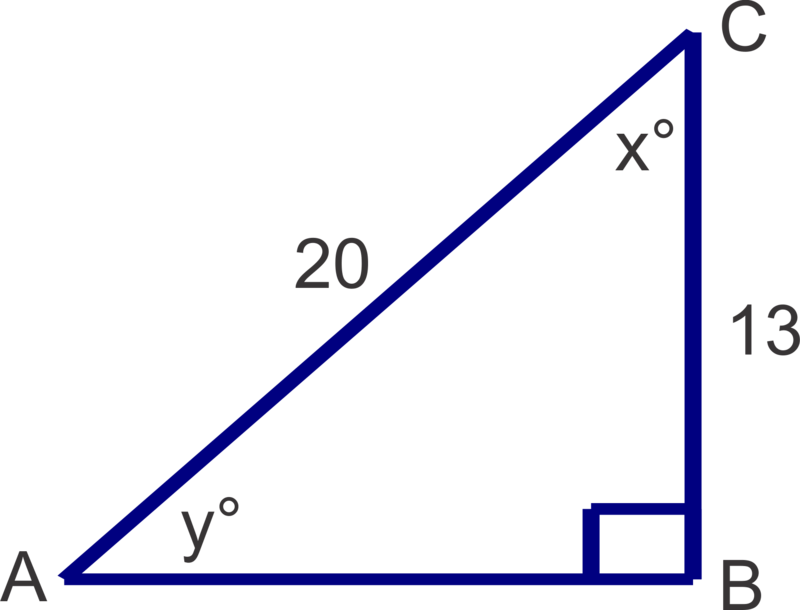
Solution
\(x=\cos^{-1} \left(\dfrac{13}{20}\right)\approx 49^{\circ} ; \quad y=\sin^{-1}(\dfrac{13}{20})\approx 41^{\circ}\)
Solve the triangle. Round side lengths to the nearest tenth and angles to the nearest degree.
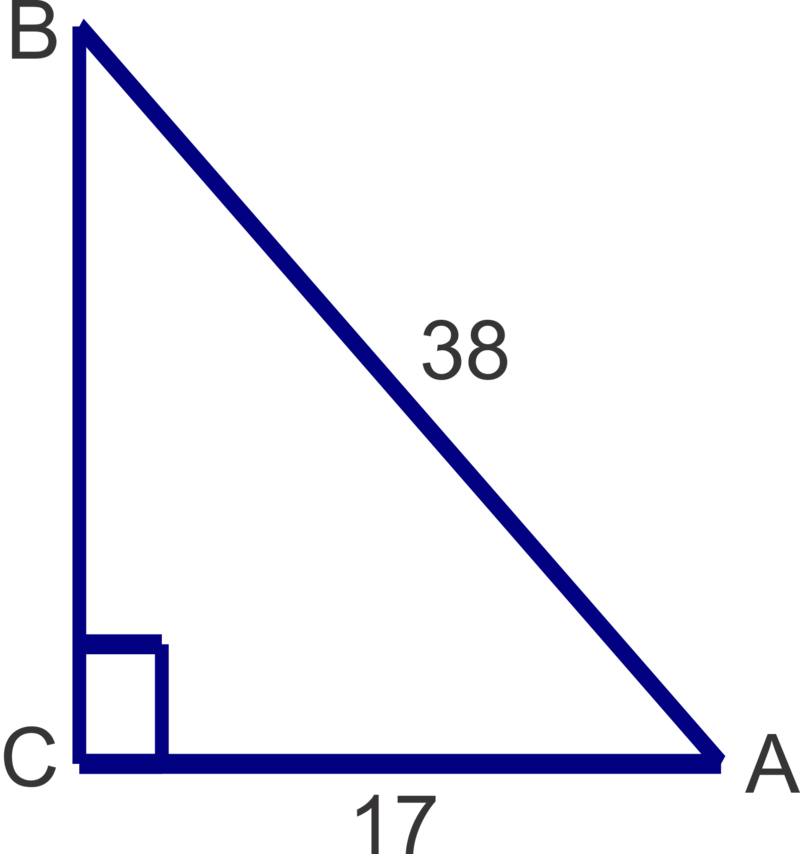
Solution
\(m\angle A=\cos^{-1} (\dfrac{17}{38})\approx 63^{\circ} ; m\angle B=\sin^{-1}(\dfrac{17}{38})\approx 27^{\circ} ; a=\sqrt{38^2−17^2} \approx 34.0\)
Review
Use your calculator to find the measure of \(\angle B\). Round answers to the nearest degree.
- \(\tan B=0.9523\)
- \(\sin B=0.8659\)
- \(\cos B=0.1568\)
- \(\sin B=0.2234\)
- \(\cos B=0.4855\)
- \(\tan B=0.3649\)
Find the measures of the unknown acute angles. Round measures to the nearest degree.
-
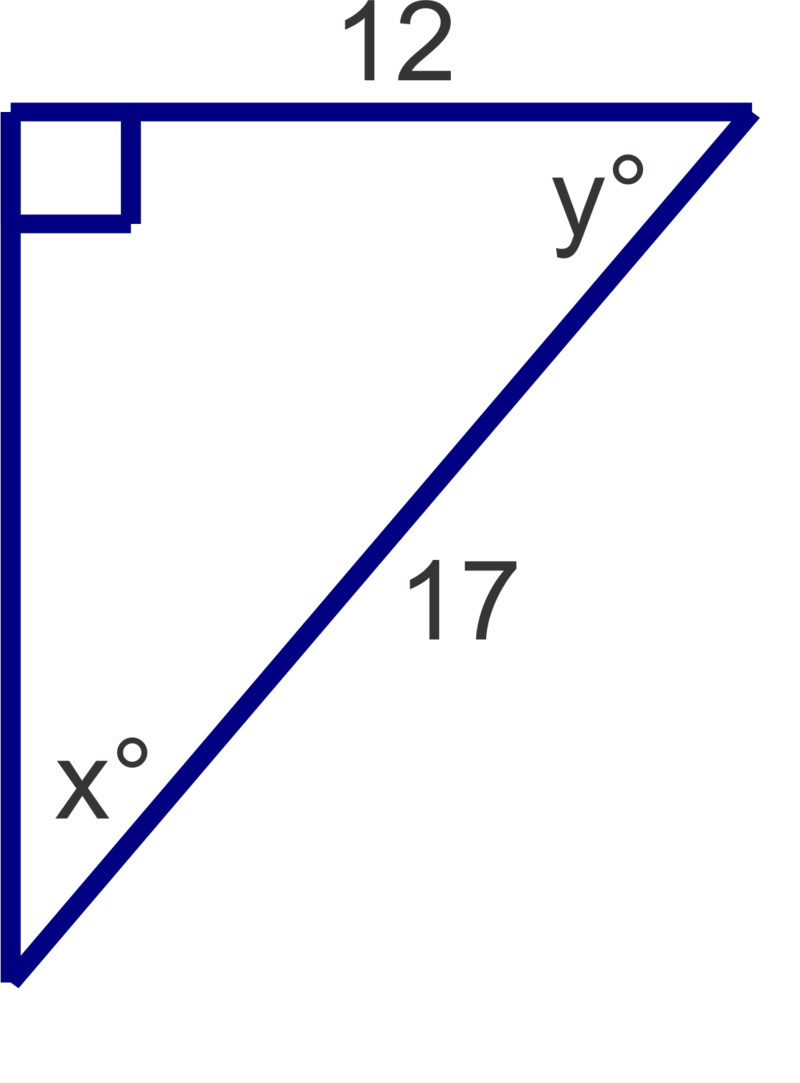
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) -
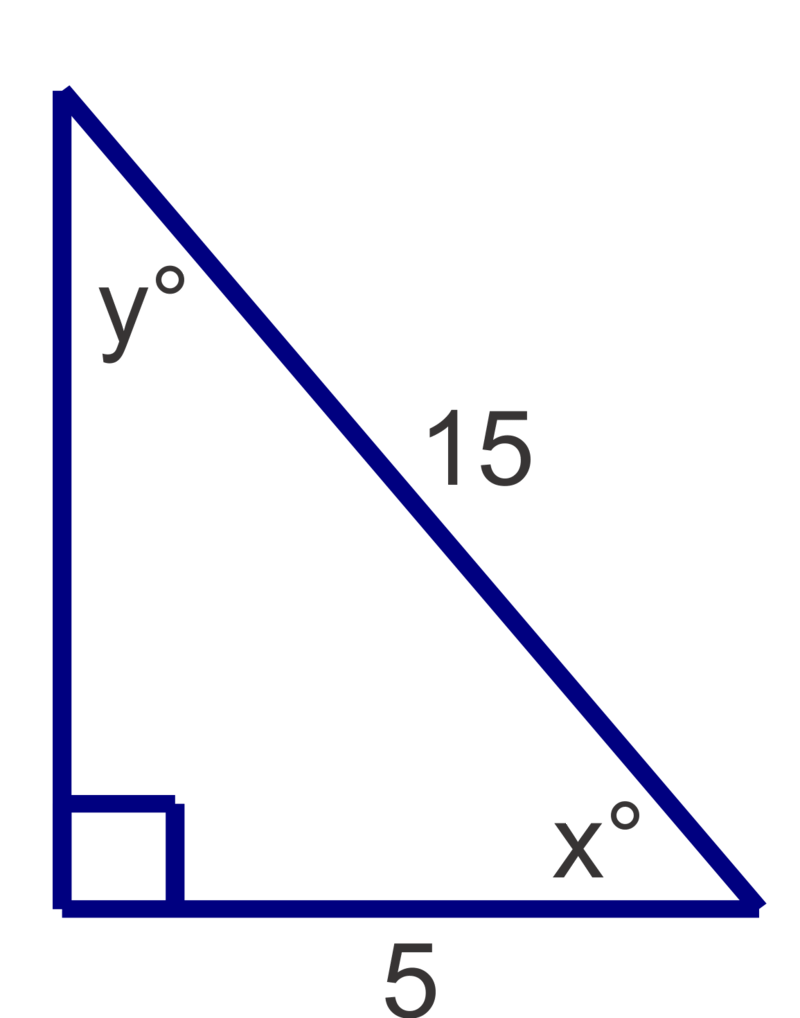
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) -
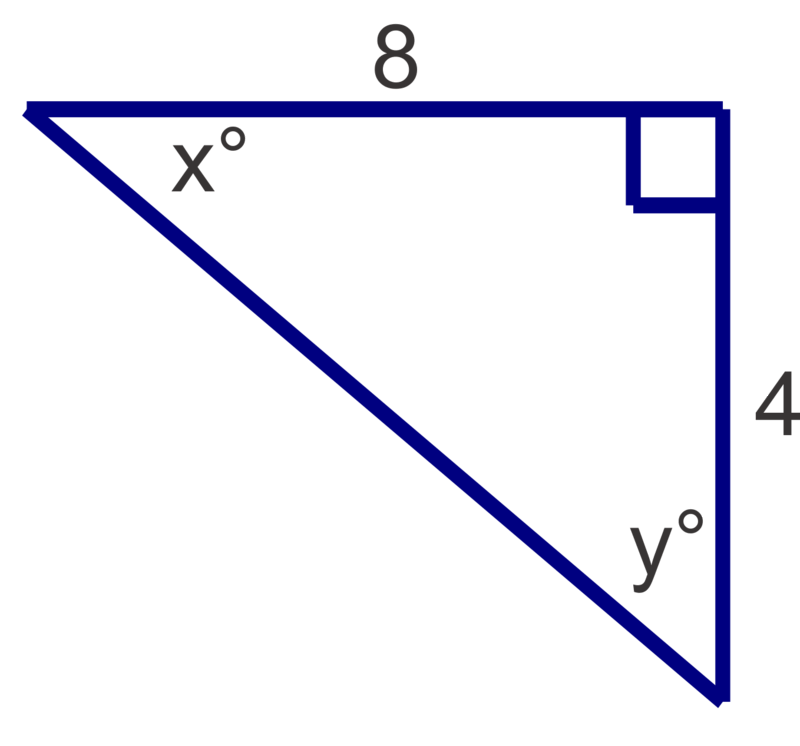
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) -
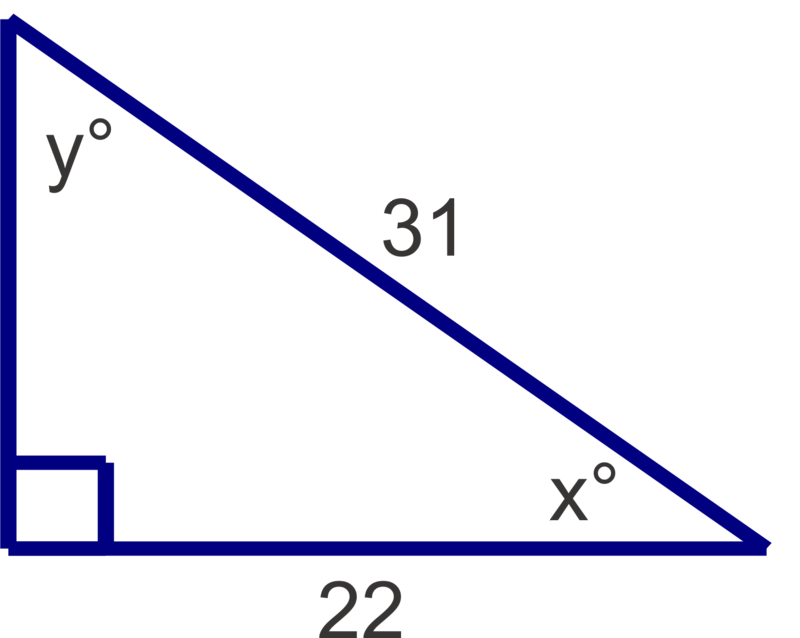
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
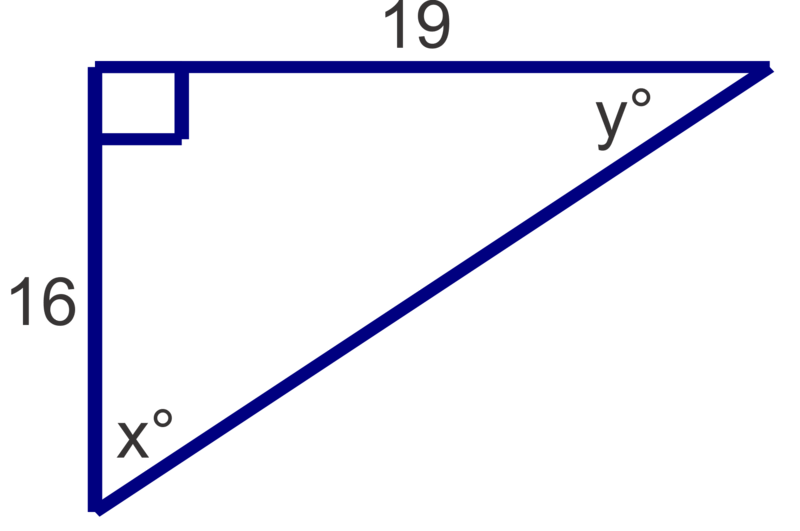
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) -
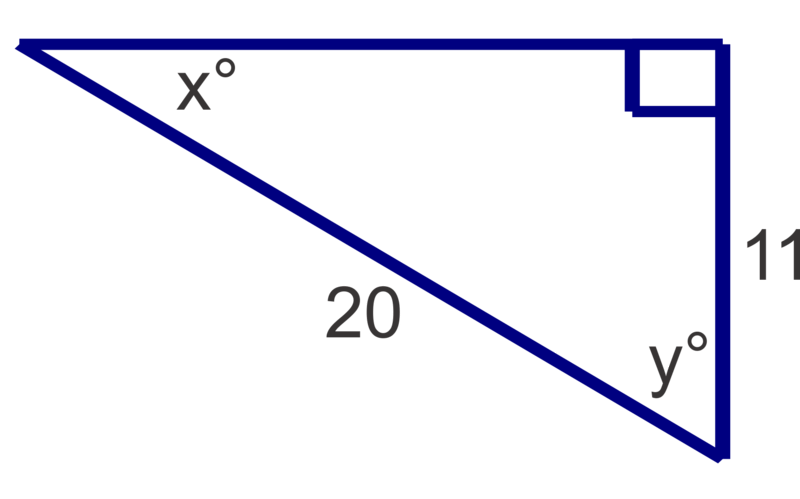
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Solve the following right triangles. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side lengths to the nearest tenth.
-
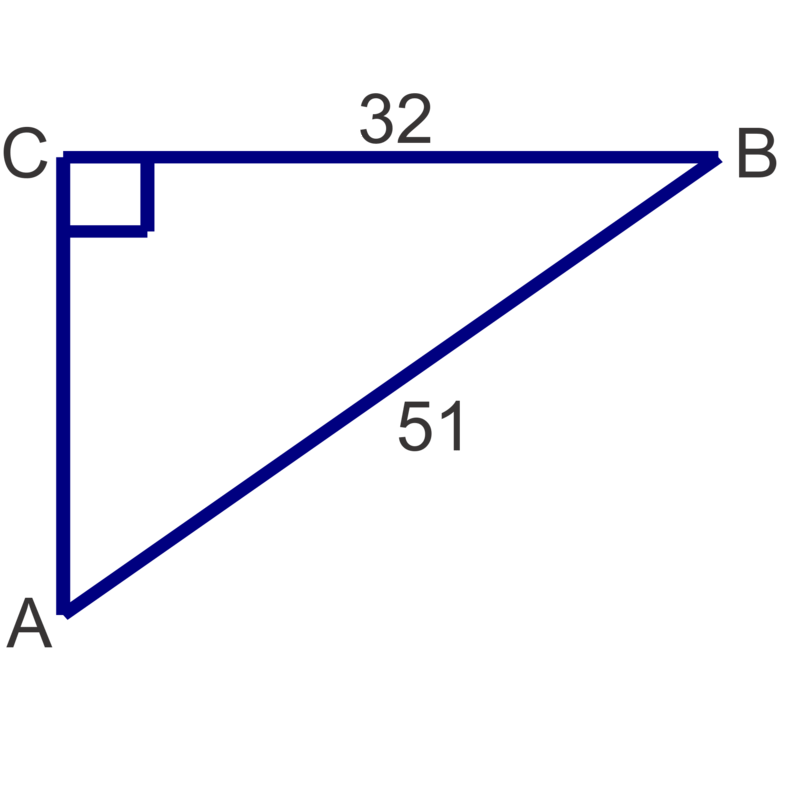
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -
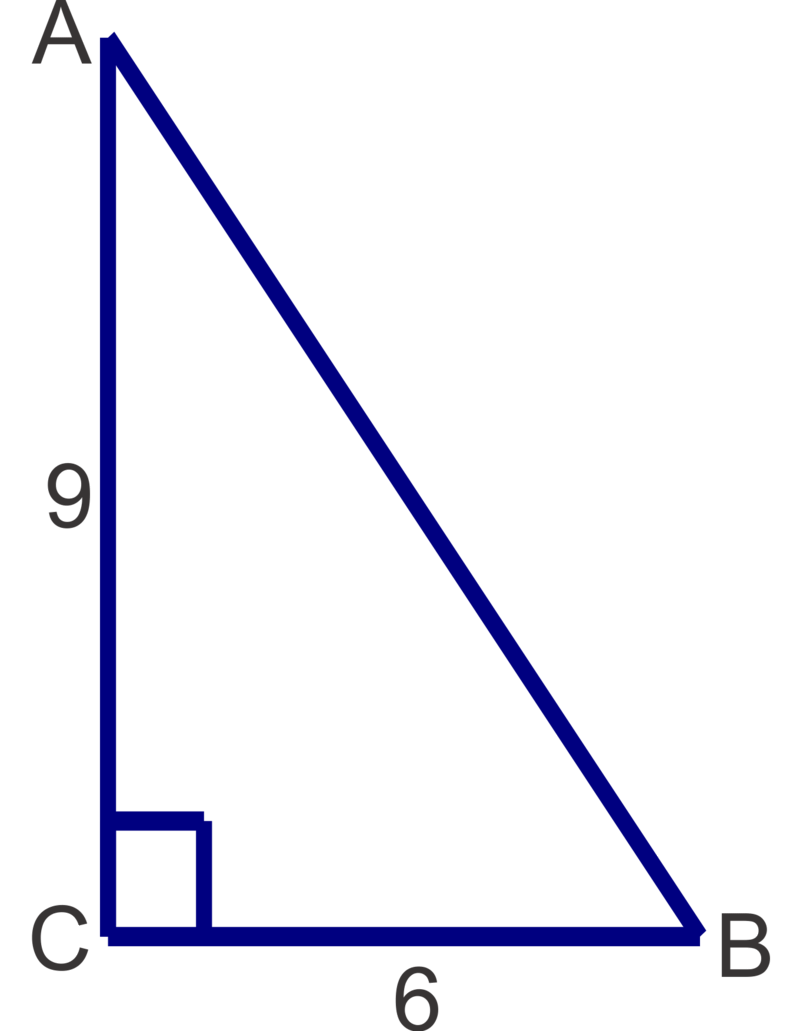
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -
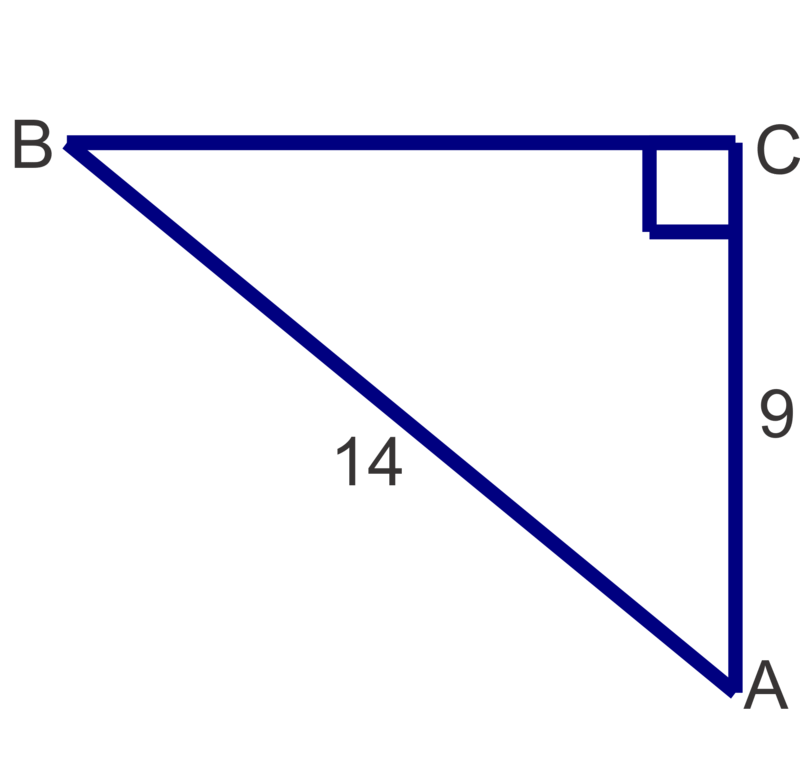
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Answers for Review Problems
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 13.3.
Additional Resources
Video: Evaluating Inverse Trigonometric Functions Without Using the Calculator - Overview
Practice: Inverse Trig Functions

