11.7: Invertebrate Classification
- Page ID
- 1387
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)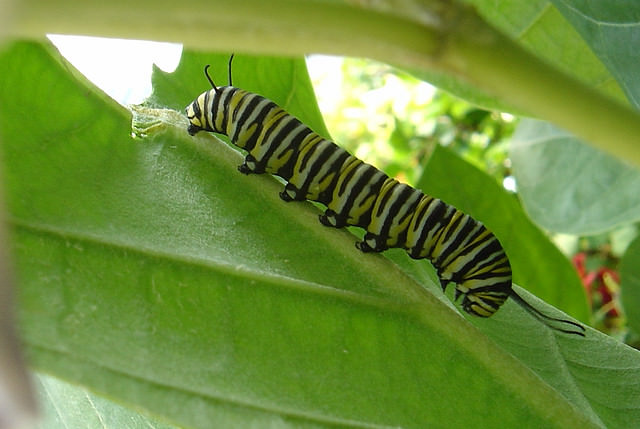
Invertebrate, arthropod or insect?
This Monarch caterpillar is an invertebrate. It is also an insect and an arthropod. Of all the animal species, it is estimated that well over 90% are invertebrates. Of all invertebrates, the insects are by far the most numerous. There are so many species of insects that scientists have yet to discover them all, let alone name or count them. Estimates of the total number of insect species fall in the range of 1 to 30 million. So, it helps if there are methods to classify not just the insects, but all invertebrates.
Classification of Invertebrates
Eight major phyla contain the majority of invertebrate species.
Major Invertebrate Phyla
Table below gives an overview of the eight invertebrate phyla with the greatest number of species.
| Phylum (includes) | Notable Characteristics | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Porifera (sponges) | multicellularity, specialized cells but no tissues, asymmetry, incomplete digestive system | sponges |
| Cnidaria (jellyfish, corals) | radial symmetry, true tissues, incomplete digestive system | jellyfish |
| Platyhelminthes (flatworms, tapeworms, flukes) | cephalization, bilateral symmetry, mesoderm, complete digestive system | flatworm |
| Nematoda (roundworms) | pseudocoelom, complete digestive system | roundworm |
| Mollusca (snails, clams, squids) | true coelom, organ systems, some with primitive brain | snail |
| Annelida (earthworms, leeches, marine worms) | segmented body, primitive brain | earthworm |
| Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans, centipedes) | segmented body, jointed appendages, exoskeleton, brain | insect (dragonfly) |
| Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers) | complete digestive system, coelom, spiny internal skeleton | sea urchin |
Protostomes and Deuterostomes
Most invertebrates (and higher animals) can be placed in one of two groups based on how they develop as embryos. The two groups are called protostomes and deuterostomes. As shown in Figure below, organisms in the two groups have different ways of forming the coelom and mouth, among other differences.
Mollusks, annelids, and arthropods are protostomes. Echinoderms and chordates are deuterostomes. This distinction is important. Why does it matter? It shows that echinoderms are more closely related to chordates than are the other invertebrate phyla. This is not apparent based on other, more obvious traits.
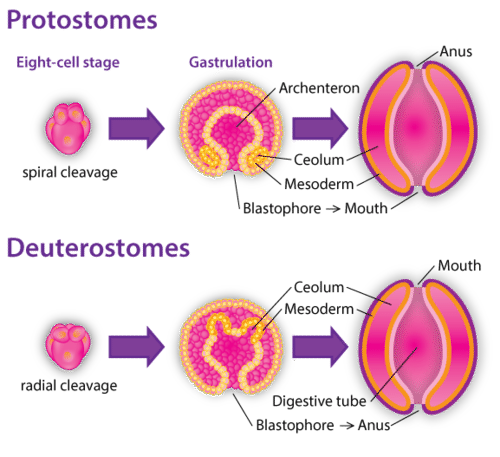 Protostomes vs. Deuterostomes. In protostomes such as mollusks, the coelom forms within the mesoderm. In deuterostomes such as echinoderms, the coelom forms from a pouch of endoderm. How does the formation of the mouth differ in these two groups of animals?
Protostomes vs. Deuterostomes. In protostomes such as mollusks, the coelom forms within the mesoderm. In deuterostomes such as echinoderms, the coelom forms from a pouch of endoderm. How does the formation of the mouth differ in these two groups of animals?Science Friday: Isn't this Octopus Adorabilis?
What do you call a tiny octopus with big eyes, gelatinous skin and is cute as a button? Nobody knows quite yet! In this video by Science Friday, Stephanie Bush aims to classify and name this presently undescribed deep-sea cephalopod.
Summary
- Eight invertebrate phyla contain most invertebrate species.
- Invertebrates (and higher animals) can also be placed in one of two groups based on how they develop as embryos.
Review
- What are protostomes?
- Describe evidence showing that echinoderms are more closely related to chordates than are other invertebrate phyla.
- Assume you have discovered a new invertebrate. It has a segmented body, a brain, and jointed appendages. In which phylum would you place it? Why?
| Image | Reference | Attributions |
 |
[Figure 1] | License: CC BY-NC |
 |
[Figure 2] | Credit: Zachary Wilson Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |

