3.9: Mendel's Second Experiment
- Page ID
- 1453
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)
Round and green, round and yellow, wrinkled and green, or wrinkled and yellow?
Can two traits be inherited together? Or are all traits inherited separately? Mendel asked these questions after his first round of experiments.
Mendel’s Second Set of Experiments
After observing the results of his first set of experiments, Mendel wondered whether different characteristics are inherited together. For example, are purple flowers and tall stems always inherited together? Or do these two characteristics show up in different combinations in offspring? To answer these questions, Mendel next investigated two characteristics at a time. For example, he crossed plants with yellow round seeds and plants with green wrinkled seeds. The results of this cross, which is a dihybrid cross, are shown in the Figure below.
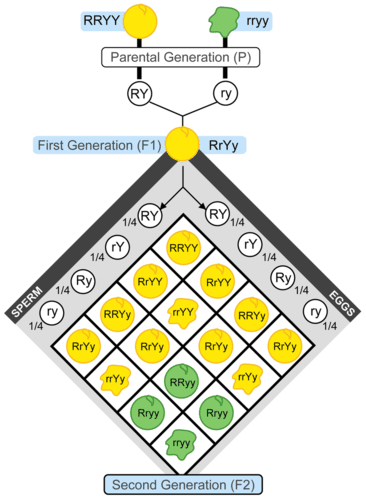 This chart represents Mendel's second set of experiments. It shows the outcome of a cross between plants that differ in seed color (yellow or green) and seed form (shown here with a smooth round appearance or wrinkled appearance). The letters R, r, Y, and y represent genes for the characteristics Mendel was studying. Mendel didn’t know about genes, however. Genes would not be discovered until several decades later. This experiment demonstrates that in the F2 generation, 9/16 were round yellow seeds, 3/16 were wrinkled yellow seeds, 3/16 were round green seeds, and 1/16 were wrinkled green seeds.
This chart represents Mendel's second set of experiments. It shows the outcome of a cross between plants that differ in seed color (yellow or green) and seed form (shown here with a smooth round appearance or wrinkled appearance). The letters R, r, Y, and y represent genes for the characteristics Mendel was studying. Mendel didn’t know about genes, however. Genes would not be discovered until several decades later. This experiment demonstrates that in the F2 generation, 9/16 were round yellow seeds, 3/16 were wrinkled yellow seeds, 3/16 were round green seeds, and 1/16 were wrinkled green seeds.F1 and F2 Generations
In this set of experiments, Mendel observed that plants in the F1 generation were all alike. All of them had yellow and round seeds like one of the two parents. When the F1 generation plants self-pollinated, however, their offspring—the F2 generation—showed all possible combinations of the two characteristics. Some had green round seeds, for example, and some had yellow wrinkled seeds. These combinations of characteristics were not present in the F1 or P generations.
Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel repeated this experiment with other combinations of characteristics, such as flower color and stem length. Each time, the results were the same as those in the Figure above. The results of Mendel’s second set of experiments led to his second law. This is the law of independent assortment. It states that factors controlling different characteristics are inherited independently of each other.
Summary
- After his first set of experiments, Mendel researched two characteristics at a time. This led to his law of independent assortment. This law states that the factors controlling different characteristics are inherited independently of each other.
Review
- What was Mendel investigating with his second set of experiments? What was the outcome?
- State Mendel’s second law.
- If a purple-flowered, short-stemmed plant is crossed with a white-flowered, long-stemmed plant, would all of the purple-flowered offspring also have short stems? Why or why not?
| Image | Reference | Attributions |
 |
[Figure 1] | Credit: Mariana Ruiz Villarreal (LadyofHats) for CK-12 Foundation Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |
 |
[Figure 2] | Credit: Mariana Ruiz Villarreal (LadyofHats) for CK-12 Foundation Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |

