2.13: Introduction to Proofs
- Page ID
- 7185
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Use two column proofs to assert and prove the validity of a statement by writing formal arguments of mathematical statements. Also learn about paragraph and flow diagram proof formats.
Two-Column Proofs
A two-column proof is one common way to organize a proof in geometry. Two-column proofs always have two columns: one for statements and one for reasons. The best way to understand two-column proofs is to read through examples.
When writing your own two-column proof, keep these things in mind:
- Number each step.
- Start with the given information.
- Statements with the same reason can be combined into one step. It is up to you.
- Draw a picture and mark it with the given information.
- You must have a reason for EVERY statement.
- The order of the statements in the proof is not always fixed, but make sure the order makes logical sense.
- Reasons will be definitions, postulates, properties and previously proven theorems. “Given” is only used as a reason if the information in the statement column was given in the problem.
- Use symbols and abbreviations for words within proofs. For example, \(\cong\) can be used in place of the word congruent. You could also use \(\angle for the word angle.
Suppose you are told that \(\angle XYZ\) is a right angle and that \(\overrightarrow{YW}\) bisects \(\angle XYZ\). You are then asked to prove \(\angle XYW\cong \angle WYZ\).
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Write a two-column proof for the following:
If \(A\),\(B\),\(C\), and \(D\) are points on a line, in the given order, and \(AB=CD\), then \(AC=BD\).
Solution
When the statement is given in this way, the “if” part is the given and the “then” part is what we are trying to prove.
Always start with drawing a picture of what you are given.
Plot the points in the order \(A\),\(B\),\(C\),\(D\) on a line.

Add the given, \(AB=CD\).

Draw the two-column proof and start with the given information.
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(A\),\(B\),\(C\), and \(D\) are collinear, in that order. | 1. Given |
| 2. \(AB=CD\) | 2. Given |
| 3. \(BC=BC\) | 3. Reflexive PoE |
| 4. \(AB+BC=BC+CD\) | 4. Addition PoE |
|
5. \(AB+BC=AC\) \(BC+CD=BD\) |
5. Segment Addition Postulate |
| 6. \(AC=BD\) | 6. Substitution or Transitive PoE |
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Write a two-column proof.
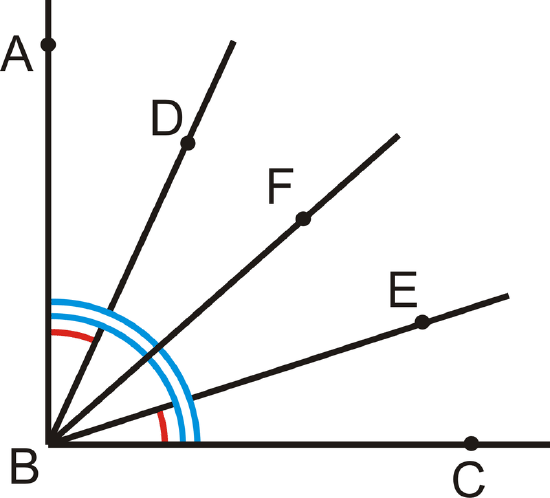
Given: \(\overrightarrow{BF}\) bisects \(\angle ABC\); \(\angle ABD\cong \angle CBE\)
Prove: \(\angle DBF\cong \angle EBF\)
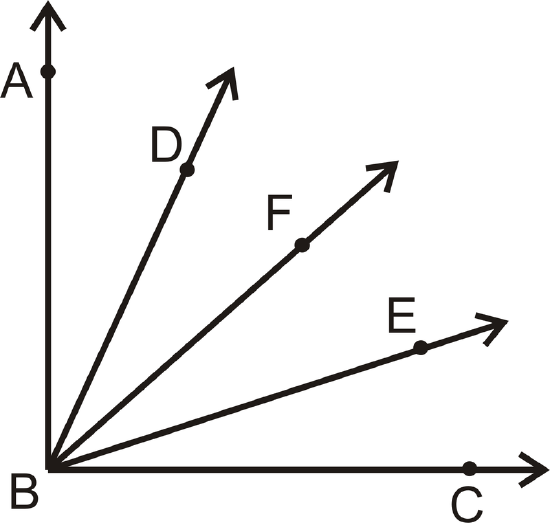 Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)Solution
First, put the appropriate markings on the picture. Recall, that bisect means “to cut in half.” Therefore, \(m\angle ABF=m\angle FBC\).
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(\overrightarrow{BF}\) bisects \(\angle ABC\), \(\angle ABD\cong \angle CBE\) | 1. Given |
| 2. \(m\angle ABF=m\angle FBC\) | 2. Definition of an Angle Bisector |
| 3. \(m\angle ABD=m\angle CBE\) | 3. If angles are \(\cong\), then their measures are equal. |
|
4. \(m\angle ABF=m\angle ABD+m\angle DBF\) \(m\angle FBC=m\angle EBF+m\angle CBE\) |
4. Angle Addition Postulate |
| 5. \(m\angle ABD+m\angle DBF=m\angle EBF+m\angle CBE\) | 5. Substitution PoE |
| 6. \(m\angle ABD+m\angle DBF=m\angle EBF+m\angle ABD\) | 6. Substitution PoE |
| 7. \(m\angle DBF=m\angle EBF\) | 7. Subtraction PoE |
| 8. \(\angle DBF\cong \angle EBF\) | 8. If measures are equal, the angles are \(\cong . |
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
The Right Angle Theorem states that if two angles are right angles, then the angles are congruent. Prove this theorem.
To prove this theorem, set up your own drawing and name some angles so that you have specific angles to talk about.
Given: \(\angle A\) and \(\angle B\) are right angles
Prove: \(\angle A\cong \angle B\)
Solution
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(\angle A\) and \(\angle B\) are right angles | 1. Given |
| 2. \(m\angle A=90^{\circ}\) and \(m\angle B=90^{\circ}\) | 2. Definition of right angles |
| 3. \(m\angle A=m\angle B\) | 3. Transitive PoE |
| 4. \(\angle A\cong \angle B\) | 4. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
Any time right angles are mentioned in a proof, you will need to use this theorem to say the angles are congruent.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
The Same Angle Supplements Theorem states that if two angles are supplementary to the same angle then the two angles are congruent. Prove this theorem.
Given: \(\angle A\) and \(\)\angle B are supplementary angles. \(\angle B\) and \(\angle C\) are supplementary angles.
Prove: \(\angle A\cong \angle C\)
Solution
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
|
1. \(\angle A\) and \(\angle B\) are supplementary \(\angle B\) and \(\angle C\) are supplementary |
1. Given |
|
2. \(m\angle A+m\angle B=180^{\circ} \(m\angle B+m\angle C=180^{\circ} |
2. Definition of supplementary angles |
| 3. \(m\angle A+m\angle B=m\angle B+m\angle C\) | 3. Substitution PoE |
| 4. \(m\angle A=m\angle C\) | 4. Subtraction PoE |
| 5. \(\angle A\cong \angle C\) | 5. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
The Vertical Angles Theorem states that vertical angles are congruent. Prove this theorem.
Given: Lines \(k\) and \(m\) intersect.
Prove: \(\angle 1\cong \angle 3\)
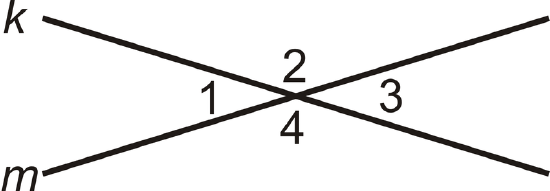
Solution
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. Lines \(k\) and \(m\) intersect | 1. Given |
|
2. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are a linear pair \(\)\angle 2 and \(\angle 3\) are a linear pair |
2. Definition of a Linear Pair |
|
3. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are supplementary \(\angle 2\) and \(\angle 3\) are supplementary |
3. Linear Pair Postulate |
|
4. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=180^{\circ}\) \(m\angle 2+m\angle 3=180^{\circ}\) |
4. Definition of Supplementary Angles |
| 5. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=m\angle 2+m\angle 3\) | 5. Substitution PoE |
| 6. \(m\angle 1=m\angle 3\) | 6. Subtraction PoE |
| 7. \(\angle 1\cong \angle 3\) | 7. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\)
\(\angle 1\cong \angle 4\) and \(\angle C\) and \(\angle F\) are right angles.
Which angles are congruent and why?
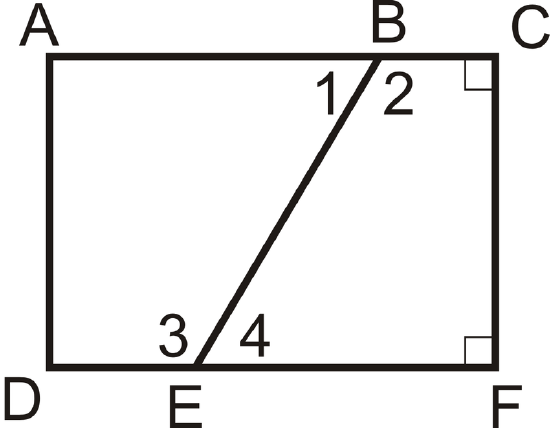
Solution
By the Right Angle Theorem, \(\angle C\cong \angle F\). Also, \(\angle 2\cong \angle 3\) by the Same Angles Supplements Theorem because \(\angle 1\cong \angle 4\) and they are linear pairs with these congruent angles.
Review
Fill in the blanks in the proofs below.
- Given: \(\angle ABC\cong \angle DEF\) and \(\angle GHI\cong \angle JKL\)
Prove: \(m\angle ABC+m\angle GHI=m\angle DEF+m\angle JKL\)
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Given |
|
2. \(m\angle ABC=m\angle DEF\) \(m\angle GHI=m\angle JKL\) |
2. |
| 3. | 3. Addition PoE |
| 4. \(m\angle ABC+m\angle GHI=m\angle DEF+m\angle JKL\) | 4. |
- Given: \(M\) is the midpoint of \(\overline{AN}\). \(N\) is the midpoint \(\overline{MB}\)
Prove: \(AM=NB\)
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | Given |
| 2. | Definition of a midpoint |
| 3. \(AM=NB\) |
- Given: \(\overline{AC}\perp \overline{BD}\) and \(\angle 1\cong \angle 4\)
Prove: \(\angle 2\cong \angle 3\)
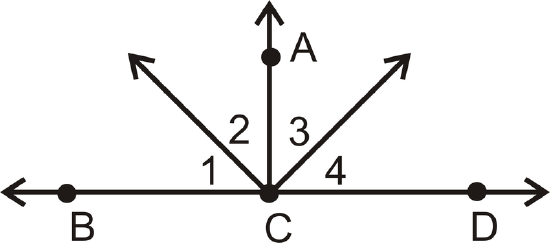
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(\overline{AC}\perp \overline{BD}, \(\angle 1\cong \angle 4 | 1. |
| 2. \(m\angle 1=m\angle 4\) | 2. |
| 3. | 3. \(\perp lines create right angles |
|
4. \(m\angle ACB=90^{\circ}\) \(m\angle ACD=90^{\circ}\) |
4. |
|
5. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=m\angle ACB\) \(m\angle 3+m\angle 4=m\angle ACD\) |
5. |
| 6. | 6. Substitution |
| 7. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=m\angle 3+m\angle 4\) | 7. |
| 8. | 8. Substitution |
| 9. | 9.Subtraction PoE |
| 10. \(\angle 2\cong \angle 3\) | 10. |
- Given: \(\angle MLN\cong \angle OLP\)
Prove: \(\angle MLO\cong \angle NLP\)
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. | 2. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
| 3. | 3. Angle Addition Postulate |
| 4. | 4. Substitution |
| 5. \(m\angle MLO=m\angle NLP\) | 5. |
| 6. | 6. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
- Given: \(\underline{AE}\perp \underline{EC}\) and \(\underline{BE}\perp \underline{ED}\)
Prove: \(\angle 1\cong \angle 3\)
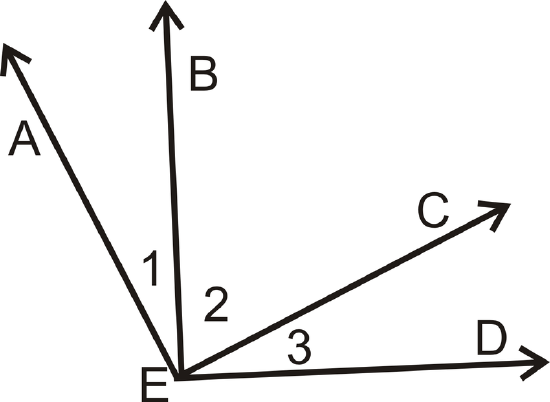
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. | 2. \(\perp\) lines create right angles |
|
3. \(m\angle BED=90^{\circ}\) \(m\angle AEC=90^{\circ}\) |
3. |
| 4. | 4. Angle Addition Postulate |
| 5. | 5. Substitution |
| 6. \(m\angle 2+m\angle 3=m\angle 1+m\angle 3\) | 6. |
| 7. | 7. Subtraction PoE |
| 8. | 8. \(\cong\) angles have = measures |
- Given: \(\angle L\) is supplementary to \(\angle M\) and \(\angle P\) is supplementary to \(\angle O\) and \(\angle L\cong \angle O\)
Prove: \(\angle P\cong \angle M\)
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. \(m\angle L=m\angle O\) | 2. |
| 3. | 3. Definition of supplementary angles |
| 4. | 4. Substitution |
| 5. | 5. Substitution |
| 6. | 6. Subtraction PoE |
| 7. \(\angle M\cong \angle P\) | 7. |
- Given: \(\angle 1\cong \angle 4\)
Prove: \(\angle 2\cong \angle 3\)

| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. \(m\angle 1=m\angle 4\) | 2. |
| 3. | 3. Definition of a Linear Pair |
|
4. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are supplementary \(\angle 3\) and \(\angle 4\) are supplementary |
4. |
| 5. | 5. Definition of supplementary angles |
| 6. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=m\angle 3+m\angle 4\) | 6. |
| 7. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=m\angle 3+m\angle 1\) | 7. |
| 8. \(m\angle 2=m\angle 3\) | 8. |
| 9. \(\angle 2\cong \angle 3\) | 9. |
- Given: \(\angle C\) and \(\angle F\) are right angles
Prove: \(m\angle C+m\angle F=180^{\circ}\)

| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. \(m\angle C=90^{\circ}, \(m\angle F=90^{\circ}\) | 2. |
| 3. \(90^{\circ}+90^{\circ}=180^{\circ}\) | 3. |
| 4. \(m\angle C+m\angle F=180^{\circ}\) | 4. |
- Given: \(l\perp m\)
Prove: \(\angle 1\cong \angle 2\)
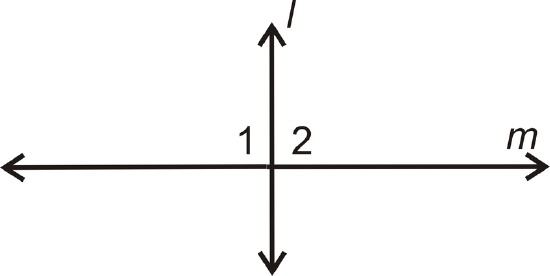
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(l\perp m\) | 1. |
| 2. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are right angles | 2. |
| 3. | 3. |
- Given: \(m\angle 1=90^{\circ}\)
Prove: \(m\angle 2=90^{\circ}\)

| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are a linear pair | 2. |
| 3. | 3. Linear Pair Postulate |
| 4. | 4. Definition of supplementary angles |
| 5. | 5. Substitution |
| 6. \(m\angle 2=90^{\circ}\) | 6. |
- Given: \(l\perp m\)
Prove: \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are complements
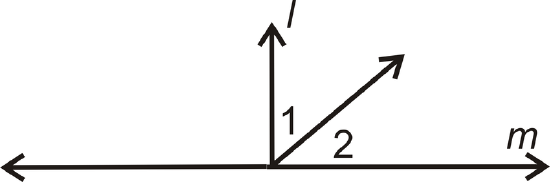
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. | 2. \(\perp\) lines create right angles |
| 3. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=90^{\circ}\) | 3. |
| 4. \(\angle 1\) and \(\angle 2\) are complementary | 4. |
- Given: \(l\perp m\) and \(\angle 2\cong \angle 6\)
Prove: \(\angle 6\cong \angle 5\)
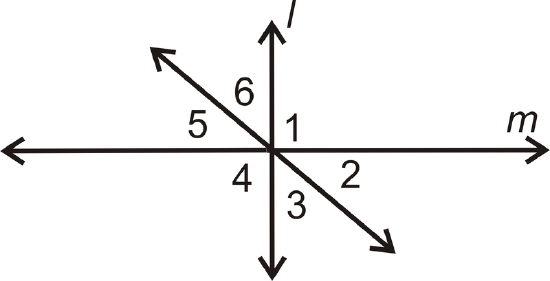
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. | 1. |
| 2. \(m\angle 2=m\angle 6\) | 2. |
| 3. \(\angle 5\cong \angle 2\) | 3. |
| 4. \(m\angle 5=m\angle 2\) | 4. |
| 5. \(m\angle 5=m\angle 6\) | 5. |
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 2.7.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| two column proof | A common way to organize a proof in geometry. Two column proofs always have two columns- statements and reasons. |
| linear pair | Two angles form a linear pair if they are supplementary and adjacent. |
Additional Resources
Video: Two Column Proofs Principles - Basic
Activities: Two-Column Proofs Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Proofs Study Guide
Practice: Introduction to Proofs
Real World: Give Me One Reason

