2.1.2: Calculator Trig Functions
- Page ID
- 4214
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Trigonometric ratios based on sides of right triangles in relation to an angle.
Trigonometric Ratios with a Calculator
There is a fixed sine, cosine, and tangent value for every angle, from \(0^{\circ}\) to \(90^{\circ}\). Your scientific (or graphing) calculator knows all the trigonometric values for any angle. Your calculator, should have [SIN], [COS], and [TAN] buttons. You can use your calculator and the trigonometric ratios is to find the missing sides of a right triangle by setting up a trig equation.
What if you were given a 20-70-90 triangle? How could you find the sine, cosine, and tangent of the \(20^{\circ}\) and \(70^{\circ}\) angles?
Find the length of the missing sides and round your answers to the nearest tenth:
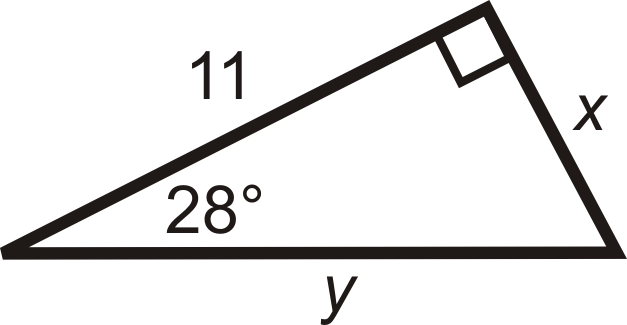
Solution
Use tangent for \(x\) and cosine for \(y\).
\(\begin{array}{rlrl}
\tan 28^{\circ} & =\dfrac{x}{11} & \cos 28^{\circ} & =\dfrac{11}{y} \\
11 \cdot \tan 28^{\circ} & =x & \dfrac{11}{\cos 28^{\circ}} & =y \\
x & \approx 5.8 & y &\approx 12.5
\end{array}\)
Find the length of the missing sides and round your answers to the nearest tenth:
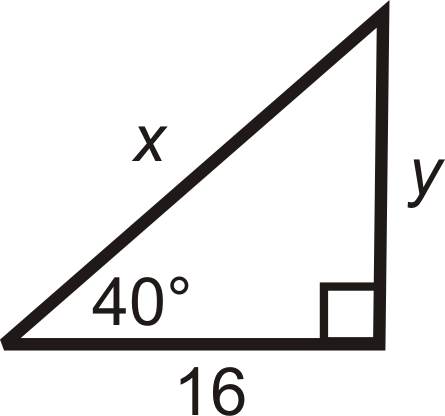
Solution
Use tangent for \(y\) and cosine for \(x\).
\(\begin{aligned}
\tan 40^{\circ} &=\dfrac{y}{16} & \cos 40^{\circ} &=\dfrac{16}{x} \\
16 \cdot \tan 40^{\circ} &=y & \dfrac{16}{\cos 40^{\circ}} &=x \\
y & \approx 13.4 & \quad x & \approx 20.9
\end{aligned}\)
Find the trigonometric values, using your calculator:
\(sin 78^{\circ}\), \(\cos 60^{\circ}\), \(\tan 15^{\circ}\)
Solution
Round to 4 decimal places.
Depending on your calculator, you enter the degree and then press the trig button or the other way around. Also, make sure the mode of your calculator is in DEGREES.
\(\begin{aligned} \sin 78^{\circ}&=0.97815 \\ \cos 60^{\circ}&=0.5 \\ \tan 15^{\circ}&=0.26795\end{aligned}\)
Find the value of each variable. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
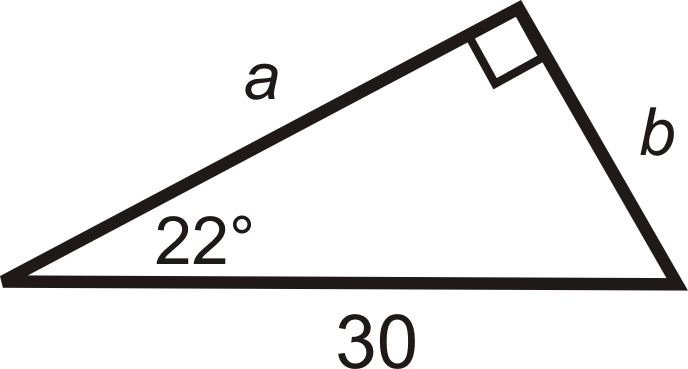
Solution
We are given the hypotenuse. Use sine to find \(b\), and cosine to find \(a\). Use your calculator to evaluate the sine and cosine of the angles.
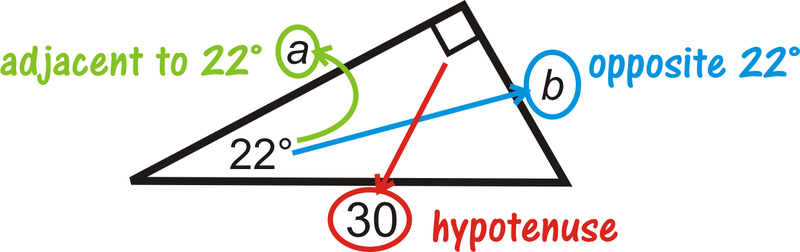
\(\begin{array}{rlrl}
\sin 22^{\circ} & =\dfrac{b}{30} & \cos 22^{\circ} & =\dfrac{a}{30} \\
30 \cdot \sin 22^{\circ} & =b & 30 \cdot \cos 22^{\circ} & =a \\
b & \approx 11.2 & a &\approx 27.8
\end{array}\)
Find the value of each variable. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Solution
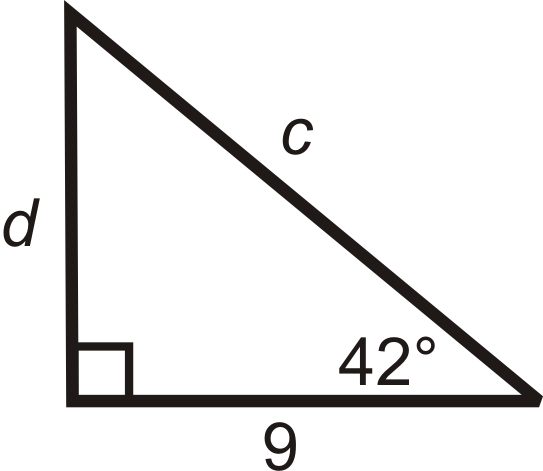
We are given the adjacent leg to \(42^{\circ}\). To find \(c\), use cosine and use tangent to find \(d\).
\(\begin{array}{rlrl}
\cos 42^{\circ} & =\dfrac{a d j a c e n t}{\text {hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{9}{c} & \tan 42^{\circ} & =\dfrac{\text {opposite}}{\text {adjacent}}=\dfrac{d}{9} \\
c \cdot \cos 42^{\circ} & =9 & 9 \cdot \tan 42^{\circ} & =d \\
c & =\dfrac{9}{\cos 42^{\circ}} \approx 12.1 & d & \approx 27.0
\end{array}\)
Any time you use trigonometric ratios, use only the information that you are given. This will result in the most accurate answers.
Review
Use your calculator to find the value of each trig function below. Round to four decimal places.
- \(\sin 24^{\circ}\)
- \(\cos 45^{\circ}\)
- \(\tan 88^{\circ}\)
- \(\sin 43^{\circ}\)
- \(\tan 12^{\circ}\)
- \(\cos 79^{\circ}\)
- \(\sin 82^{\circ}\)
Find the length of the missing sides. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
-
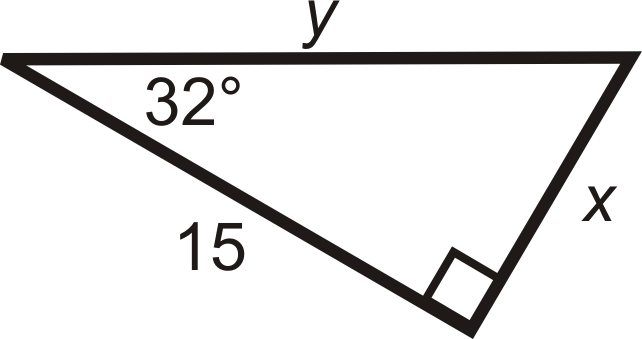
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) -
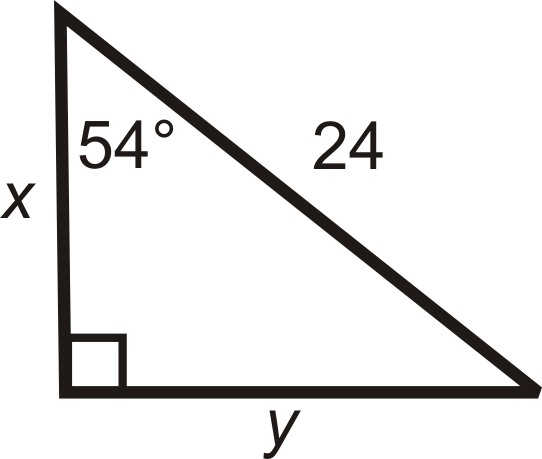
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) -
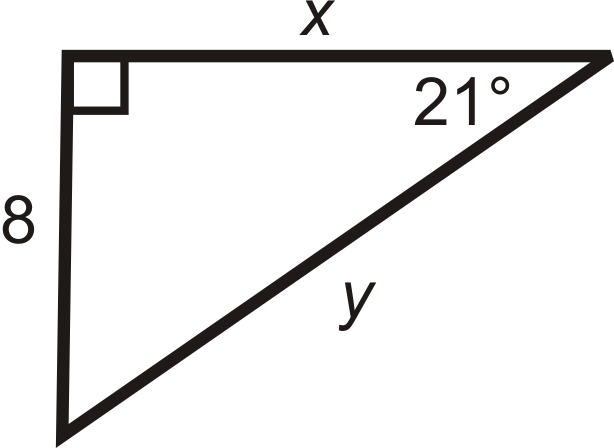 Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
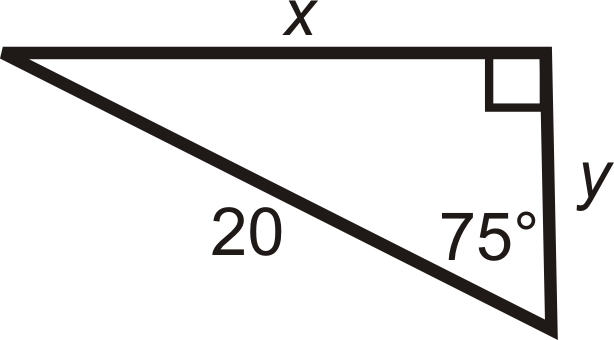 Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.8.
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| trigonometry | The study of the relationships between the sides and angles of right triangles. |
| Hypotenuse | The hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side of the right triangle. It is across from the right angle. |
| Legs of a Right Triangle | The legs of a right triangle are the two shorter sides of the right triangle. Legs are adjacent to the right angle. |
| Trigonometric Ratios | Ratios that help us to understand the relationships between sides and angles of right triangles. |
Additional Resources
Video: Introduction to Trigonometric Functions Using Triangles
Activities: Trigonometric Ratios with a Calculator Discussion Questions
Practice: Calculator Trig Functions
Real World: Sine Cosine Tangent

