12.8: Reptile Evolution
- Page ID
- 13245
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)
So what exactly is a dinosaur?
Dinosaurs were not lizards. Rather, they were a separate group of reptiles with a distinct upright posture not found in lizards. Dinosaurs can be described as large, powerful reptiles. And many were very big. But dinosaurs were more than that. They were a varied group of animals with over 1,000 non-avian species.
Evolution of Reptiles
The earliest amniotes evolved about 350 million years ago. They resembled small lizards, but they were not yet reptiles. Their amniotic eggs allowed them to move away from bodies of water and become larger. They soon became the most important land vertebrates.
Synapsids and Sauropsids
By about 320 million years ago, early amniotes had diverged into two groups, called synapsids and sauropsids. Synapsids were amniotes that eventually gave rise to mammals. Sauropsids were amniotes that evolved into reptiles, dinosaurs, and birds. The two groups of amniotes differed in their skulls. The earliest known reptile, pictured in Figure below, dates back about 315 million years.
 Earliest Reptile: Hylonomus. The earliest known reptile is given the genus name Hylonomus. It was about 20 to 30 centimeters (8 to 12 inches) long, lived in swamps, and ate insects and other small invertebrates.
Earliest Reptile: Hylonomus. The earliest known reptile is given the genus name Hylonomus. It was about 20 to 30 centimeters (8 to 12 inches) long, lived in swamps, and ate insects and other small invertebrates.At first, synapsids were more successful than sauropsids. They became the most common vertebrates on land. However, during the Permian mass extinction 245 million years ago, most synapsids went extinct. Their niches were taken over by sauropsids, which had been relatively unimportant until then. This is called the Triassic takeover.
Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs
By the middle of the Triassic about 225 million years ago, sauropsids had evolved into dinosaurs. Dinosaurs became increasingly important throughout the rest of the Mesozoic Era, as they radiated to fill most terrestrial niches. This is why the Mesozoic Era is called the Age of the Dinosaurs. During the next mass extinction, which occurred at the end of the Mesozoic Era, all of the dinosaurs went extinct. Many other reptiles survived, however, and they eventually gave rise to modern reptiles.
Evolution of Modern Reptile Orders
Figure below shows a traditional phylogenetic tree of living reptiles. Based on this tree, some of the earliest reptiles to diverge were ancestors of turtles. The first turtle-like reptiles are thought to have evolved about 250 million years ago. Ancestral crocodilians evolved at least 220 million years ago. Tuataras may have diverged from squamates (snakes and lizards) not long after that. Finally, lizards and snakes went their separate ways about 150 million years ago.
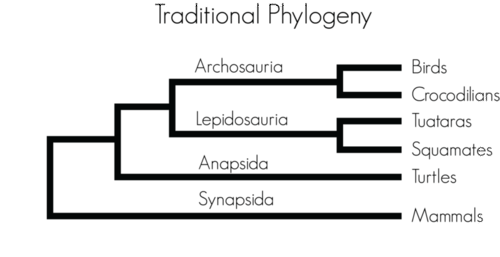 Traditional Reptile Phylogenetic Tree. This phylogenetic tree is based on physical traits of living and fossil reptiles. Trees based on DNA comparisons may differ from the traditional tree and from each other, depending on the DNA sequences used. Reptile evolution is currently an area of intense research and constant revision.
Traditional Reptile Phylogenetic Tree. This phylogenetic tree is based on physical traits of living and fossil reptiles. Trees based on DNA comparisons may differ from the traditional tree and from each other, depending on the DNA sequences used. Reptile evolution is currently an area of intense research and constant revision.Summary
- The earliest amniotes appeared about 350 million years ago, and the earliest reptiles evolved from a sauropsida ancestor by about 315 million years ago.
- Dinosaurs evolved around 225 million years ago and dominated animal life on land until 65 million years ago, when they all went extinct.
- Other reptiles survived and evolved into the classes of reptiles that exist today.
Review
- Identify amniotes called synapsids and sauropsids.
- Give a brief overview of reptile evolution.
- Explain why reptiles were able to replace amphibians as the dominant land vertebrates.
| Image | Reference | Attributions |
 |
[Figure 1] | Credit: Duncan Wright Source: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Great_Frigatebird_chick_begging.JPG License: CC BY-NC |
 |
[Figure 2] | Credit: Nobu Tamura Source: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hylonomus_BW.jpg License: CC BY 2.5 |
 |
[Figure 3] | Credit: Christopher Auyeung Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.0 |

