11.3: New Zealand (2 Days)
- Page ID
- 1989
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Outline New Zealand’s main physical features explain how the North Island is different from the South Island.
- Describe how tectonic plate activity has helped to isolate New Zealand from the rest of the world and still affects the island today.
- Summarize the situation of the Maori in New Zealand and their relationship with the dominant culture in New Zealand.
- Describe the economic geography of New Zealand and how the country gains wealth.
TEKS Regional Unit 11 Oceania: Chapter 11.3 New Zealand
WG.1A Analyze the effects of physical and human geographic patterns and processes on the past and describe their impact on the present, including significant physical features and environmental conditions that influenced migration patterns and shaped the distribution of culture groups today.
WG.2A Describe the human and physical characteristics of the same regions at different periods of time to evaluate relationships between past events and current conditions.
WG.3A Explain weather conditions and climate in relation to annual changes in Earth-Sun relationships.
WG.3B Describe the physical processes that affect the environments of regions, including weather, tectonic forces.
WG.4A Explain how elevation, latitude, wind systems, ocean currents, position on a continent, and mountain barriers influence temperature, precipitation, and distribution of climate regions.
WG.4B Describe different landforms and the physical processes that cause their development.
WG.4C Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions.
WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural elements.
WG.6A Locate and describe human and physical features that influence the size and distribution of settlements.
WG.6B Explain the processes that have caused changes in settlement patterns, including urbanization, transportation, access to and availability of resources, and economic activities.
WG.8A Compare ways that humans depend on, adapt to, and modify the physical environment, including the influences of culture and technology.
WG.8B Describe the interaction between humans and the physical environment and analyze the consequences of extreme weather and other natural disasters such as El Nino, floods. tsunamis, and volcanoes.
WG.8C Evaluate the economic and political relationships between settlements and the environments, including sustainable development and renewable/non-renewable resources.
WG.9A Identify physical and/or human factors such as climate, vegetation, language, trade networks, political units, river systems, and religion that constitute a region.
WG.10C Compare the ways people satisfy their basic needs through the production of goods and services such as subsistence agriculture versus commercial agriculture or cottage industries versus commercial industries.
WG.10D Compare global trade patterns over time and examine the implications of globalization, including outsourcing and free trade zones.
WG.11B Identify factors affecting the location of different types of economic activities, including subsistence and commercial agriculture manufacturing, and service industries.
WG.11C Assess how changes in climate, resources, and infrastructure (technology, transportation, and communication) affect the location and patterns of economic activities.
WG.18A Analyze cultural changes in specific regions caused by migration, war, trade, innovations, and diffusion.
WG.18C Identify examples of cultures that maintain traditional ways, including traditional economies.
WG.18D Evaluate the spread of cultural traits to find examples of cultural convergence and divergence such as the spread of democratic ideas, US-based fast-food franchises, the English langue, technology, or global sports.
WG.21A Analyze and evaluate the validity and utility of multiple sources of geographic information such as primary and secondary sources, aerial photographs, and maps.
WG.21C Create and interpret different types of maps to answer geographic questions, infer relationships, and analyze change.
WG.22A Design and draw appropriate graphics such as maps, diagrams tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, and relationships.
WG.22B Generate summaries, generalizations, and thesis statements supported by evidence.
WG.22E Create original work using proper citations and understanding and avoiding plagiarism.
TEKS and ELPS for Regional World Geography Unit 11--Oceania from TEKS Resource System.
New Zealand
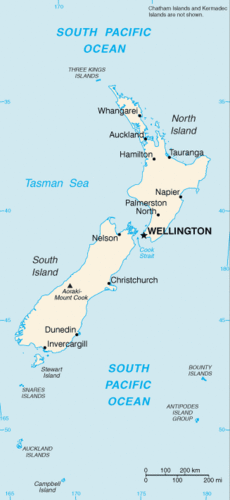 New Zealand Map
New Zealand MapPhysical Geography
To the east of Australia across the Tasman Sea is the country of New Zealand. New Zealand is one of a number of sets of islands that make up Oceania, also referred to as the Pacific Islands, a region occupying the western and central Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Islands region is generally divided into three sub-regions: Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, with New Zealand being part of Polynesia.
The Pacific Island region includes more than 25,000 individual small islands representing 25 nations and territories. Most of these islands are very small. The South and North islands of New Zealand are the second- and third-largest islands, respectively. The North and South Islands of New Zealand are separated by a body of water known as the Cook Strait, which is only about 13 miles wide at its narrowest point. The North and South Islands together are about the same size as the US state of Colorado. New Zealand also includes a number of smaller nearby islands.
New Zealand, like Australia, is in the Southern Hemisphere, which means that its seasons are expressed at the opposite times of the seasons in North America. In other words, the warmest summer months are January and February and the cooler winter months are June and July. New Zealand lies within the Temperate Zone. There are only very moderate seasonal differences, which are slightly more pronounced in the inland areas because the inland areas lack the moderating influence of the ocean.
In general, the North Island has somewhat warmer average temperatures than the South Island. In summer, average low temperatures are about 50 °F, with daytime highs around 75 °F. In the winter months, low temperatures average about 35 °F and high temperatures are about 50 °F. The occurrence of more extreme temperatures is limited to the mountainous peaks of the Southern Alps. Snow is common in these mountainous regions but rarely occurs in coastal regions.
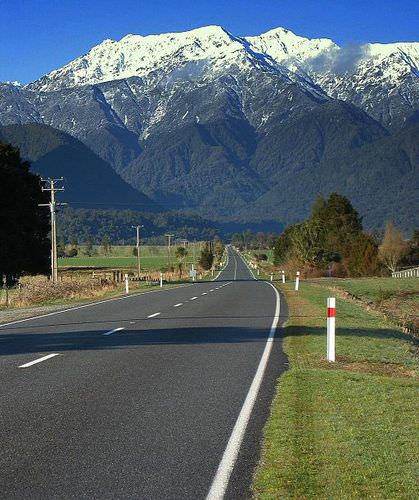 The Southern Alps is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side.
The Southern Alps is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side.Rainfall is heaviest on the western coasts of both islands, but especially on the South Island. The prevailing westerly winds, carrying moisture from the ocean, come in contact with the mountains of the Southern Alps and high precipitation results. The mountains also have the opposite effect. On the eastern side of the mountains is a rain shadow where the westerly winds blow hot, dry air and the eastern coasts are therefore substantially drier than the western coasts. Therefore, the average precipitation rates vary widely across the country.
The average annual rainfall in Christchurch, which is on the eastern coast of the South Island, is about 25 inches per year. Auckland, in the mid-portion of the North Island, receives twice that amount and areas on the wetter western coast receive as much as 115 inches per year.
As an island nation, New Zealand’s coastlines and oceans are some of its most important geographic features. New Zealand has one of the world’s largest exclusive economic zones, an oceanic zone over which a nation has exclusive rights of exploration and exploitation of marine resources. New Zealand’s exclusive economic zone covers more than one million square miles. The dramatic nature of New Zealand’s landscape is well known to many moviegoers as the landscape of Middle Earth, as depicted in New Zealand film director Peter Jackson’s version of J. R. R. Tolkein’s Lord of the Rings.
 Lake Gunn is a small lake between Lake Te Anau and Milford Sound. It lies close to the New Zealand State Highway 94 and the Divide of the Southern Alps.
Lake Gunn is a small lake between Lake Te Anau and Milford Sound. It lies close to the New Zealand State Highway 94 and the Divide of the Southern Alps.Tectonic Plates and Gondwanaland
The North Island of New Zealand features a rugged coastline with numerous harbors, bays, and inlets. The port cities of Auckland and Wellington are located on two of the largest bays. The coastline of the South Island is somewhat more regular, except along the southern portion of the eastern coastline, which has deep fjords. Though the North Island has lower relief than its southern counterpart, its few mountains are volcanic in origin.
The two main islands are accompanied by smaller islands around their shores. The North Island’s highest peak is Mount Ruapehu, which reaches almost 9,175 feet, and is an active cone volcano. It is located in the south central part of the island. A range of highlands runs along its eastern side. The volcanism associated with Mount Ruapehu results from New Zealand’s location atop two tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate.
The boundary of these two plates forms a subduction zone under the North Island. Consequently, New Zealand experiences tens of thousands of earthquakes per year. Though most of the earthquakes do not greatly disrupt human activity, some have registered higher than 7 on the Richter scale. New Zealanders have made use of the geothermal power generated by this and the tectonic features of this area and hence, New Zealand is home to several hydrothermal power plants.
A range of mountains, the Southern Alps, divides the South Island lengthwise. Many of the peaks reach over 10,000 feet. The highest peak is Mount Cook, which reaches higher than 12,000 feet. These mountains are also formed by the area’s tectonic situation. However, the two plates meet in a different way under the South Island. Rather than creating a subduction zone, the plates move laterally.
The lateral movement created the South Alps. New Zealand’s location places it along one of the edges of the Ring of Fire, which encircles the Pacific Ocean basin. The positions and activity of the tectonic plates in this zone cause most of the world’s earthquakes and have formed more than 75 percent of the world’s volcanoes.
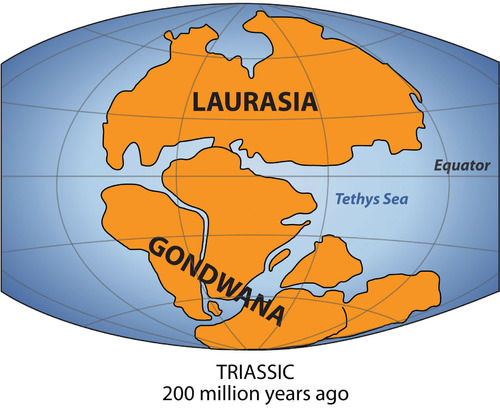 The southern portion was called Gondwana (Gondwanaland). New Zealand and Australia come from Gondwana; their origin explains why their fauna and flora are so unique.
The southern portion was called Gondwana (Gondwanaland). New Zealand and Australia come from Gondwana; their origin explains why their fauna and flora are so unique.New Zealand has a fascinating ecological history. New Zealand was once part of Gondwana, also known as Gondwanaland. About 200 to 500 million years ago, Gondwana was the southern portion of the supercontinent of Pangaea. Gondwana included most of the land in what is the Southern Hemisphere today, including Australia and New Zealand. Over time, through various forms of tectonic activity, the earth’s plates shifted and the supercontinent of Gondwana broke apart, leaving New Zealand geographically isolated for millennia. The species of flora and fauna found in New Zealand either descended from the species found on Gondwana, flew there, floated there via the ocean, or were brought by people.
Biodiversity in New Zealand
New Zealand’s geological history has laid the groundwork for more than 2,000 indigenous plant species, about 1,500 of which are found nowhere else in the world. The biomes of the North Island include a subtropical area, including mangrove swamps, an evergreen forest with dense undergrowth of mosses and ferns, and a small grasslands area in the central volcanic plain. The South Island biomes include extensive grasslands in the east, which are excellent for agricultural pursuits; forest areas, dominated by native beech trees in the west; and an alpine vegetation zone in the Southern Alps.
In terms of fauna, the most influential factor may be the relative absence of predatory mammals, again related to New Zealand’s geological history. With few ground predators and a favorable climate, bats, small reptiles, and birds were able to thrive and flourish. Without predators, many species of birds became flightless, such as the noted Kiwi. New Zealand’s most famous bird, the moa, was similar to the ostrich but is now extinct. Moa could grow to more than 12 feet high and weigh more than 500 pounds. New Zealand is known for its large number of species of wild birds. The Kiwi is the most noted and is often used to refer to people from New Zealand, as it is the national symbol of the country.
 Kiwis are flightless birds native to New Zealand.
Kiwis are flightless birds native to New Zealand.New Zealand has a variety of landscapes that have been attractive for economic activity and tourism. The South Island is larger than the North Island and is more mountainous. The snowcapped peaks of the Southern Alps run the western length of the South Island. Large livestock-raising operations and agricultural activities can be found on the vast grasslands of the South Island. Millions of sheep and cattle are raised on the grassy highlands and the valley pasturelands. The North Island has more low-lying terrain, which is also good for agriculture and is home to a large dairy industry. The central highlands of the north offer some rugged relief and provide for a diverse physical landscape.
Cultural Dynamics and the Maori
New Zealand is home to many Polynesian groups. Its original inhabitants were the Maori, who came to the islands around the 10th century. They grew crops of gourds and sweet potatoes. Fur seals were hunted regularly, as were moa, which were hunted to extinction before the Europeans arrived. The Maori had created extensive trading networks with other island groups and developed a heritage of traditional rituals and cultural ways. The Maori culture thrived for hundreds of years and was well established in New Zealand before the arrival of the colonial ships from Europe.
Britain was the main colonizer of the islands. The British settled in to establish their presence and gain control. In 1840, the British colonizers and the Maori signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which granted British sovereignty over the islands but allowed the Maori certain rights over tribal lands. The actual language in this treaty has been debated between the English version and the Maori version.
Over time the tribal lands were codified into legal arrangements by the European colonizers. Since the Treaty of Waitangi, the situation has evolved, with subsequent land exchanges, some legal and others questionable. The Maori have complained about unfair treatment and the loss of land and rights in the process. These issues have finally reached a point of negotiation in the past couple of decades. Starting in the 1990s, treaty settlements have been made to help correct the actions of the colonial activity and compensate the Maori for the conditions to which they were subjugated.
 Many Maori participate in performances in New Zealand both for tourism and to maintain their heritage and traditions.
Many Maori participate in performances in New Zealand both for tourism and to maintain their heritage and traditions.Most of the Maori have lived on the North Island. They were a real concern for the European colonizers. Claimed by Great Britain in their colonial empire, the country of New Zealand became independent of Britain in 1901. According to the CIA World Factbook, the estimate of the population in 2017 of the country was at about 4.5 million. According to the New Zealand 2013 census, Europeans are 74 percent of the population and the Maori are 14.09 percent. There are also many people who are of mixed ethnic background, including Maori and other groups. Asians, Polynesians, and other ethnic minorities make up the rest. New Zealand’s main religion is Christianity and English is the official language.
The Maori have not been integrated into New Zealand society to the same extent as Europeans have. The Maori now join the ranks of other Pacific Islanders that have moved to New Zealand from Samoa, Tonga, Cook Islands, and many other places in the South Pacific. New Zealand’s urban areas reflect diversity in the various cultural landscapes and ethnic communities that have established themselves in specific neighborhoods within the main cities.
A common dilemma with all peoples is the draw to return to their heritage and roots, which typically results in a more traditional lifestyle with stronger cultural ways. At the same time, the modern world pulls people toward a more global and cosmopolitan culture that is steeped in modernity with changing fashions. The Maori and other ethnic groups in New Zealand find themselves facing a challenge to balance their traditional lifestyles and the modern world.
Economic Conditions
Land and climate could be said to be New Zealand’s most important natural resources. Fertile soils and a mild climate, complete with thousands of hours of sunshine annually, create ideal conditions for agriculture. Grass continues to grow throughout the year, which means that sheep and other livestock have plenty to graze upon. Wool and other agricultural products, notably meat and butter, are important exports for New Zealand’s economy. Healthy forests produce timber products, which are important to the economy as well. Some of New Zealand’s natural resources are found underground, including coal, natural gas, gold, and other minerals.
Wellington is the capital of the country and is located on the southern end of the North Island. Wellington is one-fourth the size of the primary city, Auckland, which has 1.45 million people and is located in the north. The major cities are located along the coastal regions and provide a connection to sea transportation. Christchurch is the largest city of the South Island and is located along the eastern seaboard on the productive Canterbury Plain. The soils and conditions on the Canterbury Plain are excellent for productive agriculture of all types. Coastal plains also provide access to building transportation systems of highways and railroads that are more costly to construct in the mountainous regions of the Southern Alps or the northern highlands.
 Agricultural products make up a large portion of the nation’s exports that contribute to the country’s economy.
Agricultural products make up a large portion of the nation’s exports that contribute to the country’s economy.The modern cities are home to many processing centers that prepare the abundant agricultural products for domestic consumption and for export products. The ever-growing populations of Asia and the rest of the world continue to place a high demand on food products and welcome New Zealand’s agricultural exports. In relation to how countries gain wealth, agricultural profits are competitive and normally provide a low profit margin.
New Zealand does not gain a large part of its national income from mining or manufacturing, though these industries do exist. The high standard of living that in New Zealand is similar to that of Australia in that the population is not large. This allows the national wealth to be distributed through the private sector economy to provide a comfortable standard of living.
New Zealand has a market economy. The mainstay of the economy is, and has been for many years, a productive agricultural sector that has been geared toward export profits. New Zealand’s climate and soils help give it a place in the economy of the region through agricultural exports. A “wool boom” in the 1950s furthered the emphasis on agricultural products as tremendous profits were made in the wool production and export industry.
Today, New Zealand’s economy is still heavily focused on the export of agricultural products, though the economy has diversified into other areas such as tourism and exploitation of natural resources, especially natural gas. The development of hydroelectricity generation in recent years has been important to the economy.
- New Zealand has been isolated by the separation of continents through tectonic plate action. Shifting plates continue to create earthquakes and volcanic activity in the region.
- New Zealand has high mountains, with the Southern Alps along the western coast of the South Island and highlands along the eastern side of the North Island. Adequate rainfall and good soils provide for excellent agricultural production, which has been the traditional economic activity.
- The Maori were established in New Zealand before the British colonized it. Various agreements were made to work out common arrangements, with varying degrees of success. The Maori continue to be a minority population and have not acculturated into the mainstream society of the country.
- New Zealand has historically relied on agricultural exports for national income. Shifting global markets and changes in government policies and structures have highly affected the economy of New Zealand. The country continues to work its way through the transition to a more global economy.
Vocabulary Terms
|
Maori |
a Polynesian people who were the first inhabitants of New Zealand |
|
pakeha |
a Maori word that means "European white people" |
|
Ring of Fire |
A chain of volcanoes that line the Pacific Ocean |
Interactive Notebook Activities
- Outline New Zealand’s main physical features explain how the North Island is different from the South Island.
- Describe how tectonic plate activity has helped to isolate New Zealand from the rest of the world and still affects the island today.
- Summarize the situation of the Maori in New Zealand and their relationship with the dominant culture in New Zealand.
- Describe the economic geography of New Zealand and how the country gains wealth.
Discussion and Study Questions
- What are the main physical features of the South Island and North Island of New Zealand?
- How is the North Island different from the South Island in population and economic activities?
- How has physical geography been helpful in the economic development of New Zealand?
- Where are the main cities of New Zealand? What are the capital and the largest cities on each island?
- Who were the inhabitants of New Zealand before the colonial era? Where did they come from?
- What issues do these inhabitants of New Zealand have with the current government?
- How are the dynamics with the Maori similar to those with the Aborigines in Australia?
- What are the main methods that New Zealand has used to gain national wealth?
- How has the economic situation in New Zealand changed over the past few decades?
- How is New Zealand different in physical and human geography from Australia?
Real-World Geography Exercise
- Using Google Maps, complete the following activities:
- Locate each place on the bulleted list below.
- Find the nearest city with an international airport in proximity to each location on the bulleted list below.
- Calculate the distance and travel time by plane to each city from the Philadelphia International Airport in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
- Using NASA Latitude and Longitude Finder, determine the latitude and longitude for each location on the bulleted list below.
- Be prepared to share and discuss your answers.
- Auckland
- Canterbury Plain
- Cook Strait
- Christchurch
- Mount Cook
- Mount Ruapehu
- Southern Alps
- Wellington
Current Events
New Zealand Bans Terror Suspect's Racist Manifesto; Citizens Told To 'Destroy Any Copies
New Zealand: 25 Measles Cases Reported In Canterbury
Oceania Tops Vegan List: Australia, New Zealand Seize Top Spots For Veganism Popularity In 2018
New Zealand Unveils Food Safety Campaign As Southern Hemisphere Heads Into Summer
Videos for Geography Enrichment
Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
Canadian Encyclopedia is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
CIA World Factbook provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
Congress.gov is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
Library of Congress is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
NASA Earth Observatory (NEO) is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
National Archives is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
National Map is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
NationMaster is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
Real-Time World Air Quality Index is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
StateMaster is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
United States Census Bureau is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
United States Geological Survey (USGS) is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
Whitehouse.gov is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
World Health Organization (WHO) is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health; shapes the research agenda on health; and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.

