4.17: Triangle Angle Sum Theorem
- Page ID
- 4814
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The interior angles of a triangle add to 180 degrees Use equations to find missing angle measures given the sum of 180 degrees.
Triangle Sum Theorem
The Triangle Sum Theorem says that the three interior angles of any triangle add up to \(180^{\circ}\).
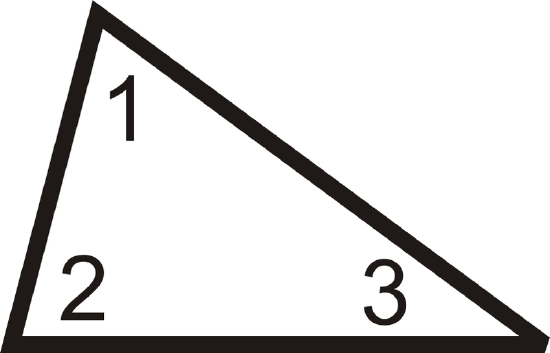
\(m\angle 1+m\angle 2+m\angle 3=180^{\circ}\).
Here is one proof of the Triangle Sum Theorem.
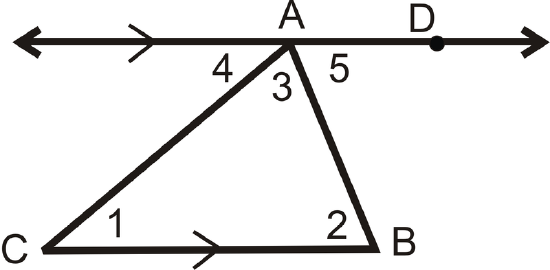
Given: \(\Delta ABC\) with \(\overleftrightarrow{AD} \parallel \overline{BC}\)
Prove: \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2+m\angle 3=180^{\circ}\)
| Statement | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1. \(\Delta ABC with \overleftrightarrow{AD} \parallel \overline{BC}\) | Given |
| 2. \\(angle 1\cong \angle 4,\: \angle 2\cong \angle 5\) | Alternate Interior Angles Theorem |
| 3. \(m\angle 1=m\angle 4,\: m\angle 2=m\angle 5\) | \cong angles have = measures |
| 4. \(m\angle 4+m\angle CAD=180^{\circ}\) | Linear Pair Postulate |
| 5. \(m\angle 3+m\angle 5=m\angle CAD\) | Angle Addition Postulate |
| 6. \(m\angle 4+m\angle 3+m\angle 5=180^{\circ}\) | Substitution PoE |
| 7. \(m\angle 1+m\angle 3+m\angle 2=180^{\circ}\) | Substitution PoE |
You can use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find missing angles in triangles.
What if you knew that two of the angles in a triangle measured \(55^{\circ}\)? How could you find the measure of the third angle?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Two interior angles of a triangle measure \(50^{\circ}\) and \(70^{\circ}\). What is the third interior angle of the triangle?
Solution
\(50^{\circ}+70^{\circ}+x=180^{\circ}\).
Solve this equation and you find that the third angle is \(60^{\circ}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find the value of \(x\) and the measure of each angle.
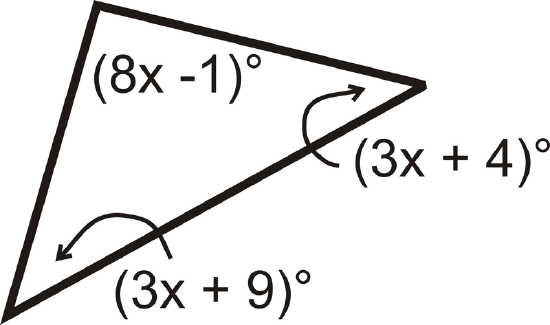
Solution
All the angles add up to \(180^{\circ}\).
\(\begin{align*} (8x−1)^{\circ}+(3x+9)^{\circ}+(3x+4)^{\circ}&=180^{\circ} \\ (14x+12)^{\circ}&=180^{\circ} \\ 14x&=168 \\ x&=12\end{align*} \)
Substitute in 12 for \(x\) to find each angle.
\([3(12)+9]^{\circ}=45^{\circ} \qquad [3(12)+4]^{\circ}=40^{\circ} \qquad [8(12)−1]^{\circ}=95^{\circ}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
What is m\angle T?
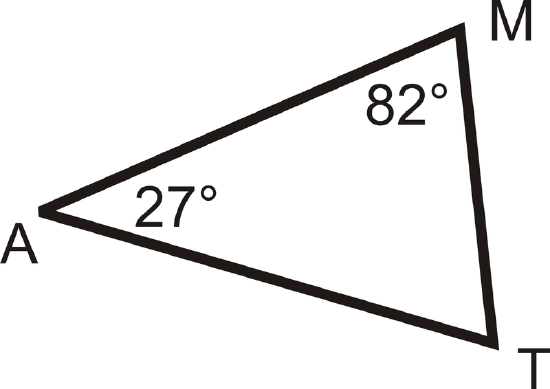
Solution
We know that the three angles in the triangle must add up to \(180^{\circ}\). To solve this problem, set up an equation and substitute in the information you know.
\(\begin{align*} m\angle M+m\angle A+m\angle T&=180^{\circ} \\ 82^{\circ}+27^{\circ}+m\angle T&=180^{\circ} \\ 109^{\circ}+m\angle T&=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle T &=71^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
What is the measure of each angle in an equiangular triangle?
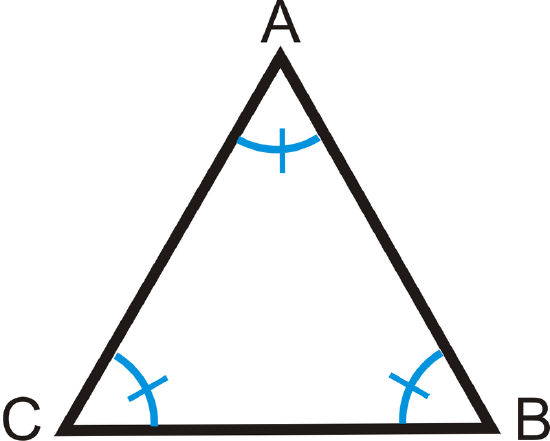
Solution
To solve, remember that \(\Delta ABC\) is an equiangular triangle, so all three angles are equal. Write an equation.
\(\begin{align*} m\angle A+m\angle B+m\angle C &=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle A+m\angle A+m\angle A&=180^{\circ} \qquad &Substitute,\: all\: angles\: are \: equal. \\ 3m\angle A&=180^{\circ} \qquad &Combine\:like \:terms. \\ m\angle A&=60^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
If \(m\angle A=60^{\circ}\), then \(m\angle B=60^{\circ}\) and \(m\angle C=60^{\circ}\).
Each angle in an equiangular triangle is \(60^{\circ}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Find the measure of the missing angle.
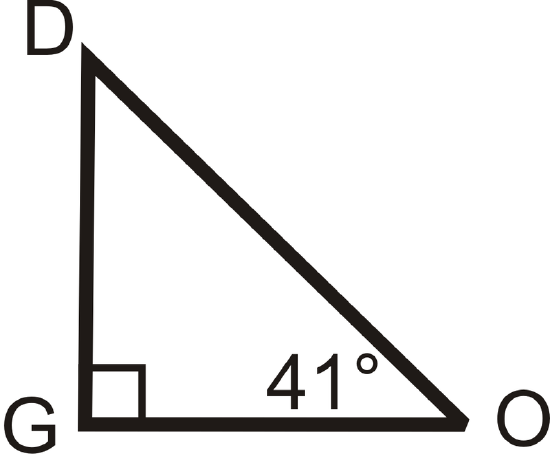
Solution
We know that \(m\angle O=41^{\circ}\) and \(m\angle G=90^{\circ}\) because it is a right angle. Set up an equation like in Example 3.
\(\begin{align*} m\angle D+m\angle O+m\angle G&=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle D+41^{\circ}+90^{\circ}&=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle D+41^{\circ}&=90^{\circ}\\ m\angle D=49^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Review
Determine \(m\angle 1\) in each triangle.
1.
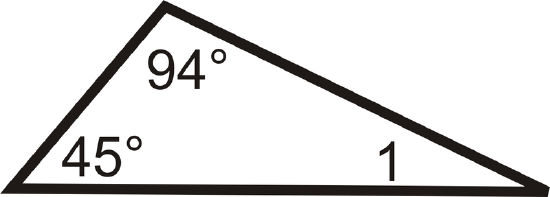
2.
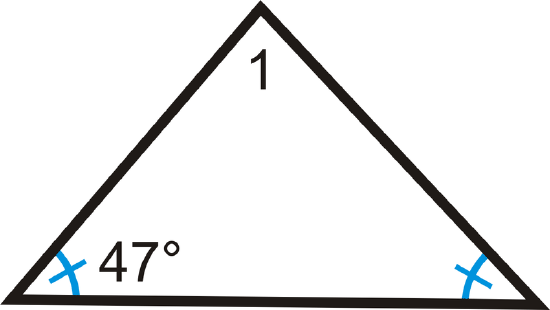
3.
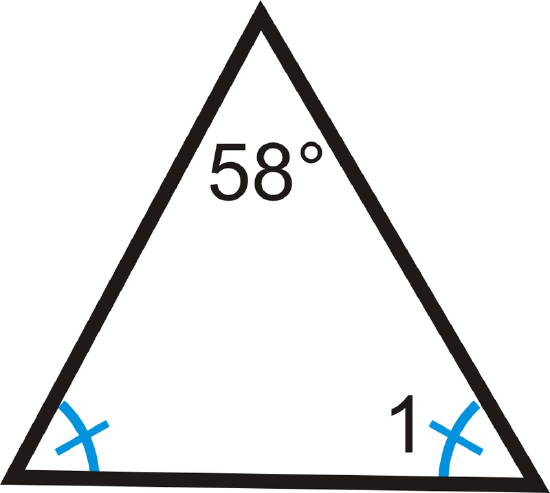
4.

5.
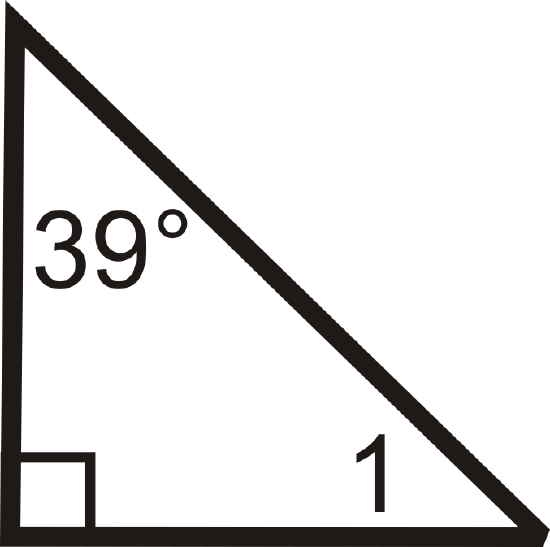
6.

7.
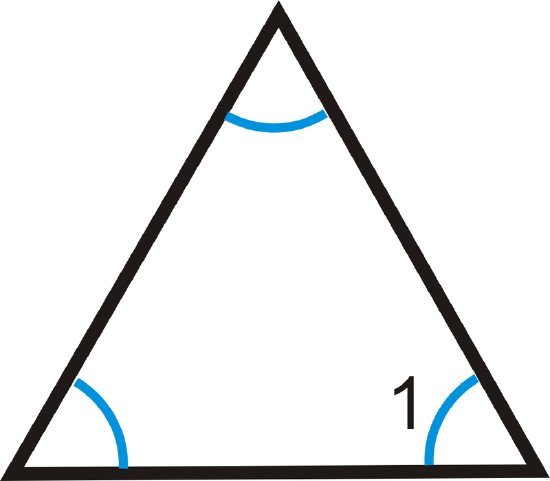
8. Two interior angles of a triangle measure \(32^{\circ}\) and \(64^{\circ}\). What is the third interior angle of the triangle?
9. Two interior angles of a triangle measure \(111^{\circ}\) and \(12^{\circ}\). What is the third interior angle of the triangle?
10. Two interior angles of a triangle measure \(2^{\circ}\) and \(157^{\circ}\). What is the third interior angle of the triangle?
Find the value of \(x\) and the measure of each angle.
11.

12.
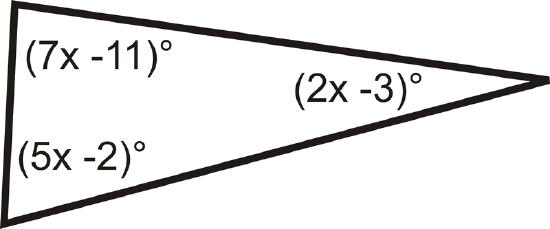
13.
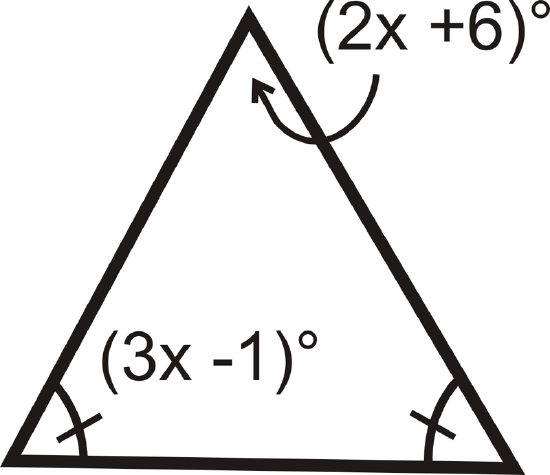
14.
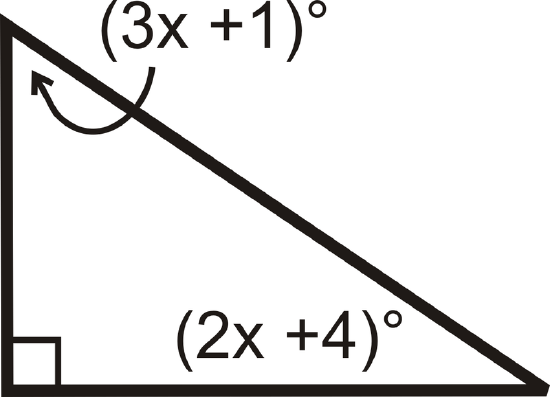
15.
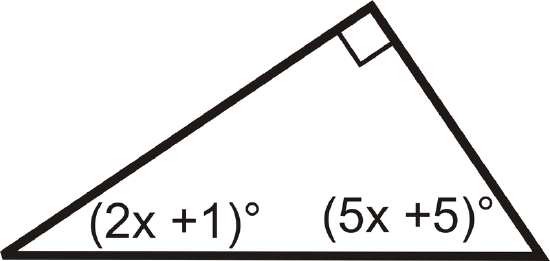
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 4.1.
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Triangle Sum Theorem | The Triangle Sum Theorem states that the three interior angles of any triangle add up to 180 degrees. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Triangle Sum Theorem Principles - Basic
Activities: Triangle Sum Theorem Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Triangle Relationships Study Guide
Practice: Triangle Angle Sum Theorem
Real World: Triangle Sum Theorem

