4.18: Exterior Angles and Theorems
- Page ID
- 4815
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Exterior angles equal the sum of the remote interiors.
Exterior Angles
An Exterior Angle is the angle formed by one side of a polygon and the extension of the adjacent side.
In all polygons, there are two sets of exterior angles, one that goes around clockwise and the other goes around counterclockwise.
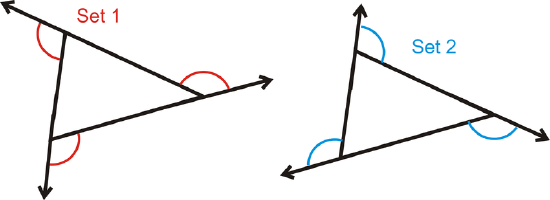
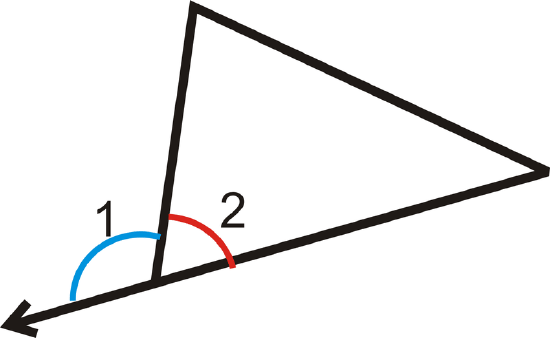
Notice that the interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle form a linear pair and add up to \(180^{\circ}\).
\(m\angle 1+m\angle 2=180^{\circ} \)
There are two important theorems to know involving exterior angles: the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem and the Exterior Angle Theorem.
The Exterior Angle Sum Theorem states that the exterior angles of any polygon will always add up to \(360^{\circ}\).
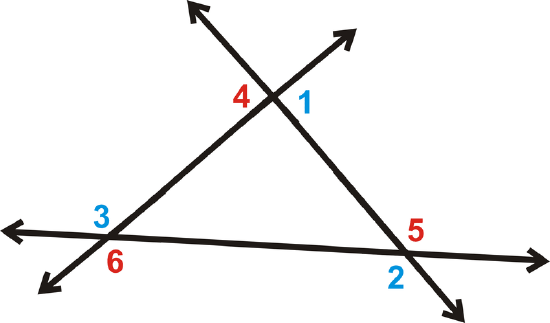
\(m\angle 1+m\angle 2+m\angle 3=360^{\circ}\)
\(m\angle 4+m\angle 5+m\angle 6=360^{\circ}\).
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of its remote interior angles. (Remote Interior Angles are the two interior angles in a triangle that are not adjacent to the indicated exterior angle.)
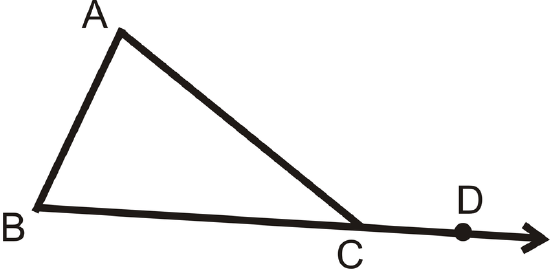 Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)\(m\angle A+m\angle B=m\angle ACD\)
What if you knew that two of the exterior angles of a triangle measured \(130^{\circ}\)? How could you find the measure of the third exterior angle?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Two interior angles of a triangle are \(40^{\circ}\) and \(73^{\circ}\). What are the measures of the three exterior angles of the triangle?
Solution
Remember that every interior angle forms a linear pair (adds up to \(180^{\circ}\)) with an exterior angle. So, since one of the interior angles is \(40^{\circ}\) that means that one of the exterior angles is \(140^{\circ}\) (because \(40+140=180\)). Similarly, since another one of the interior angles is \(73^{\circ}\), one of the exterior angles must be \(107^{\circ}\). The third interior angle is not given to us, but we could figure it out using the Triangle Sum Theorem. We can also use the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem. If two of the exterior angles are \(140^{\circ}\) and \(107^{\circ}\), then the third Exterior Angle must be \(113^{\circ}\) since \(140+107+113=360\).
So, the measures of the three exterior angles are 140, 107 and 113.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find the value of \(x\) and the measure of each angle.
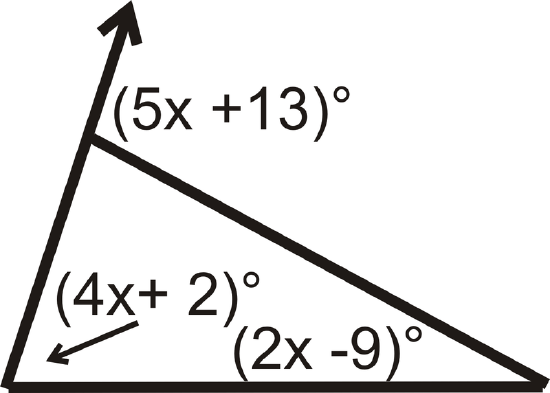
Solution
Set up an equation using the Exterior Angle Theorem.
\(\begin{align*} \underbrace{(4x+2)^{\circ}+(2x−9)^{\circ}}_\text{remote interior angles}&=\underbrace{(5x+13)^{\circ}}_\text{exterior angle} \\ (6x−7)^{\circ}&=(5x+13)^{\circ} \\ x&=20 \end{align*}\)
Substitute in 20 for \(x\) to find each angle.
\([4(20)+2]^{\circ}=82^{\circ}[2(20)−9]^{\circ}=31^{\circ} \qquad Exterior \:angle:\: [5(20)+13]^{\circ}=113^{\circ}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find the measure of \(\angle RQS\).
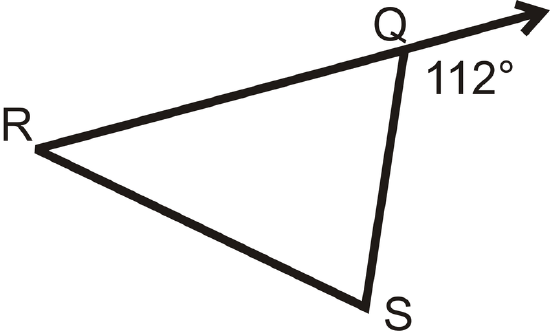 Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)Solution
Notice that \(112^{\circ}\) is an exterior angle of \(\Delta RQS\) and is supplementary to \(\angle RQS\).
Set up an equation to solve for the missing angle.
\(\begin{align*}112^{\circ}+m\angle RQS &=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle RQS&=68^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Find the measures of the numbered interior and exterior angles in the triangle.
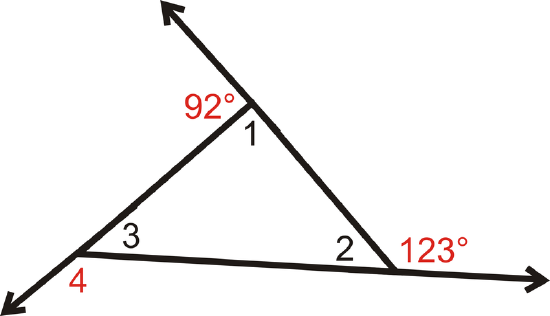 Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)Solution
We know that \(m\angle 1+92^{\circ}=180^{\circ}\) because they form a linear pair. So, m\angle 1=88^{\circ}\).
Similarly, \(m\angle 2+123^{\circ}=180^{\circ}\) because they form a linear pair. So, m\angle 2=57^{\circ}\).
We also know that the three interior angles must add up to 180^{\circ}\) by the Triangle Sum Theorem.
\(\begin{align*} m\angle 1+m\angle 2+m\angle 3&=180^{\circ} \qquad by\: the \:Triangle \:Sum \:Theorem. \\ 88^{\circ}+57^{\circ}+m\angle 3&=180 \\ m\angle 3&=35^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Lastly, \(m\angle 3+m\angle 4=180^{\circ} \qquad because\: they\: form \:a \:linear \:pair.\)
\(\begin{align*} 35^{\circ}+m\angle 4&=180^{\circ} \\ m\angle 4&=145^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
What is the value of \(p\) in the triangle below?
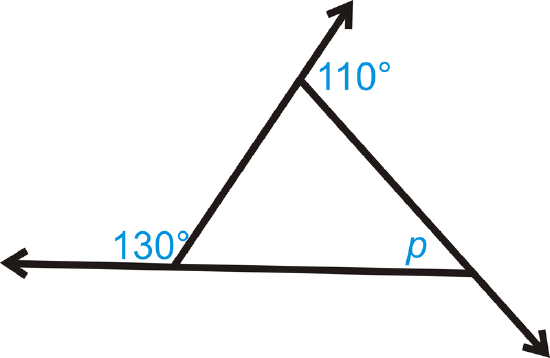
Solution
First, we need to find the missing exterior angle, which we will call \(x\). Set up an equation using the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem.
\(\begin{align*} 130^{\circ}+110^{\circ}+x&=360^{\circ} \\ x&=360^{\circ}−130^{\circ}−110^{\circ} \\ x&=120^{\circ}\end{align*} \)
\(x\) and \(p\) add up to \(180^{\circ}\) because they are a linear pair.
\(\begin{align*} x+p&=180^{\circ} \\ 120^{\circ}+p&=180^{\circ} \\ p&=60^{\circ}\end{align*}\)
Review
Determine \(m\angle 1\).
-
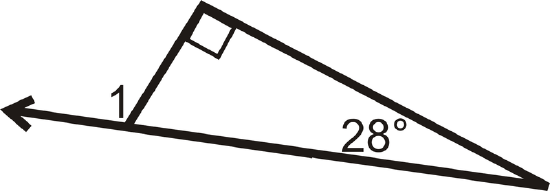
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
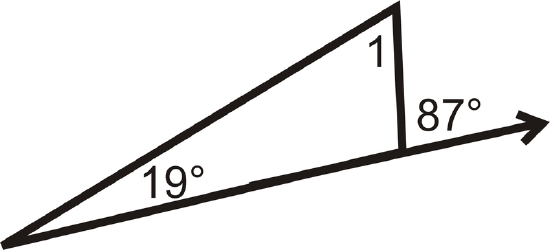
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) -
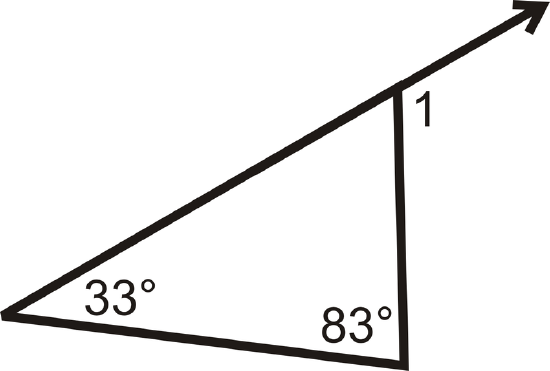
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) -
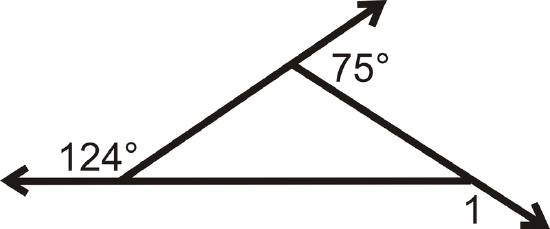
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -

Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -

Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Use the following picture for the next three problems:
- What is \(m\angle 1+m\angle 2+m\angle 3\)?
- What is \(m\angle 4+m\angle 5+m\angle 6\)?
- What is \(m\angle 7+m\angle 8+m\angle 9\)?
Solve for \(x\).
-
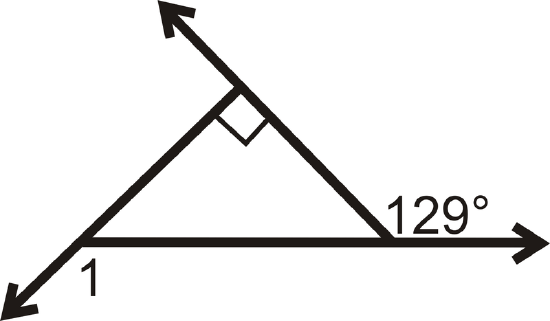
Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\) -
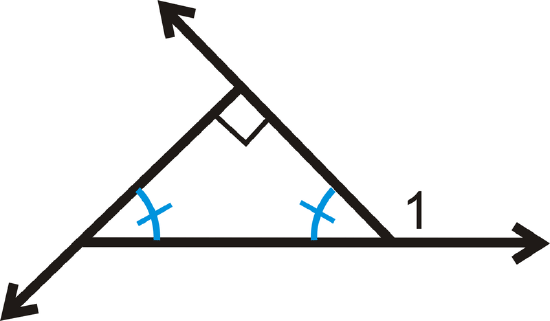
Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\) -
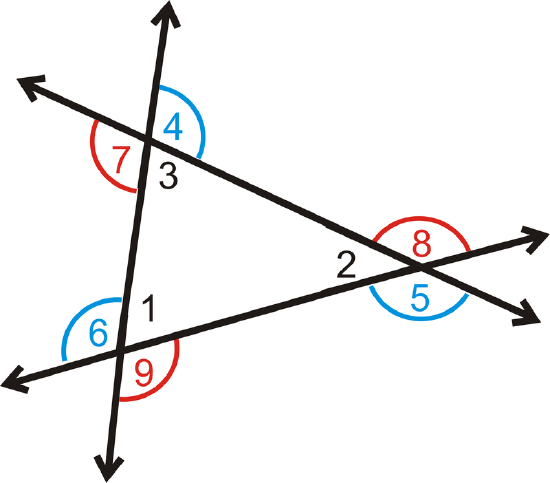
Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Exterior angles | An exterior angle is the angle formed by one side of a polygon and the extension of the adjacent side. |
| interior angles | The angles on the inside of a polygon. |
| remote interior angles | The remote interior angles (of a triangle) are the two interior angles that are not adjacent to the indicated exterior angle. |
| Triangle Sum Theorem | The Triangle Sum Theorem states that the three interior angles of any triangle will always add up to \(180^{\circ}\). |
| Exterior Angle Sum Theorem | Exterior Angle Sum Theorem states that the exterior angles of any polygon will always add up to 360 degrees. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Exterior Angles Theorems Examples - Basic
Activities: Exterior Angles Theorems Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Triangle Relationships Study Guide
Practice: Exterior Angles and Theorems
Real World: Exterior Angles Theorem

