8.5: Geometric Translation
- Page ID
- 2169
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Understand translations as movement of every point in a figure the same distance in the same direction. Graph images given preimage and translation.
Translations
A transformation is an operation that moves, flips, or otherwise changes a figure to create a new figure. A rigid transformation (also known as an isometry or congruence transformation) is a transformation that does not change the size or shape of a figure.
The rigid transformations are translations, reflections, and rotations. The new figure created by a transformation is called the image. The original figure is called the preimage. If the preimage is \(A\), then the image would be \(A′\), said “a prime.” If there is an image of \(A′\), that would be labeled \(A′′\), said “a double prime.”
A translation is a transformation that moves every point in a figure the same distance in the same direction. For example, this transformation moves the parallelogram to the right 5 units and up 3 units. It is written \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+5, y+3)\).
What if you were given the coordinates of a quadrilateral and you were asked to move that quadrilateral 3 units to the left and 2 units down? What would its new coordinates be?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Triangle \(\Delta ABC\) has coordinates \(A(3,−1)\), \(B(7,−5)\) and \(C(−2,−2)\). Translate \(\Delta ABC\) to the left 4 units and up 5 units. Determine the coordinates of \(\Delta A′B′C′\).
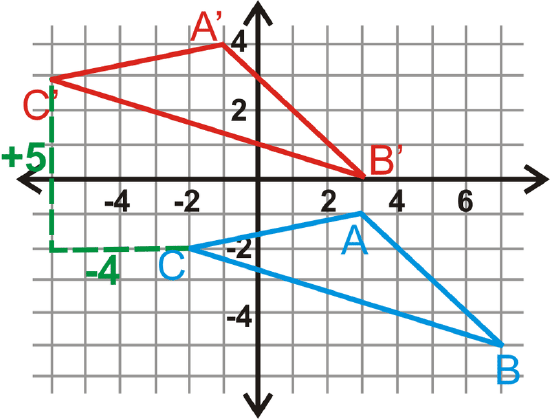
Solution
Graph \(\Delta ABC\). To translate \(\Delta ABC\), subtract 4 from each \(x\) value and add 5 to each \(y\) value of its coordinates.
\(\begin{aligned} &A(3,−1)\rightarrow (3−4,−1+5)=A′(−1,4) \\ &B(7,−5)\rightarrow (7−4,−5+5)=B′(3,0) \\ &C(−2,−2)\rightarrow (−2−4,−2+5)=C′(−6,3) \end{aligned}\)
The rule would be \((x,y)\rightarrow (x−4, y+5)\).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Using the translation \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+2, y−5)\), what is the image of \(A(−6, 3)\)?
Solution
\(A′(−4,−2)\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Graph square \(S(1,2)\), \(Q(4,1)\), \(R(5,4)\) and \(E(2,5)\). Find the image after the translation \((x,y)\rightarrow (x−2,y+3)\). Then, graph and label the image.
Solution
We are going to move the square to the left 2 and up 3.
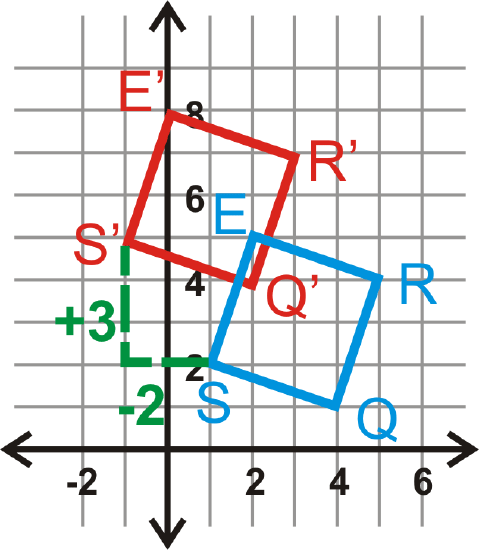
\(\begin{aligned}(x,y)&\rightarrow (x−2,y+3) \\ S(1,2)&\rightarrow S′(−1,5) \\ Q(4,1)&\rightarrow Q′(2,4) \\ R(5,4)&\rightarrow R′(3,7) \\ E(2,5)&\rightarrow E′(0,8)\end{aligned}\)
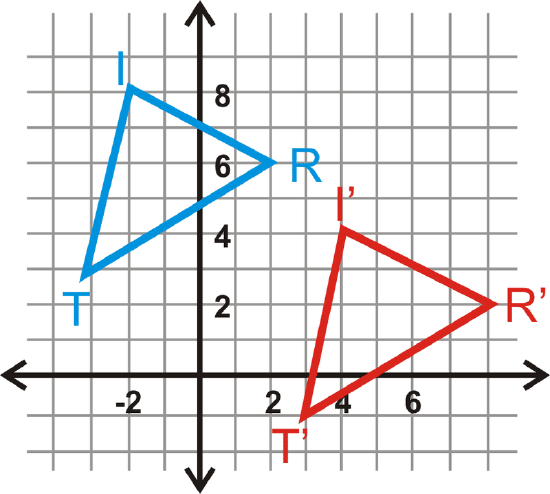
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
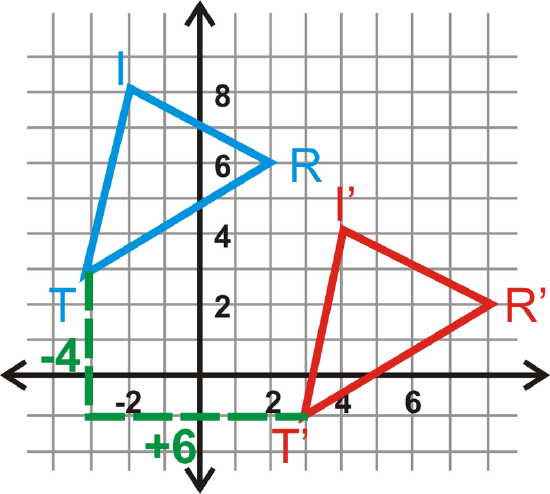
Find the translation rule for \(\Delta TRI\) to \(\Delta T′R′I′\).
Solution
Look at the movement from \(T\) to \(T′\). The translation rule is \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+6, y−4)\).
Review
Use the translation \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+5, y−9)\) for questions 1-7.
- What is the image of \(A(−1,3)\)?
- What is the image of \(B(2,5)\)?
- What is the image of \(C(4,−2)\)?
- What is the image of \(A′\)?
- What is the preimage of \(D′(12,7)\)?
- What is the image of \(A′′\)?
- Plot \(A\), \(A′\), \(A′′\), and \(A′′′\) from the questions above. What do you notice?
The vertices of \(\Delta ABC\) are \(A(−6,−7)\), \(B(−3,−10)\) and \(C(−5,2)\). Find the vertices of \(\Delta A′B′C′\), given the translation rules below.
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x−2, y−7)\)
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+11, y+4)\)
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x, y−3)\)
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x−5, y+8)\)
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+1, y)\)
- \((x,y)\rightarrow (x+3, y+10)\)
In questions 14-17, \(\Delta A′B′C′\) is the image of \(\Delta ABC\). Write the translation rule.
-
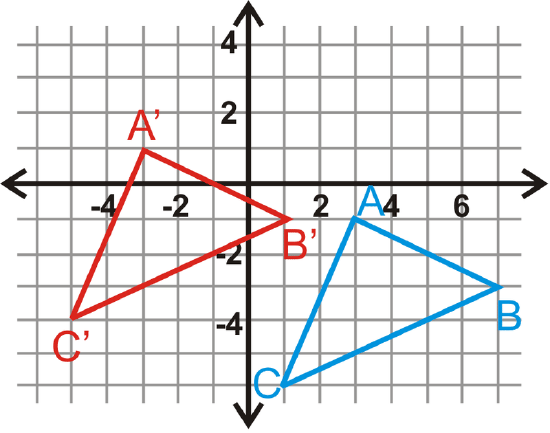
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) -
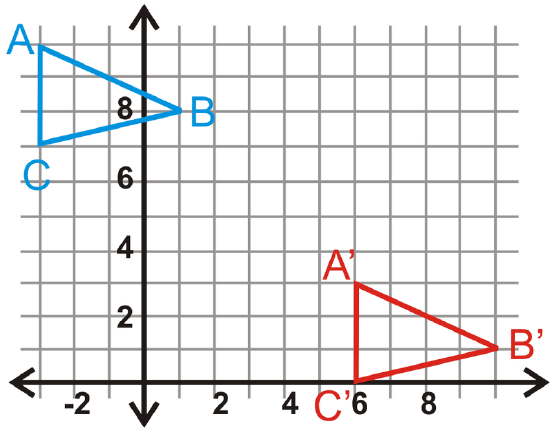
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) -
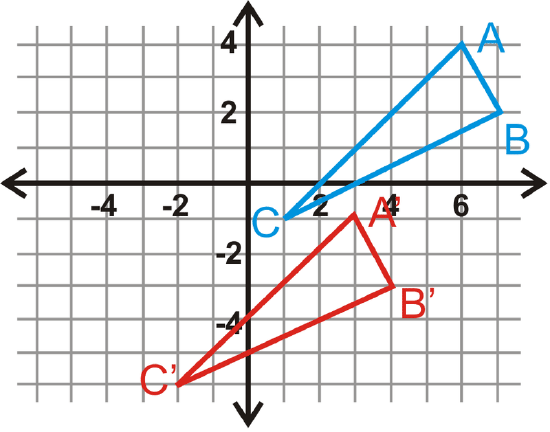
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
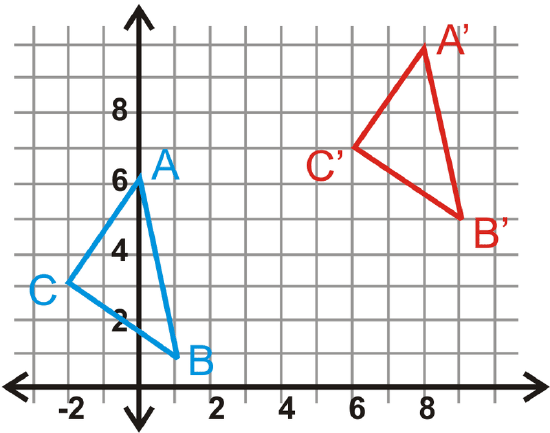
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Use the triangles from #17 to answer questions 18-20.
- Find the lengths of all the sides of \(\Delta ABC\).
- Find the lengths of all the sides of \(\Delta A′B′C′\).
- What can you say about \(\Delta ABC\) and \(\Delta A′B′C′\)? Can you say this for any translation?
- If \(\Delta A′B′C′\) was the preimage and \(\Delta ABC\) was the image, write the translation rule for #14.
- If \(\Delta A′B′C′\) was the preimage and \(\Delta ABC\) was the image, write the translation rule for #15.
- Find the translation rule that would move \(A\) to \(A′(0,0)\), for #16.
- The coordinates of \(\Delta DEF\) are \(D(4,−2)\), \(E(7,−4)\) and \(F(5,3)\). Translate \(\Delta DEF\) to the right 5 units and up 11 units. Write the translation rule.
- The coordinates of quadrilateral \(QUAD\) are \(Q(−6,1)\), \(U(−3,7)\), \(A(4,−2)\) and \(D(1,−8)\). Translate \(QUAD\) to the left 3 units and down 7 units. Write the translation rule.
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 12.3.
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Transformation: Translation Principles - Basic
Activities: Translations Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Types of Transformations Study Guide
Practice: Geometric Translation

