4.1.7: Trigonometry Word Problems
- Page ID
- 14875
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Contextual use of triangle properties, ratios, theorems, and laws.
Angle of Depression and Angle of Elevation
One application of the trigonometric ratios is to find lengths that you cannot measure. Very frequently, angles of depression and elevation are used in these types of problems.
Angle of Depression: The angle measured down from the horizon or a horizontal line.

Angle of Elevation: The angle measured up from the horizon or a horizontal line.
What if you placed a ladder 10 feet from a haymow whose floor is 20 feet from the ground? How tall would the ladder need to be to reach the haymow's floor if it forms a \(30^{\circ}\) angle with the ground?
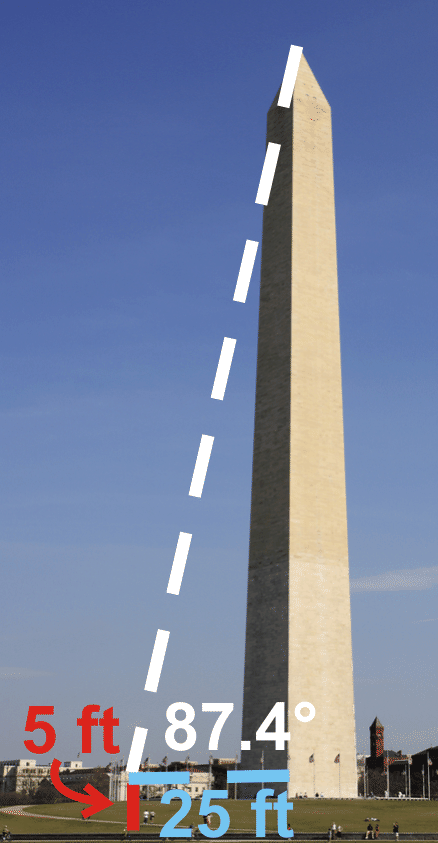
A math student is standing 25 feet from the base of the Washington Monument. The angle of elevation from her horizontal line of sight is \(87.4^{\circ}\). If her “eye height” is 5 ft, how tall is the monument?
Solution
We can find the height of the monument by using the tangent ratio.
\(\begin{aligned} \tan 87.4^{\circ} &=\dfrac{h}{25} \\ h&=25\cdot \tan 87.4^{\circ}=550.54 \end{aligned}\)
Adding 5 ft, the total height of the Washington Monument is 555.54 ft.
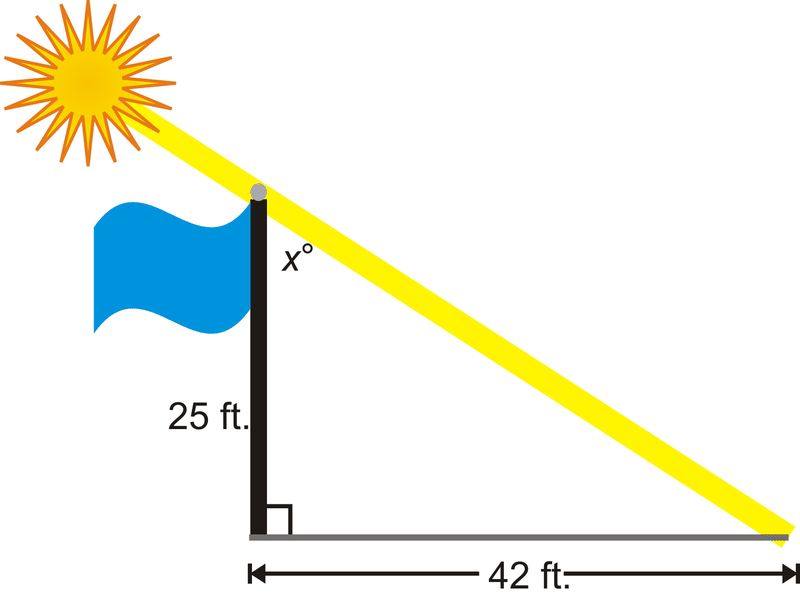
A 25 foot tall flagpole casts a 42 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the flagpole?
Solution
Draw a picture. The angle that the sun hits the flagpole is \(x^{\circ}\). We need to use the inverse tangent ratio.
\(\begin{aligned} \tan x &=\dfrac{42}{25} \\ \tan^{−1} \dfrac{42}{25}&\approx 59.2^{\circ}=x \end{aligned}\)
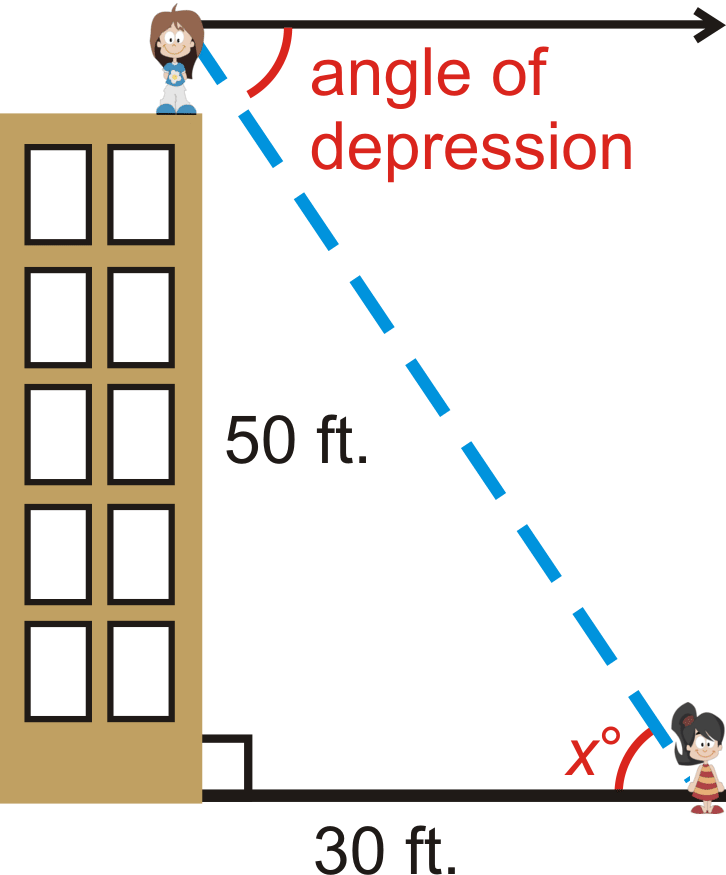
Elise is standing on top of a 50 foot building and sees her friend, Molly. If Molly is 30 feet away from the base of the building, what is the angle of depression from Elise to Molly? Elise’s eye height is 4.5 feet.
Solution
Because of parallel lines, the angle of depression is equal to the angle at Molly, or \(x^{\circ}\). We can use the inverse tangent ratio.
\(\tan^{−1} \left(\dfrac{54.5}{30}\right)=61.2^{\circ}=x\)
Mark is flying a kite and realizes that 300 feet of string are out. The angle of the string with the ground is \(42.5^{\circ}\). How high is Mark's kite above the ground?
Solution
It might help to draw a picture. Then write and solve a trig equation.
\(\begin{aligned} \sin 42.5^{\circ} &=\dfrac{x}{300}\\ 300\cdot \sin 42.5^{\circ} &=x \\ x&\approx 202.7\end{aligned}\)
The kite is about 202.7 feet off of the ground.
A 20 foot ladder rests against a wall. The base of the ladder is 7 feet from the wall. What angle does the ladder make with the ground?
Solution
It might help to draw a picture.
\(\begin{aligned} \cos x &=\dfrac{7}{20}\\ x&=\cos ^{−1}\dfrac{7}{20}\\ x&\approx 69.5^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Review
- Kristin is swimming in the ocean and notices a coral reef below her. The angle of depression is \(35^{\circ}\) and the depth of the ocean, at that point is 250 feet. How far away is she from the reef?
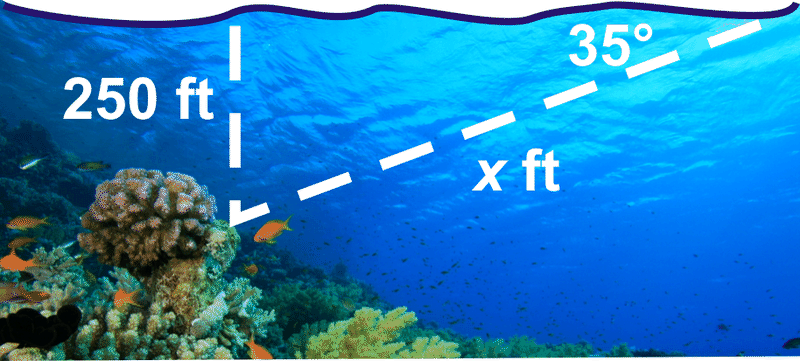
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) - The Leaning Tower of Piza currently “leans” at a \(4^{\circ}\) angle and has a vertical height of 55.86 meters. How tall was the tower when it was originally built?
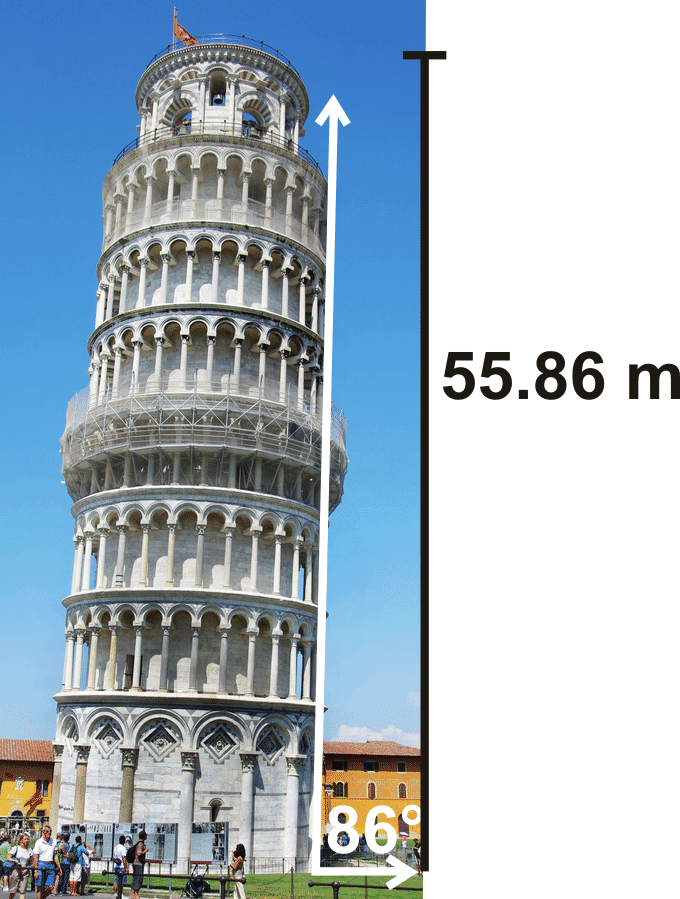

Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Use what you know about right triangles to solve for the missing angle. If needed, draw a picture. Round all answers to the nearest tenth of a degree.
- A 75 foot building casts an 82 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the building?
- Over 2 miles (horizontal), a road rises 300 feet (vertical). What is the angle of elevation?
- A boat is sailing and spots a shipwreck 650 feet below the water. A diver jumps from the boat and swims 935 feet to reach the wreck. What is the angle of depression from the boat to the shipwreck?
- Standing 100 feet from the base of a building, Sam measures the angle to the top of the building from his eye height to be \(50^{\circ}\). If his eyes are 6 feet above the ground, how tall is the building?
- Over 4 miles (horizontal), a road rises 200 feet (vertical). What is the angle of elevation?
- A 90 foot building casts an 110 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the building?
- Luke is flying a kite and realizes that 400 feet of string are out. The angle of the string with the ground is \(50^{\circ}\). How high is Luke's kite above the ground?
- An 18 foot ladder rests against a wall. The base of the ladder is 10 feet from the wall. What angle does the ladder make with the ground?
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.9.
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Angle of Depression | The angle of depression is the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight down to an object when the image of an object is located beneath the horizontal line. |
| Angle of Elevation | The angle of elevation is the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight up to an object when the image of an object is located above the horizontal line. |
| ASA | ASA, angle-side-angle, refers to two known angles in a triangle with one known side between the known angles. |
| law of cosines | The law of cosines is a rule relating the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines states that c2=a2+b2−2abcosC, where C is the angle across from side c. |
| law of sines | The law of sines is a rule applied to triangles stating that the ratio of the sine of an angle to the side opposite that angle is equal to the ratio of the sine of another angle in the triangle to the side opposite that angle. |
| Tangent | The tangent of an angle in a right triangle is a value found by dividing the length of the side opposite the given angle by the length of the side adjacent to the given angle. |
| Trigonometric Ratios | Ratios that help us to understand the relationships between sides and angles of right triangles. |
Additional Resources
Video: Trigonometry Word Problems Principles - Basic
Activities: Trigonometry Word Problems Discussion Questions
Practice: Trigonometry Word Problems
Real World: Measuring Mountains

