6.9: Arcs in Circles
- Page ID
- 5024
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Sections of a circle and central angles.
A circle has \(360^{\circ}\). An arc is a section of the circle. A semicircle is an arc that measures \(180^{\circ}\).
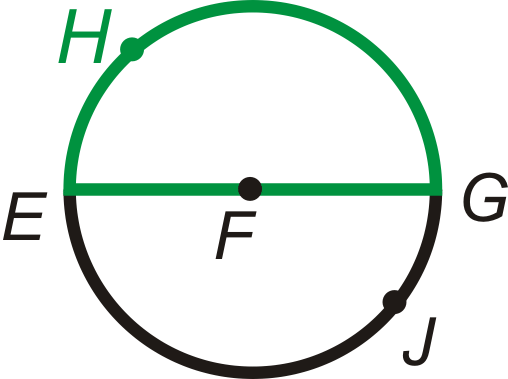
\(\widehat{EHG}\) and \(\widehat{EJG}\) are semicircles
A central angle is the angle formed by two radii with its vertex at the center of the circle. A minor arc is an arc that is less than \(180^{\circ}\). A major arc is an arc that is greater than \(180^{\circ}\). Always use 3 letters to label a major arc.
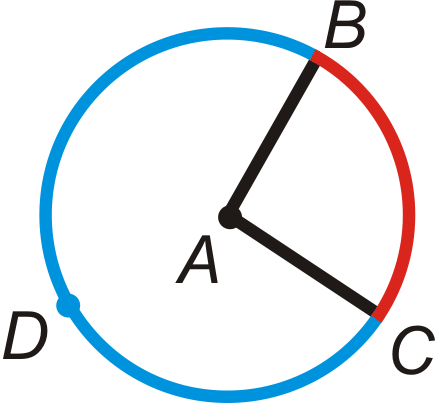
The central angle is \(\angle BAC\). The minor arc is \(\widehat{BC}\). The major arc is \(\widehat{BDC}\).
An arc can be measured in degrees or in a linear measure (cm, ft, etc.). In this concept we will use degree measure. The measure of a minor arc is the same as the measure of the central angle that corresponds to it. The measure of a major arc is \(360^{\circ}\) minus the measure of the corresponding minor arc. The measure of the arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs (Arc Addition Postulate).
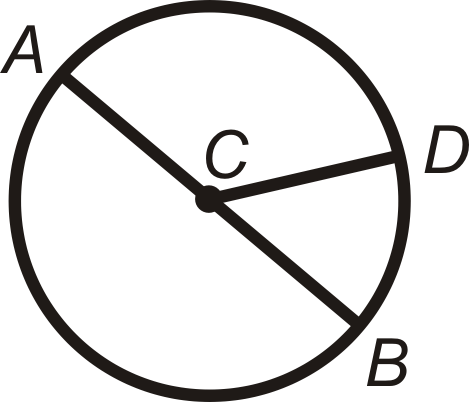
\(m\widehat{AD}+m\widehat{DB}=m\widehat{ADB}\)
What if a circle were divided into pieces by various radii? How could you find the measures of the arcs formed by these radii?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Find \(m\widehat{AB}\) and \(m\widehat{ADB}\) in \(\bigodot C\).
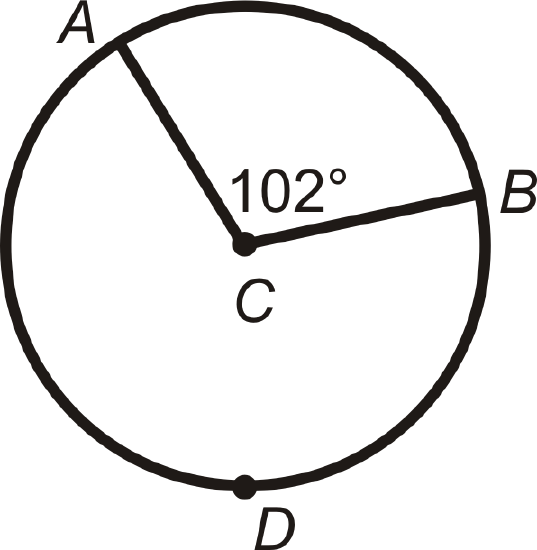
Solution
\(m\widehat{AB}=m\angle ACB\). So, \(m\widehat{AB}=102^{\circ}\).
\(m\widehat{ADB}=360^{\circ}−m\widehat{AB}=360^{\circ}−102^{\circ}=258^{\circ}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
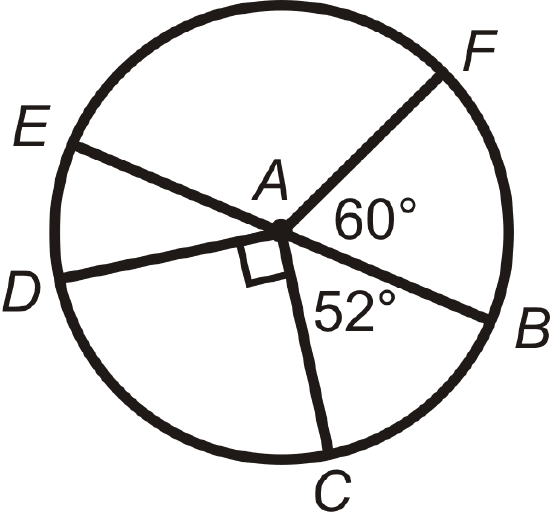
Find the measures of the minor arcs in \(\bigodot A\). \(\overline{EB}\) is a diameter.
Solution
Because \(\overline{EB}\) is a diameter, \(m\angle EAB=180^{\circ}\). Each arc has the same measure as its corresponding central angle.
\(\begin{aligned} m\widehat{BF}&=m\angle FAB=60^{\circ} \\ m\widehat{EF}&=m\angle EAF=120^{\circ}\rightarrow 180^{\circ}−60^{\circ} \\ m\widehat{ED}&=m\angle EAD=38^{\circ} \rightarrow 180^{\circ}−90^{\circ}−52^{\circ} \\ m\widehat{DC}&=m\angle DAC=90^{\circ} \\ m\widehat{BC}&=m\angle BAC=52^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find the measures of the indicated arcs in \(\bigodot A\). \(\overline{EB}\) is a diameter.

Use the Arc Addition Postulate.
- \(m\widehat{FED}\)
- \(m\widehat{CDF}\)
- \(m\widehat{DFC}\)
Solution
- \(m\widehat{FED}=m\widehat{FE}+m\widehat{ED}=120^{\circ}+38^{\circ}=158^{\circ}\)
- \(m\widehat{CDF}=m\widehat{CD}+m\widehat{DE}+m\widehat{EF}=90^{\circ}+38^{\circ}+120^{\circ}=248^{\circ}\)
- \(m\widehat{DFC}=m\widehat{ED}+m\widehat{EF}+m\widehat{FB}+m\widehat{BC}=38^{\circ}+120^{\circ}+60^{\circ}+52^{\circ}=270^{\circ}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
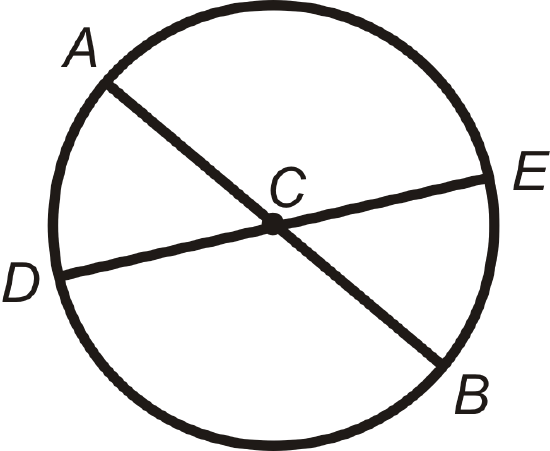
List the congruent arcs in \(\bigodot C\) below. \(\overline{AB}\) and \(\overline{DE}\) are diameters.
Solution
\(\angle ACD\cong \angle ECB\) because they are vertical angles. \(\angle DCB\cong \angle ACE\) because they are also vertical angles.
\(\widehat{AD}\cong \widehat{EB}\) and \(\widehat{AE}\cong \widehat{DB}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
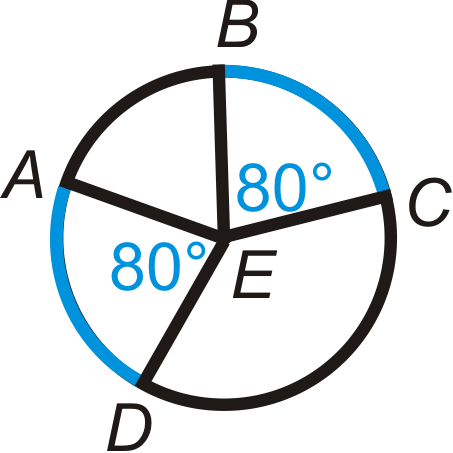
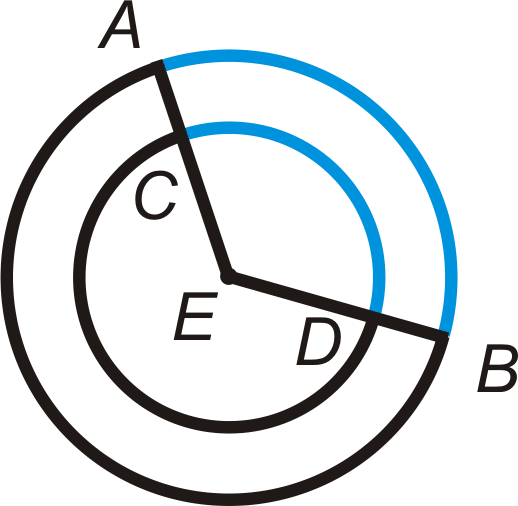
For each of the circles below, are the blue arcs congruent? Explain why or why not.
Solution
For the first circle, \(\widehat{AD}\cong \widehat{BC}\) because they have the same central angle measure and are in the same circle.
For the second circle, the two arcs have the same measure, but are not congruent because the circles have different radii.
Review
Determine whether the arcs below are a minor arc, major arc, or semicircle of \(\bigodot G\). \(\overline{EB}\) is a diameter.
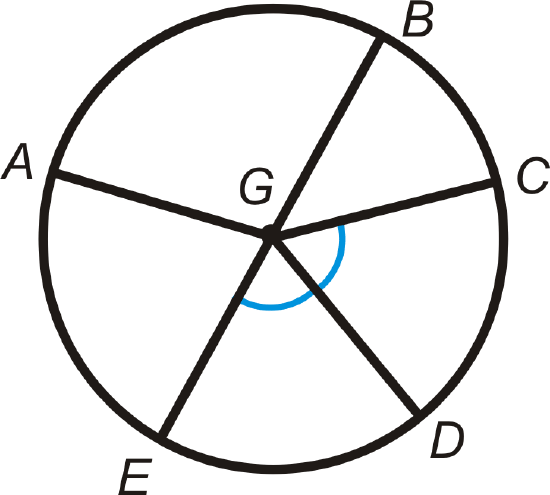
- \(\widehat{AB}\)
- \(\widehat{ABD}\)
- \(\widehat{BCE}\)
- \(\widehat{CAE}\)
- \(\widehat{ABC}\)
- \(\widehat{EAB}\)
- Are there any congruent arcs? If so, list them.
- If \(m\widehat{BC}=48^{\circ}\), find m\widehat{CD}\).
- Using #8, find m\widehat{CAE}\).
Find the measure of the minor arc and the major arc in each circle below.
-
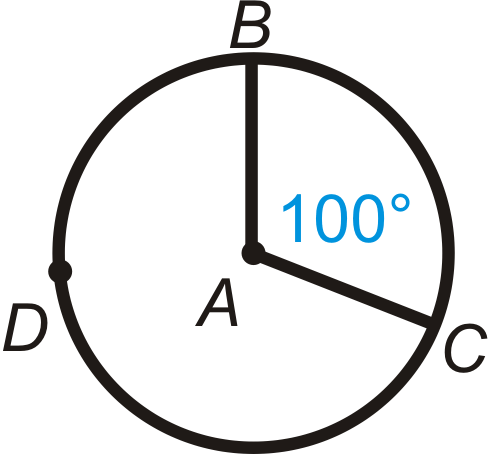
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -
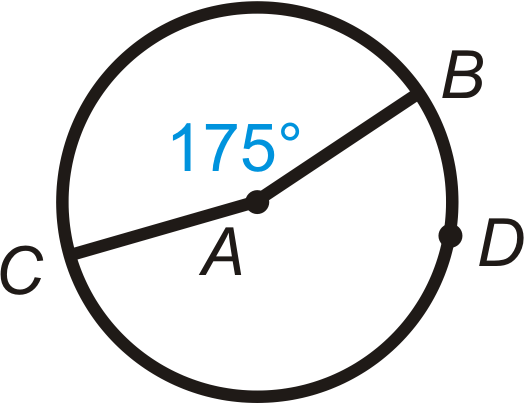
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -
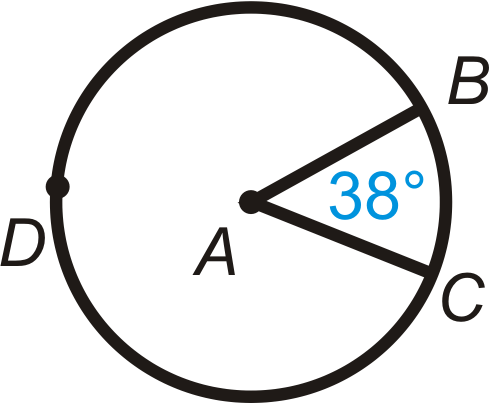
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\) -
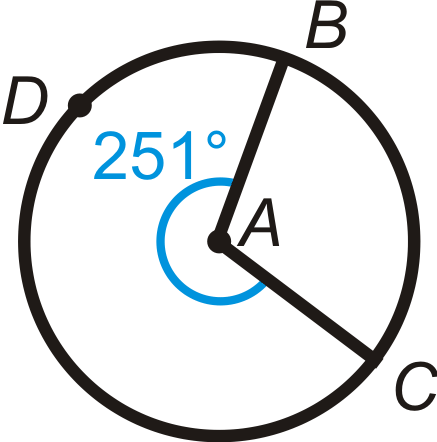
Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\) -
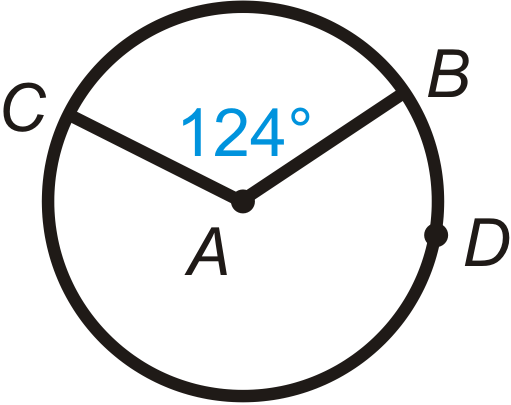
Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\) -
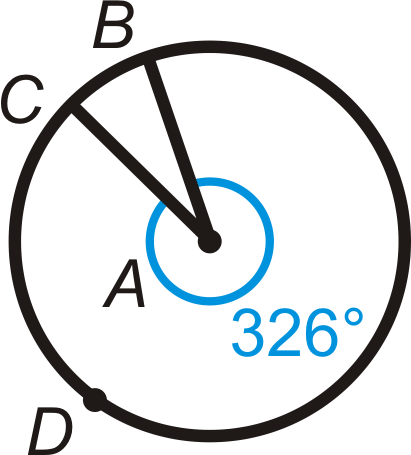
Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)
Determine if the blue arcs are congruent. If so, state why.
-
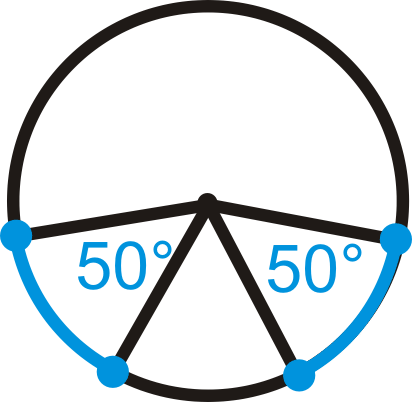
Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)
-
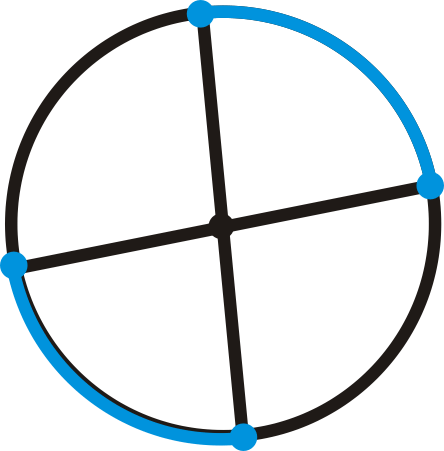
Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)
-
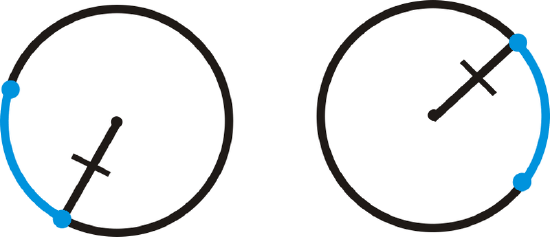
Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)
Find the measure of the indicated arcs or central angles in \bigodot A\).\overline{DG}\) is a diameter.
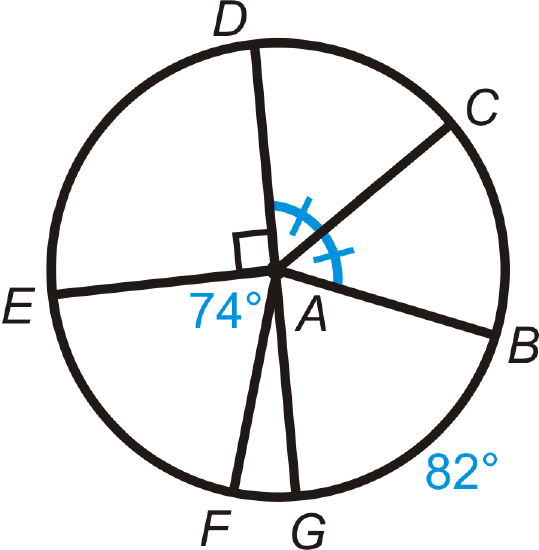
- \widehat{DE}\)
- \widehat{DC}\)
- \widehat{GAB}\)
- \widehat{FG}\)
- \widehat{EDB}
- \widehat{EAB}\)
- \widehat{DCF}\)
- \widehat{DBE}\)
Find the measure of x\) in \bigodot P\).
-
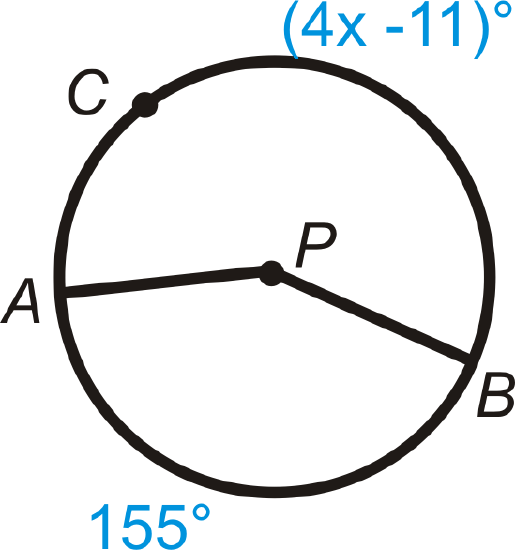
Figure \(\PageIndex{19}\) -
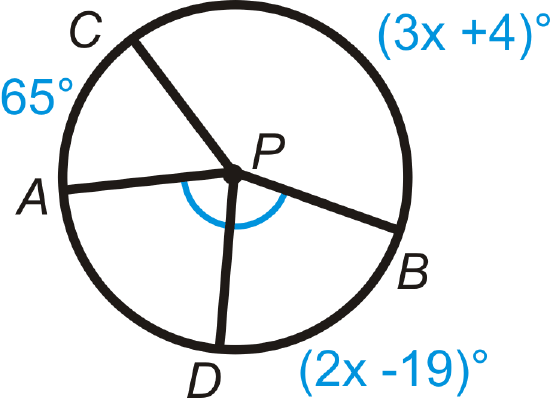
Figure \(\PageIndex{20}\) -
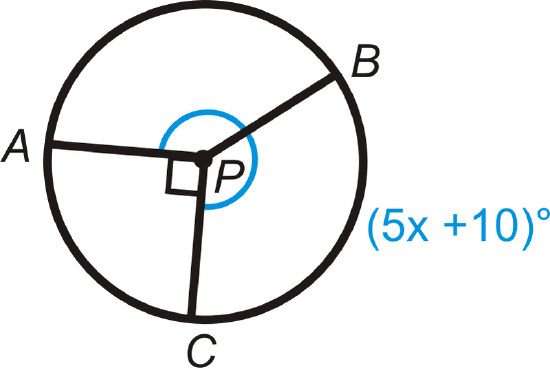
Figure \(\PageIndex{21}\)
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 9.3.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| arc | A single section of the circle, that describes a particular angle. |
| central angle | An angle formed by two radii and whose vertex is at the center of the circle. |
| circle | The set of all points that are the same distance away from a specific point, called the center. |
| major arc | An arc that is greater than \(180^{\circ}\). |
| minor arc | An arc that is less than \(180^{\circ}\). |
| radius | The distance from the center to the outer rim of a circle. |
| semicircle | An arc that measures \(180^{\circ}\). |
| Arc Addition Postulate | Arc addition postulate states that the measure of the arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs. |
| Diameter | Diameter is the measure of the distance across the center of a circle. The diameter is equal to twice the measure of the radius. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Arcs in Circles Principles - Basic
Activities: Arcs in Circles Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Properties of a Circle Study Guide
Practice: Arcs in Circles
Real World: Farming the Arc

