1.9: Measuring Angles
- Page ID
- 2136
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Measurement of angles with protractors and the Angle Addition Postulate.
Angles
An angle is formed when two rays have the same endpoint. The vertex is the common endpoint of the two rays that form an angle. The sides are the two rays that form an angle.
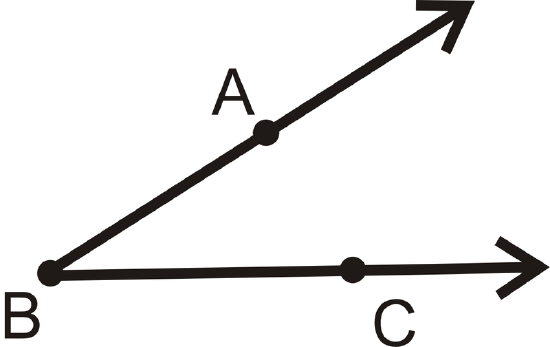 Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)| Label It | Say It |
|---|---|
| \(\angle ABC\) | Angle \(ABC\) |
| \(\angle CBA\) | Angle \(CBA\) |
The vertex is \(B\) and the sides are \(\overrightarrow{BA}\) and \(\overrightarrow{BC}\). Always use three letters to name an angle, \(\angle\) SIDE-VERTEX-SIDE.
Angles are measured with something called a protractor. A protractor is a measuring device that measures how “open” an angle is. Angles are measured in degrees and are labeled with a \( ^{\circ}\) symbol. For now, angles are always positive.
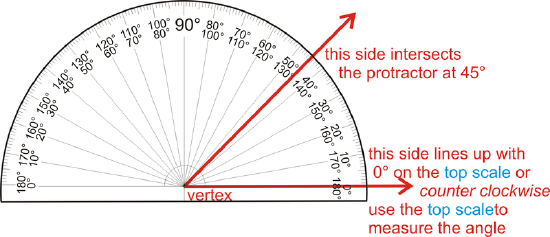 Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)There are two sets of measurements, one starting on the left and the other on the right side of the protractor. Both go around from \( 0 ^{\circ}\) to \(180 ^{\circ}\). When measuring angles, you can line up one side with \( 0 ^{\circ}\), and see where the other side hits the protractor. The vertex lines up in the middle of the bottom line.
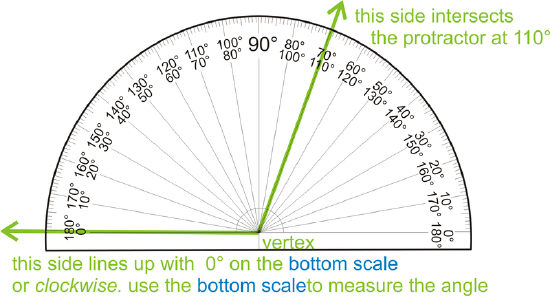 Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)Note that if you don't line up one side with \( 0 ^{\circ}\), the angle's measure will be the difference of the degrees where the sides of the angle intersect the protractor.
Sometimes you will want to draw an angle that is a specific number of degrees. Follow the steps below to draw a \( 50 ^{\circ}\) angle with a protractor:
- Start by drawing a horizontal line across the page, 2 in long.
 Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)- Place an endpoint at the left side of your line.
- Place the protractor on this point, such that the line passes through the \( 0 ^{\circ}\) mark on the protractor and the endpoint is at the center. Mark \( 50 ^{\circ}\) on the appropriate scale.
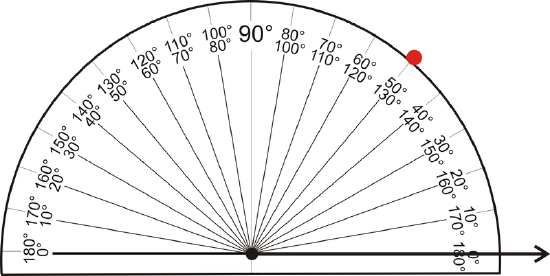 Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)- Remove the protractor and connect the vertex and the \(50 ^{\circ}\) mark.
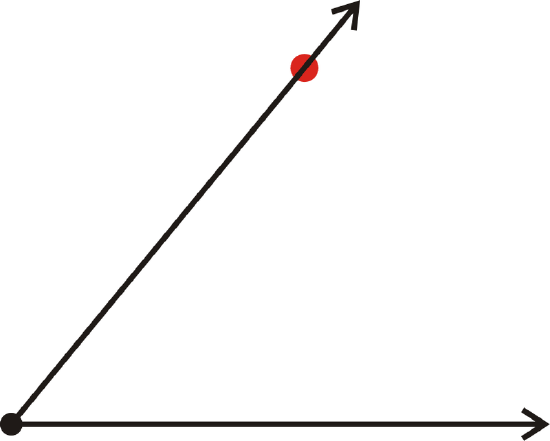 Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)This process can be used to draw any angle between \(0 ^{\circ}\) and \(180 ^{\circ}\).
When two smaller angles form to make a larger angle, the sum of the measures of the smaller angles will equal the measure of the larger angle. This is called the Angle Addition Postulate. So, if B is on the interior of \(\angle ADC\), then
\(\angle ADC = m \angle ADB + \angle BDC\)
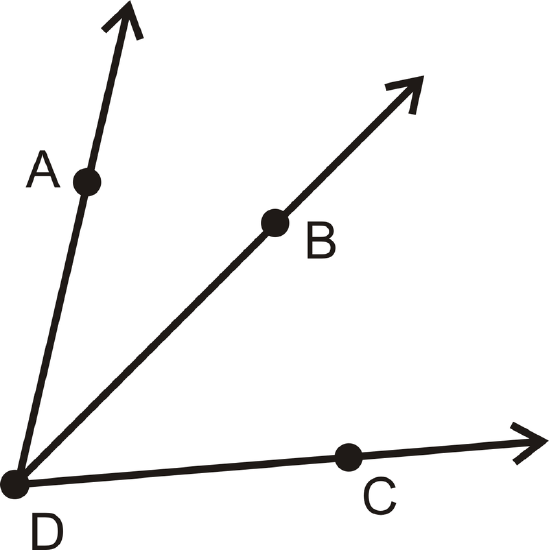 Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
How many angles are in the picture below? Label each one.
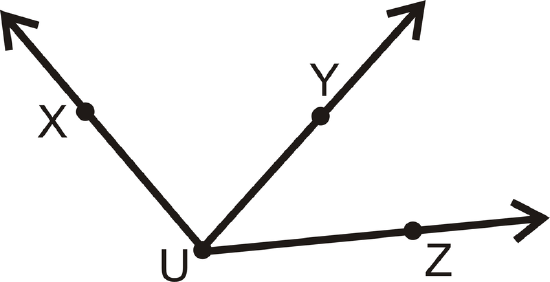 Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)Solution
There are three angles with vertex \(U\). It might be easier to see them all if we separate them.
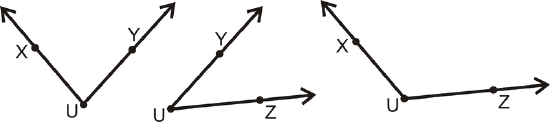 Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)So, the three angles can be labeled, ( \(\angle XUY\) or \(\angle YUX\)), \(\angle YUZ\) (or \(\angle ZUY\)), and \(\angle XUZ\) (or \(\angle ZUX\)).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Measure the three angles from Example 1, using a protractor.
 Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)Solution
Just like in Example 1, it might be easier to measure these three angles if we separate them.
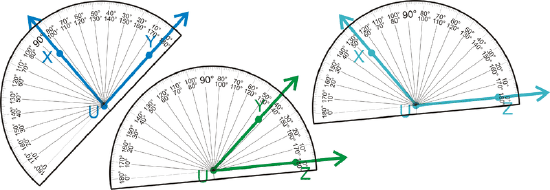 Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)With measurement, we put an m in front of the \(\angle\) sign to indicate measure. So, \(m \angle XUY = 84^{\circ}\), \(m \angle YUZ = 42^{\circ}\) and \(m \angle XUZ = 126^{\circ}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
What is the measure of the angle shown below?
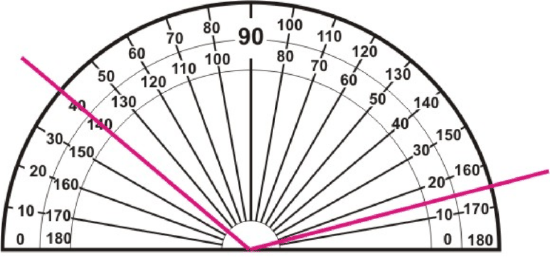 Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)Solution
This angle is not lined up with 0∘, so use subtraction to find its measure. It does not matter which scale you use, as long as you are consistent.
Inner scale: \(140^{\circ} - 15 ^{\circ} = 125 ^{\circ}\)
Outer scale: \(165^{\circ} - 40 ^{\circ} = 125 ^{\circ}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Use a protractor to measure \(\angle RST\) below.
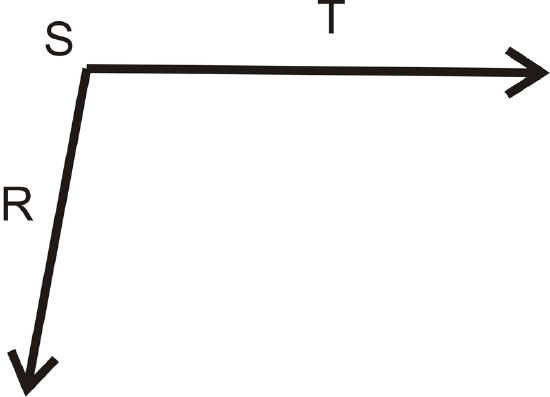 Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)Solution
Lining up one side with \(0 ^{\circ}\) on the protractor, the other side hits \(100 ^{\circ}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
What is \(m \angle QRT\) in the diagram below?
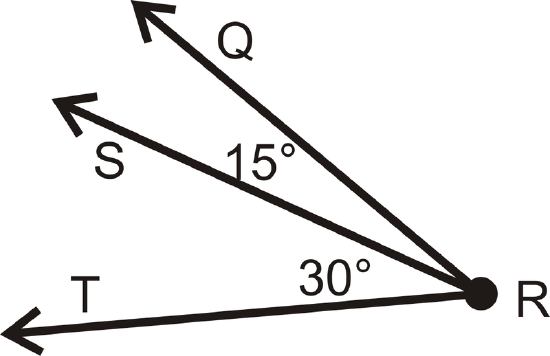 Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)Solution
Using the Angle Addition Postulate, \(m\angle QRT = 15^{\circ}+30^{\circ}=45^{\circ}\).
Review
1. What is \(m \angle LMN\) if \(m \angle LMO = 85^{\circ}\) and \(m \angle NMO = 53^{\circ}\)?
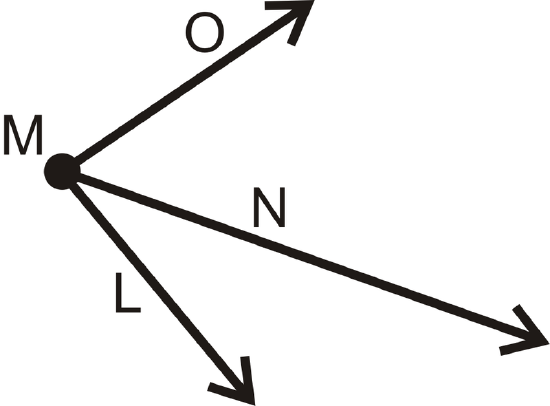 Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)2. If \(m \angle ABD = 100^{\circ}\), find \(x\).
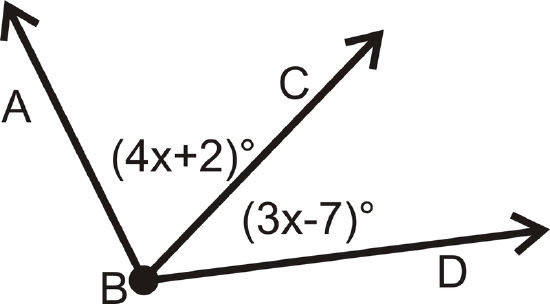 Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)For questions 3-6, determine if the statement is true or false.
- For an angle \(\angle ABC\),\(C\) is the vertex.
- For an angle \(\angle ABC\), \(\overline{AB}\) and \(\overline{BC}\) are the sides.
- The \(m\) in front of \(m \angle ABC\) means measure.
- The Angle Addition Postulate says that an angle is equal to the sum of the smaller angles around it.
For 7-12, draw the angle with the given degree, using a protractor and a ruler.
- \(55 ^{\circ}\)
- \(92 ^{\circ}\)
- \(178 ^{\circ}\)
- \(5 ^{\circ}\)
- \(120 ^{\circ}\)
- \(73 ^{\circ}\)
For 13-16, use a protractor to determine the measure of each angle.
-
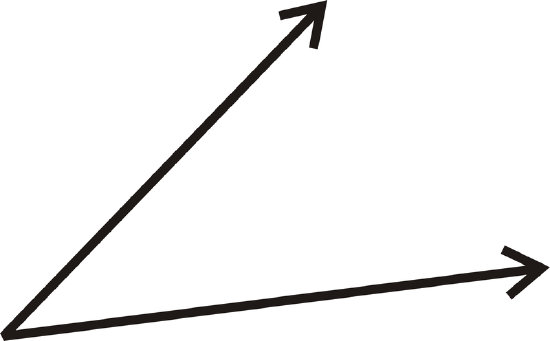 Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\) -
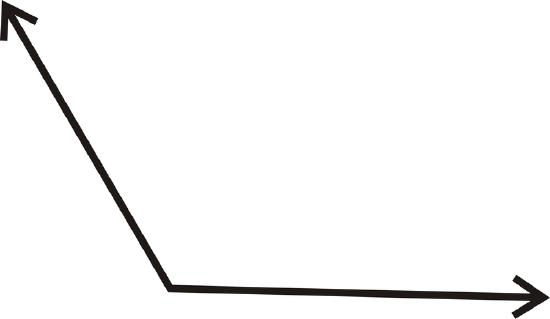 Figure \(\PageIndex{18}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{18}\) -
 Figure \(\PageIndex{19}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{19}\) -
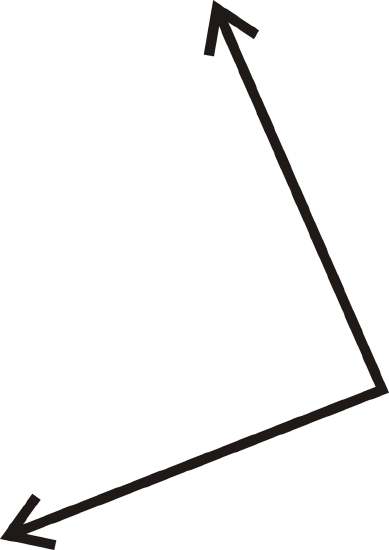 Figure \(\PageIndex{20}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{20}\)
Solve for \(x\).
- \(m \angle ADC = 56^{\circ}\)
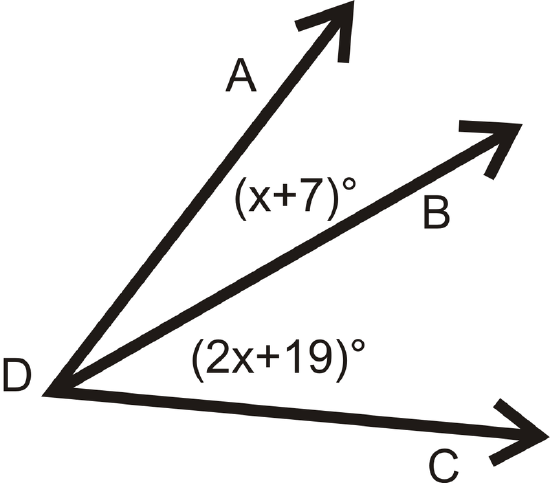 Figure \(\PageIndex{21}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{21}\)Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 1.5.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Angle | A geometric figure formed by two rays that connect at a single point or vertex. |
| Protractor | A protractor is a tool used to measure an angle in terms of degrees. |
| Vertex | A vertex is a point of intersection of the lines or rays that form an angle. |
Additional Resource
Interactive Element
Video: Angle Basics
Activities: Angle Measurement Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Angles Study Guide
Practice: Measuring Angles
Real World: Angle Measurement

