5.18: Area and Perimeter of Composite Shapes
- Page ID
- 5002
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Find area and perimeter of figures made up of two or more common shapes.
Area of Composite Shapes
Perimeter is the distance around a shape. The perimeter of any figure must have a unit of measurement attached to it. If no specific units are given (feet, inches, centimeters, etc.), write “units.”
Area is the amount of space inside a figure. If two figures are congruent, they have the same area (Congruent Areas Postulate).
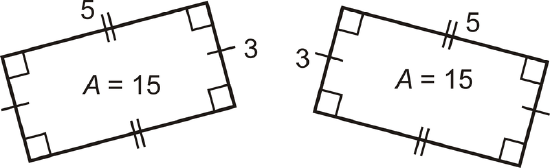
A composite shape is a shape made up of other shapes. To find the area of such a shape, simply find the area of each part and add them up.
Area Addition Postulate: If a figure is composed of two or more parts that do not overlap each other, then the area of the figure is the sum of the areas of the parts.
Consider a basic house drawn as a triangle on top of a square. How could you find the area of this composite shape?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Find the area of the figure below. All angles that look like right angles are right angles.
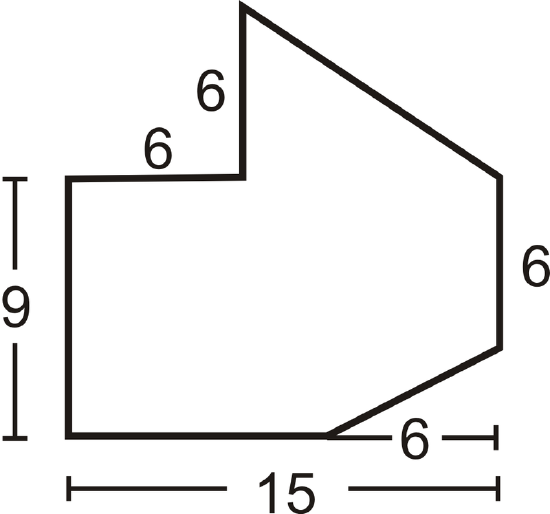
Solution
Divide the figure into a triangle and a rectangle with a small rectangle cut out of the lower right-hand corner.
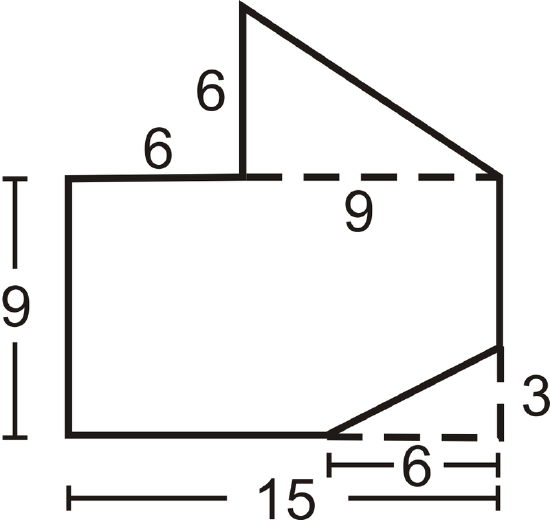
\(A=A_{\text{top triangle}}+A_{\text{rectangle}}−A_{\text{small triangle}} \\ A=(\dfrac{1}{2} \cdot 6\cdot 9)+(9\cdot 15))−(\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot 3\cdot 6) \\ A&=27+135−9 \\ A&=153\text{ units}^2\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Divide the shape into two rectangles and one triangle. Find the area of the two rectangles and triangle. All angles that look like right angles are right angles.
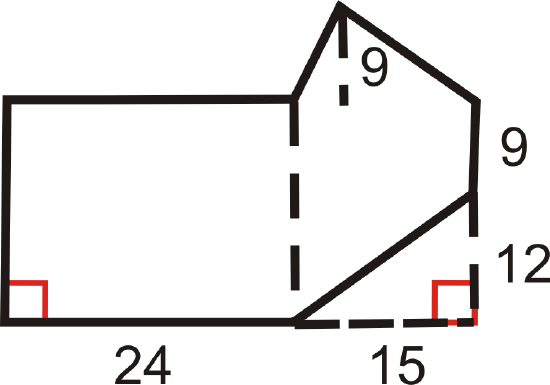
Solution
Rectangle #1: \(\text{Area} =24(9+12)=504\text{ units}^2\)
Rectangle #2: \(\text{Area}=15(9+12)=315\text{ units}^2\)
Triangle: \(\text{Area} =15(9)2=67.5\text{ units}^2\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find the area of the entire shape from Example 2 (you will need to subtract the area of the small triangle in the lower right-hand corner).
Solution
\(\text{Total Area} =504+315+67.5−\dfrac{15(12)}{2}=796.5 \text{ units}^2\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
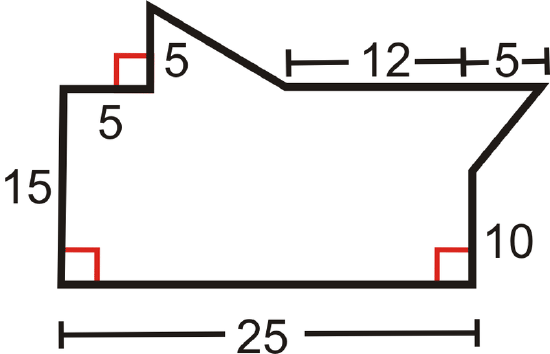
All angles that look like right angles are right angles.
- Divide the shape into two triangles and one rectangle.
- Find the area of the two triangles and rectangle.
- Find the area of the entire shape.
Solution
- One triangle on the top and one on the right, the rest of the shape is a rectangle.
- The area of the triangle on top is \(\dfrac{8(5)}{2}=20\text{ units}^2\). The area of the triangle on the right is \(\dfrac{5(5)}{2}=12.5\text{ units}^2\). The area of the rectangle is \(375\text{ units}^2\).
- The total area is \(407.5\text{ units}^2\).
Review
Use the picture below for questions 1-4. The composite shape is formed of a square within a square.
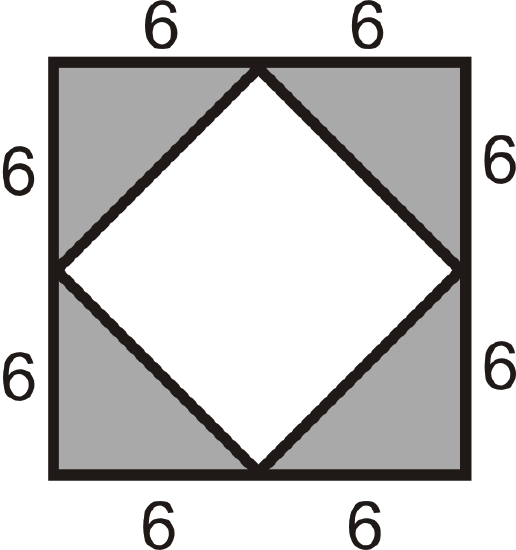
- Find the area of the outer square.
- Find the area of one grey triangle.
- Find the area of all four grey triangles.
- Find the area of the inner square.
Find the areas of the figures below. You may assume all sides are perpendicular.
-
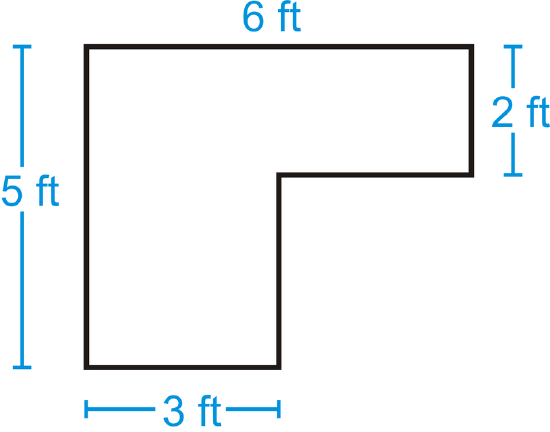
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) -
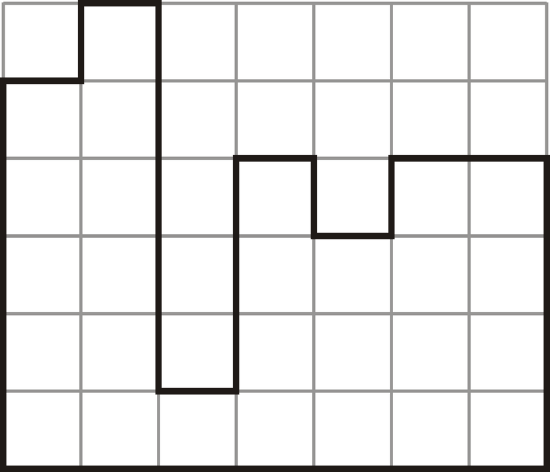
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Find the areas of the composite figures.
-
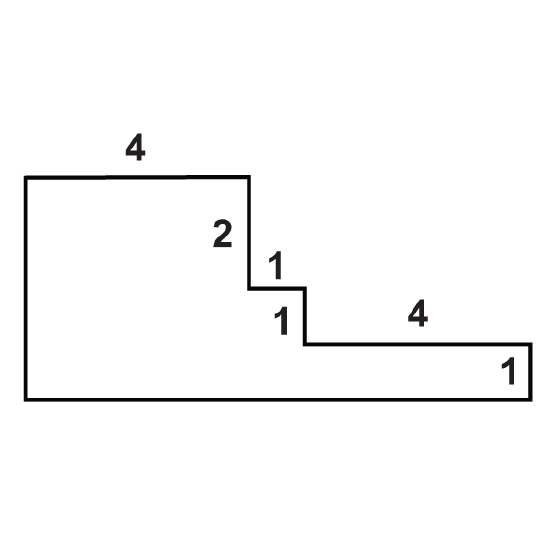
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) -
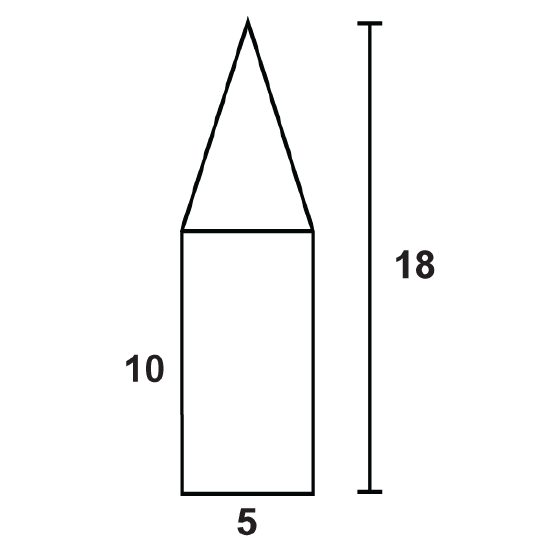
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) -
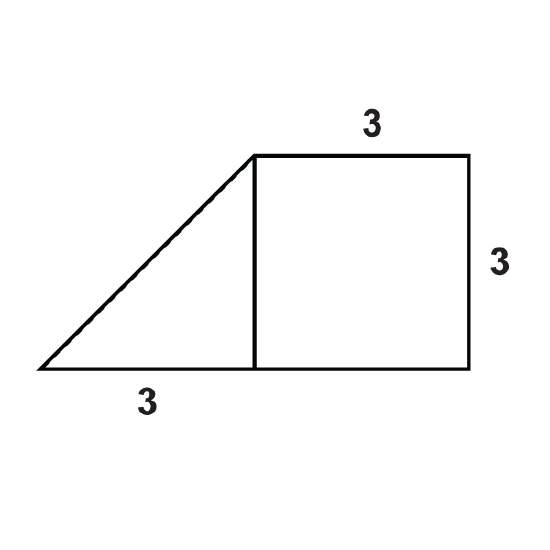
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -
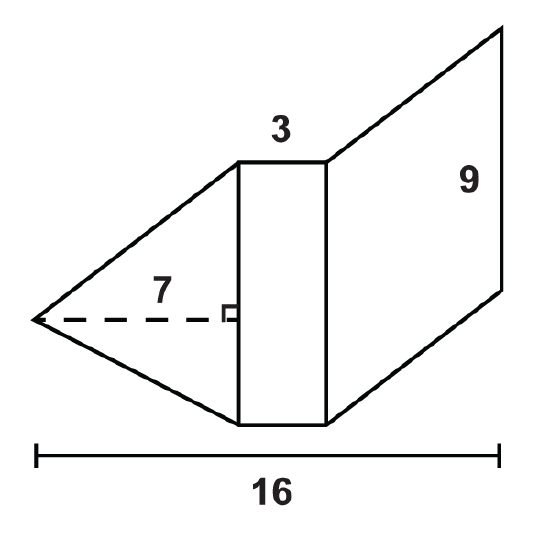
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -
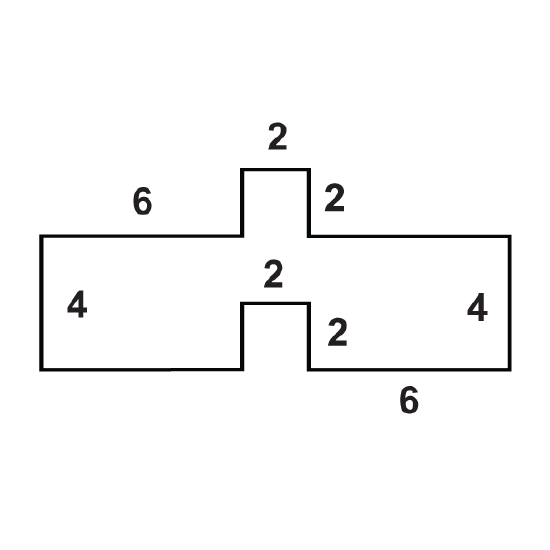
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\) -
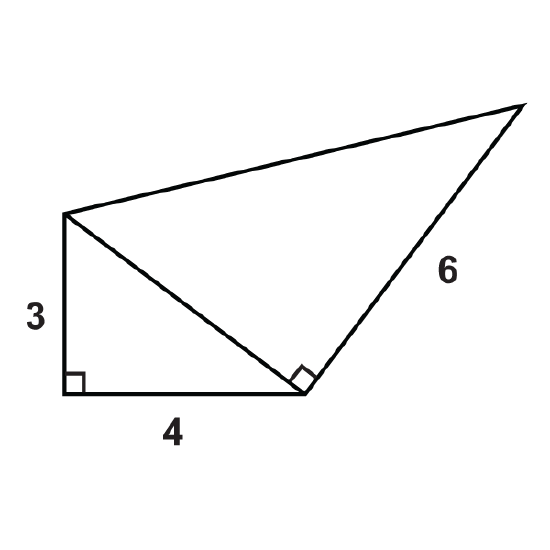
Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)
Use the figure to answer the questions.
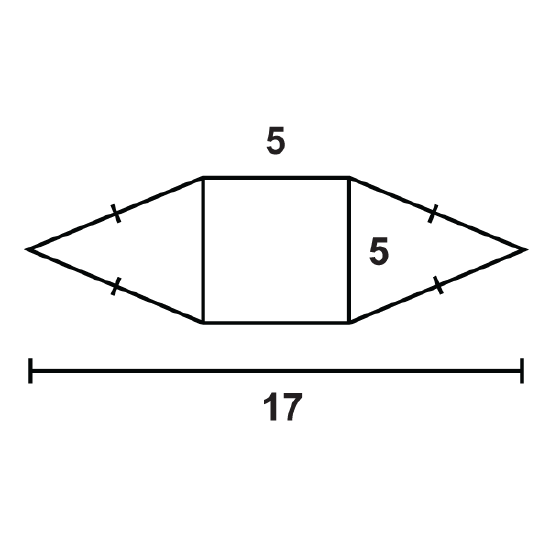
- What is the area of the square?
- What is the area of the triangle on the left?
- What is the area of the composite figure?
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 10.6.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| area | The amount of space inside a figure. Area is measured in square units. |
| composite shape | A shape made up of other shapes. |
| perimeter | The distance around a shape. The perimeter of any figure must have a unit of measurement attached to it. If no specific units are given (feet, inches, centimeters, etc), write units. |
| Composite | A number that has more than two factors. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Area of a Triangle (Whole Numbers)
Activites: Area of Composite Shapes Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Perimeter and Area Study Guide
Practice: Area and Perimeter of Composite Shapes

