7.6: Indirect Measurement Applications
- Page ID
- 2160
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Use ratios and proportions to solve for missing lengths in similar figures in real world situations.
Indirect Measurement
An application of similar triangles is to measure lengths indirectly. You can use this method to measure the width of a river or canyon or the height of a tall object. The idea is that you model a situation with similar triangles and then use proportions to find the missing measurement indirectly.
What if you were standing next to a building and wanted to know how tall the building was? How could you use your own height and the length of the shadows cast by you and the building to determine the building's height?
For Examples 1, 2, and 3, use the following information:
In order to estimate the width of a river, the following technique can be used. Use the diagram.
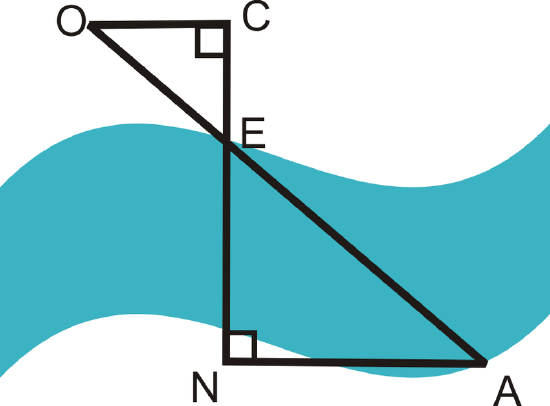
Place three markers, \(O\), \(C\), and \(E\) on the upper bank of the river. \(E\) is on the edge of the river and \(\overline{OC}\perp \overline{CE}\). Go across the river and place a marker, \(N\) so that it is collinear with \(C\) and \(E\). Then, walk along the lower bank of the river and place marker A\), so that \(\overline{CN}\perp \overline{NA}\). \(OC=50 feet\), \(CE=30\: feet\), \(NA=80\: feet\).
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Is \(\Delta OCE\sim \Delta ANE\)? How do you know?
Solution
Yes. \(\angle C\cong \angle N\) because they are both right angles. \(\angle OEC\cong \angle AEN\) because they are vertical angles. This means \(\Delta OCE\sim \Delta ANE\) by the AA Similarity Postulate.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Is \(\overline{OC}\parallel \overline{NA}\)? How do you know?
Solution
Since the two triangles are similar, we must have \(\angle EOC\cong \angle EAN\). These are alternate interior angles. When alternate interior angles are congruent then lines are parallel, so \(\overline{OC}\parallel \overline{NA}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
What is the width of the river? Find \(EN\).
Solution
Set up a proportion and solve by cross-multiplying.
\(\dfrac{30\: ft}{EN}=\dfrac{50\: ft}{80\: ft}\)
\(50(EN)=2400\)
\(EN=48\)
The river is 48 feet wide.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
A tree outside Ellie’s building casts a 125 foot shadow. At the same time of day, Ellie casts a 5.5 foot shadow. If Ellie is 4 feet 10 inches tall, how tall is the tree?
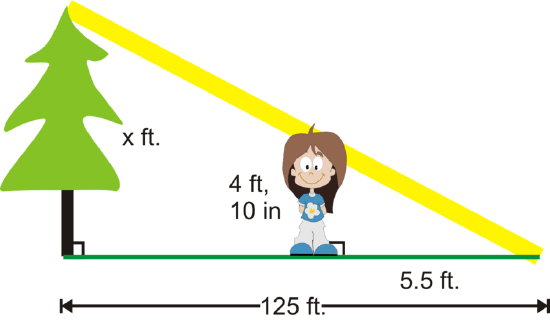
Solution
To solve, start by drawing a picture. We see that the tree and Ellie are parallel, so the two triangles are similar.
\(\dfrac{4\: ft,10\: in}{x}=\dfrac{5.5\: ft}{125\: ft}\)
The measurements need to be in the same units. Change everything into inches and then we can cross multiply.
\(\dfrac{58\: in}{x}=\dfrac{66\: in}{1500\: in}\)
\(87000=66x\)
\(x\approx 1318.\overline{18} in or 109.85\: ft\)
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Cameron is 5 ft tall and casts a 12 ft shadow. At the same time of day, a nearby building casts a 78 ft shadow. How tall is the building?
Solution
To solve, set up a proportion that compares height to shadow length for Cameron and the building. Then solve the equation to find the height of the building. Let x represent the height of the building.
\dfrac{5ft}{12\: ft}=\dfrac{x}{78\: ft}\)
12x=390\)
x=32.5\: ft\)
The building is 32.5 feet tall.
Review
The technique from the guided practice section was used to measure the distance across the Grand Canyon. Use the picture below and \(OC=72\: ft\), \(CE=65\: ft\), and \(NA=14,400\: ft\) for problems 1 - 3.

1. Find \(EN\) (the distance across the Grand Canyon).
2. Find \(OE\).
3. Find \(EA\).
4. Mark is 6 ft tall and casts a 15 ft shadow. A the same time of day, a nearby building casts a 30 ft shadow. How tall is the building?
5. Karen and Jeff are standing next to each other. Karen casts a 10 ft shadow and Jeff casts an 8 ft shadow. Who is taller? How do you know?
6. Billy is 5 ft 9 inches tall and Bobby is 6 ft tall. Bobby's shadow is 13 feet long. How long is Billy's shadow?
7. Sally and her little brother are walking to school. Sally is 4 ft tall and has a shadow that is 3 ft long. Her little brother's shadow is 2 ft long. How tall is her little brother?
8. Ryan is outside playing basketball. He is 5 ft tall and at this time of day is casting a 12 ft shadow. The basketball hoop is 10 ft tall. How long is the basketball hoop's shadow?
9. Jack is standing next to a very tall tree and wonders just how tall it is. He knows that he is 6 ft tall and at this moment his shadow is 8 ft long. He measures the shadow of the tree and finds it is 90 ft. How tall is the tree?
10. Thomas, who is 4 ft 9 inches tall is casting a 6 ft shadow. A nearby building is casting a 42 ft shadow. How tall is the building?
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| AA Similarity Postulate | If two angles in one triangle are congruent to two angles in another triangle, then the two triangles are similar. |
| Proportion | A proportion is an equation that shows two equivalent ratios. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Scale and Indirect Measurements
Activities: Indirect Measurement Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Polygon Similarity Study Guide
Practice: Indirect Measurement Applications
Real World: Mighty Measurements

