9.7: Composite Solids
- Page ID
- 6193
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Solids made up of two or more solids.
A composite solid is a solid that is composed, or made up of, two or more solids. The solids that it is made up of are generally prisms, pyramids, cones, cylinders, and spheres. In order to find the surface area and volume of a composite solid, you need to know how to find the surface area and volume of prisms, pyramids, cones, cylinders, and spheres. For more information on any of those specific solids, consult the concept that focuses on them. This concept will assume knowledge of those five solids.
Most composite solids problems that you will see will be about volume, so most of the examples and practice problems below are about volume. There is one surface area example as well.
What if you built a solid three-dimensional house model consisting of a pyramid on top of a square prism? How could you determine how much two-dimensional and three-dimensional space that model occupies?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Find the volume of the following solid.
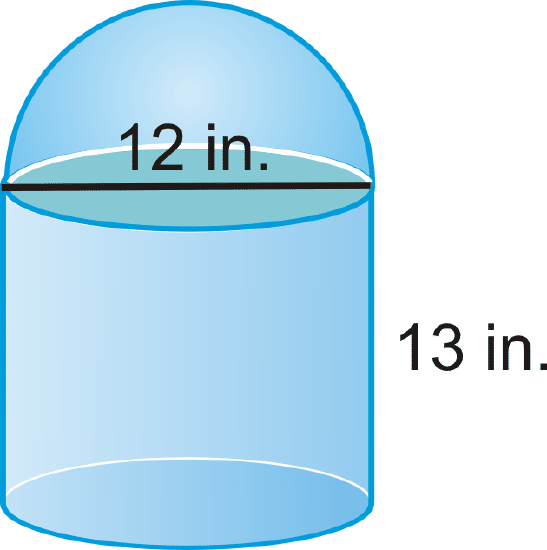
Solution
Use what you know about cylinders and spheres. The top of the solid is a hemisphere.
\(\begin{aligned} V_{cylinder}&= \pi 6^{2}(13)=468 \pi \\ V_{hemisphere}&=12(\dfrac{4}{3} \pi 6^{3})=144 \pi \\ V_{total}&=468 \pi +144 \pi =612 \pi \text{ in}^{3} \end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find the volume of the base prism. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
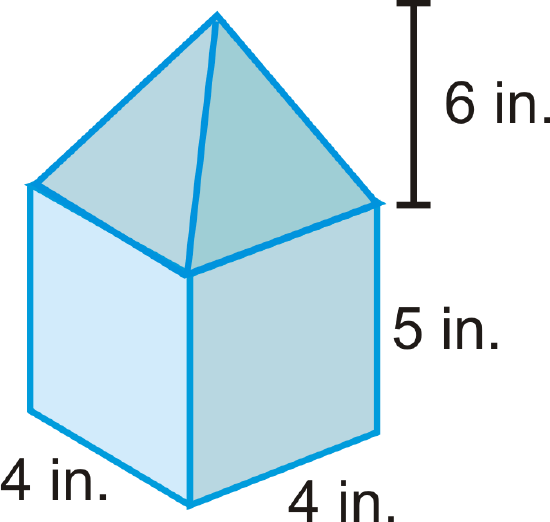
Solution
Use what you know about prisms.
\(\begin{aligned} V_{prism}=B\cdot h \\ V_{prism}=(4\cdot 4)\cdot 5 \\ V_{prism}=80\text{ in}^{3}\end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find the volume of the solid below.
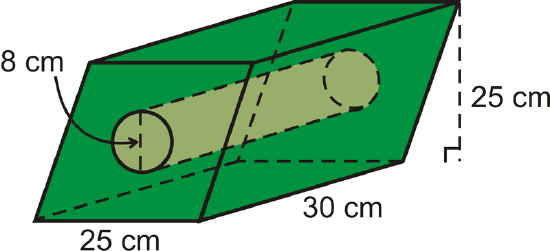
Solution
This solid is a parallelogram-based prism with a cylinder cut out of the middle.
\(\begin{aligned} V_{prism}=(25\cdot 25)30=18,750\text{ cm}^{3} \\ V_{cylinder}= \pi (4)^{2}(30)=480 \pi \text{ cm}^{3}\end{aligned}\)
The total volume is \(18750−480 \pi \approx 17,242.04 cm^{3}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Find the volume of the composite solid. All bases are squares.
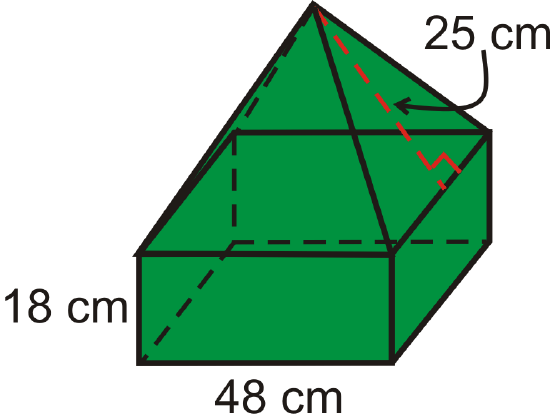
Solution
This is a square prism with a square pyramid on top. First, we need the height of the pyramid portion. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we have, \(h=\sqrt{25^{2}−24^{2}}=7\).
\(\begin{aligned} V_{prism}&=(48)(48)(18)=41,472\text{ cm}^{3} \\ V_{pyramid}&=\dfrac{1}{3}(48^{2})(7)=5376\text{ cm}^{3}\end{aligned}\)
The total volume is \(41,472+5376=46,848 cm^{3}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Find the surface area of the following solid.

Solution
This solid is a cylinder with a hemisphere on top. It is one solid, so do not include the bottom of the hemisphere or the top of the cylinder.
\(\begin{aligned}SA&=LA_{cylinder}+LA_{hemisphere}+A_{base\: circle} \\ &=2 \pi rh+\dfrac{1}{2}4 \pi r^{2}+ \pi r^{2} \\ &=2 \pi (6)(13)+2 \pi 6^{2}+ \pi 6^{2} \\ &=156 \pi +72 \pi +36 \pi \\ &=264 \pi in^{2}\end{aligned}\)
“LA” stands for lateral area.
Review
Round your answers to the nearest hundredth. The solid below is a cube with a cone cut out.
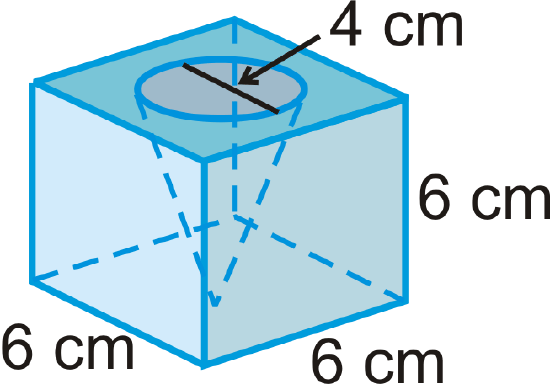
- Find the volume of the cube.
- Find the volume of the cone.
- Find the volume of the entire solid.
The solid below is a cylinder with a cone on top.
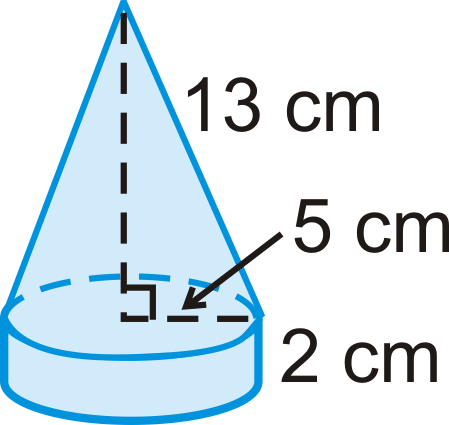
- Find the volume of the cylinder.
- Find the volume of the cone.
- Find the volume of the entire solid.
-
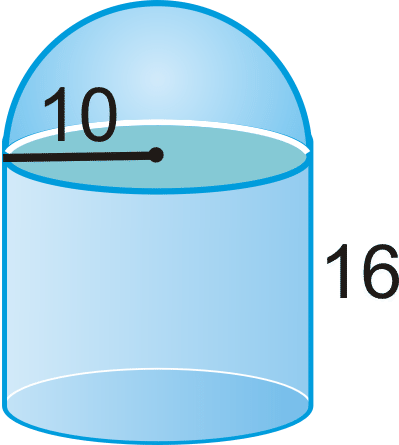
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
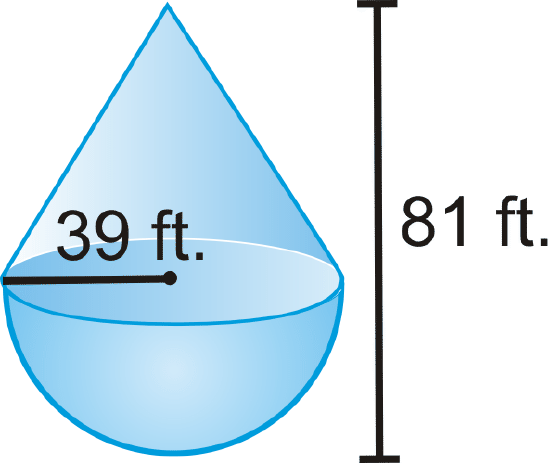
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) - You may assume the bottom is open.
Find the volume of the following shapes. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth.
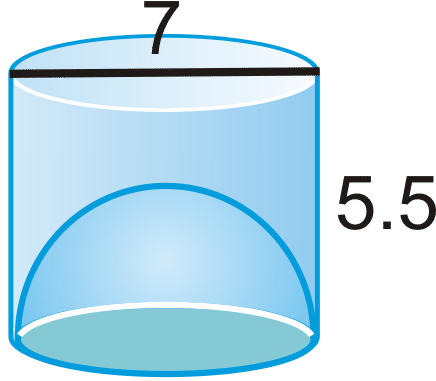
-

Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -

Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -

Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Copy and Paste Caption here. (Copyright; author via source) - A sphere has a radius of 5 cm. A right cylinder has the same radius and volume. Find the height of the cylinder.
The bases of the prism are squares and a cylinder is cut out of the center.
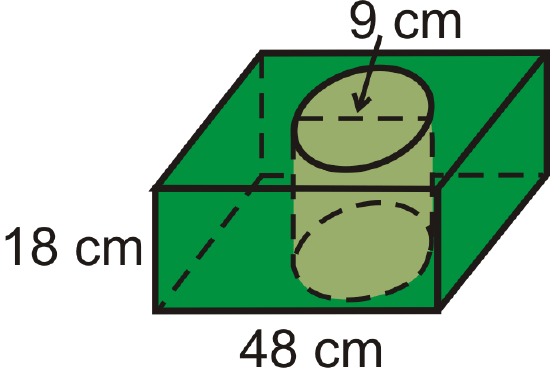 Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)- Find the volume of the prism.
- Find the volume of the cylinder in the center.
- Find the volume of the figure.
This is a prism with half a cylinder on the top.
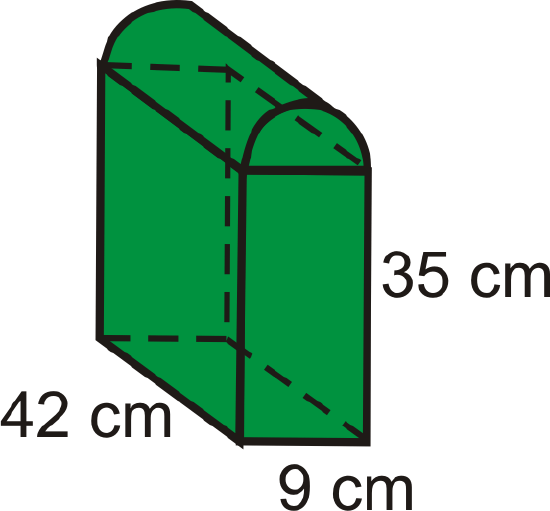 Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)- Find the volume of the prism.
- Find the volume of the half-cylinder.
- Find the volume of the entire figure.
Tennis balls with a 3 inch diameter are sold in cans of three. The can is a cylinder. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth.
 Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)
Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)- What is the volume of one tennis ball?
- What is the volume of the cylinder?
- Assume the balls touch the can on the sides, top and bottom. What is the volume of the space not occupied by the tennis balls?
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 11.8.
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| composite solid | A solid that is composed, or made up of, two or more solids. |
| volume | A three-dimensional measurement that is a measure of how much three-dimensional space a solid occupies. |
| Pythagorean Theorem | The Pythagorean Theorem is a mathematical relationship between the sides of a right triangle, given by \(a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}\), where a and b are legs of the triangle and c is the hypotenuse of the triangle. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Composite Solids Principles - Basic
Activities: Composite Solids Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Surface Area and Volume Study Guide
Practice: Composite Solids
Real World: Nature's Arches

