4.43: 30-60-90 Right Triangles
- Page ID
- 4984
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Hypotenuse equals twice the smallest leg, while the larger leg is \(\sqrt{3}\) times the smallest.
One of the two special right triangles is called a 30-60-90 triangle, after its three angles.
30-60-90 Theorem: If a triangle has angle measures \(30^{\circ}\), \(60^{\circ}\) and \(90^{\circ}\), then the sides are in the ratio \(x:x\sqrt{3}:2x\).
The shorter leg is always x, the longer leg is always \(x\sqrt{3}\), and the hypotenuse is always \(2x\). If you ever forget these theorems, you can still use the Pythagorean Theorem.
What if you were given a 30-60-90 right triangle and the length of one of its side? How could you figure out the lengths of its other sides?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Find the value of \(x\) and \(y\).
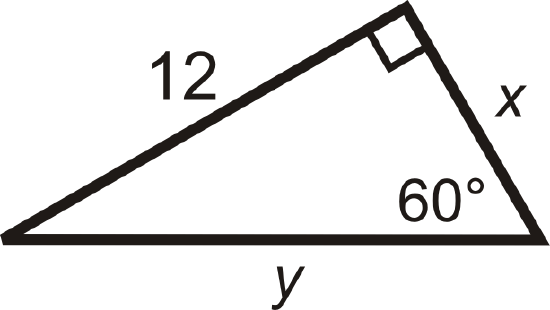
Solution
We are given the longer leg.
\(\begin{aligned} &x\sqrt{3} =12 \\ &x=\dfrac{12}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{12\sqrt{3}}{3}=4\sqrt{3} \\ &\text{The hypotenuse is} \\ &y=2(4\sqrt{3})=8\sqrt{3}\end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Find the value of \(x\) and \(y\).
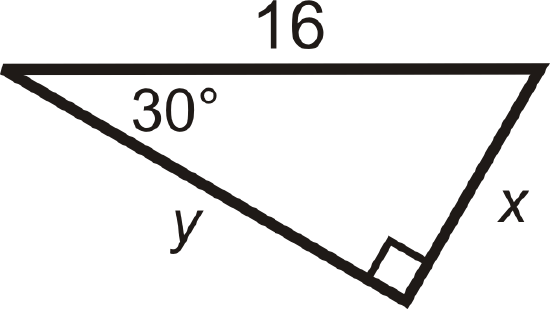
Solution
We are given the hypotenuse.
\(\begin{aligned}&2x=16 \\ &x=8 \\ &\text{The longer leg is} \\ &y=8\cdot \sqrt{3}=8\sqrt{3}\end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Find the length of the missing sides.
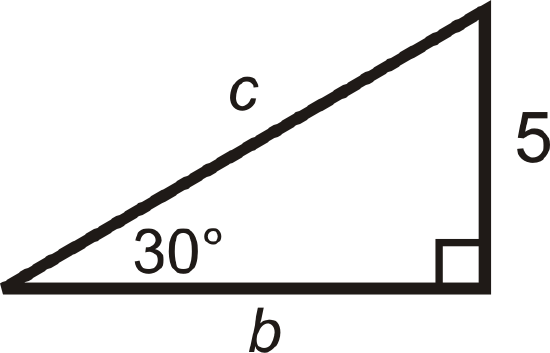
Solution
We are given the shorter leg. If \(x=5\), then the longer leg, \(b=5\sqrt{3}\), and the hypotenuse, \(c=2(5)=10\).
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Find the length of the missing sides.
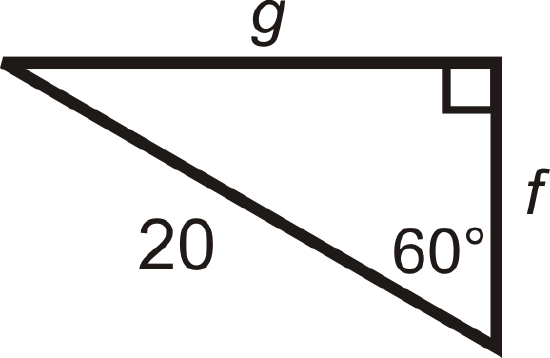
Solution
We are given the hypotenuse. \(2x=20\), so the shorter leg, \(f=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\), and the longer leg, \(g=10\sqrt{3}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
A rectangle has sides 4 and \(4\sqrt{3}\). What is the length of the diagonal?
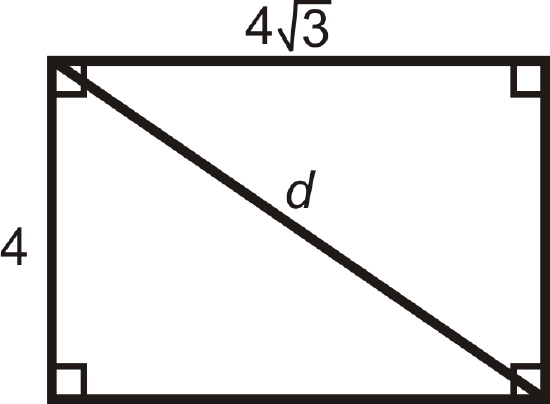
Solution
The two lengths are \(x\), \(x\sqrt{3}\), so the diagonal would be \(2x\), or \(2(4)=8\).
If you did not recognize this is a 30-60-90 triangle, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem too.
\(\begin{aligned} 4^2+(4\sqrt{3})^2&=d^2 \\ 16+48&=d^2 \\ d&=\sqrt{64}=8\end{aligned}\)
Review
- In a 30-60-90 triangle, if the shorter leg is 5, then the longer leg is __________ and the hypotenuse is ___________.
- In a 30-60-90 triangle, if the shorter leg is x, then the longer leg is __________ and the hypotenuse is ___________.
- A rectangle has sides of length 6 and \(6\sqrt{3}\). What is the length of the diagonal?
- Two (opposite) sides of a rectangle are 10 and the diagonal is 20. What is the length of the other two sides?
For questions 5-12, find the lengths of the missing sides. Simplify all radicals.
-
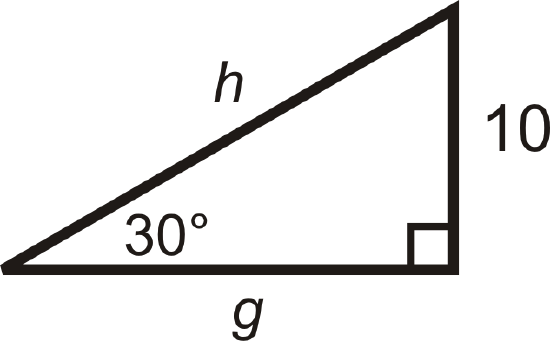
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) -
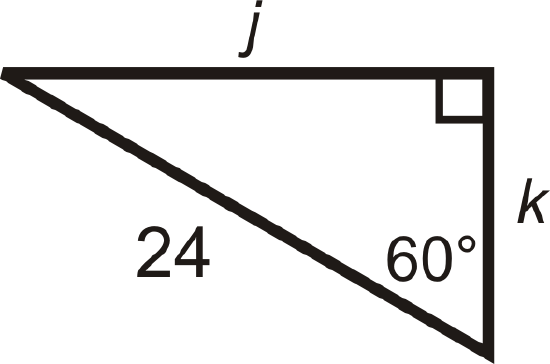
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) -
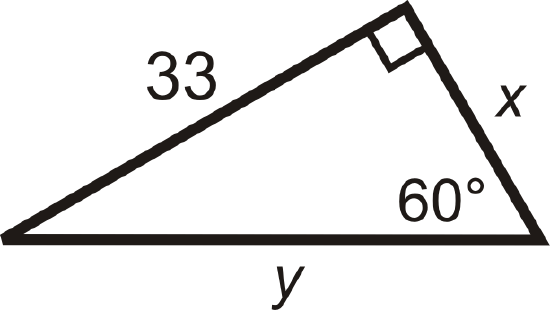
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\) -
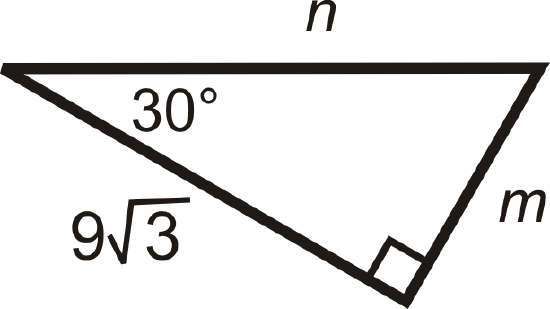
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) -
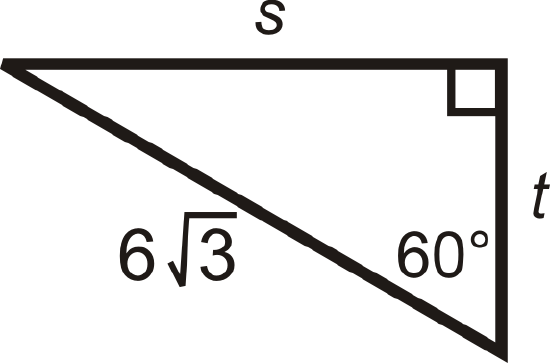
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) -
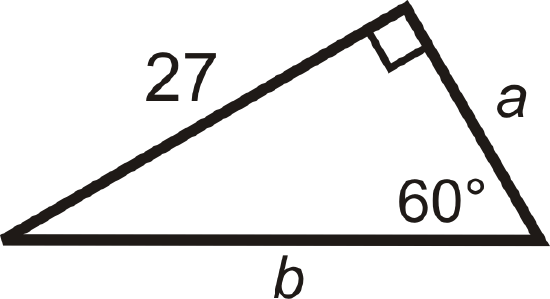
Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) -
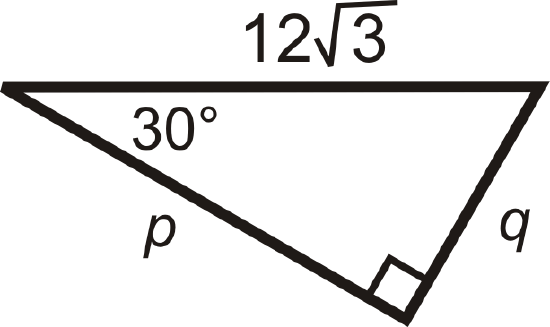
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\) -
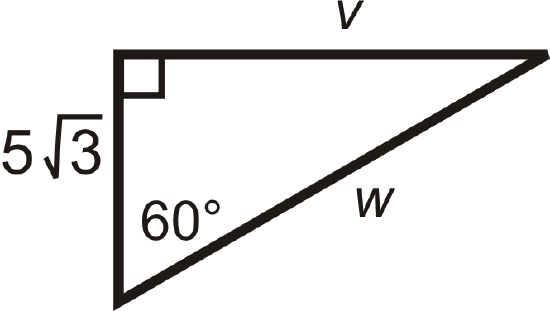
Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.6.
Resources
Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| 30-60-90 Theorem | If a triangle has angle measures of 30, 60, and 90 degrees, then the sides are in the ratio \(x : x \sqrt{3} : 2x\) |
| 30-60-90 Triangle | A 30-60-90 triangle is a special right triangle with angles of \(30^{\circ}\), \(60^{\circ}\), and \(90^{\circ}\). |
| Hypotenuse | The hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side of the right triangle. It is across from the right angle. |
| Legs of a Right Triangle | The legs of a right triangle are the two shorter sides of the right triangle. Legs are adjacent to the right angle. |
| Pythagorean Theorem | The Pythagorean Theorem is a mathematical relationship between the sides of a right triangle, given by \(a^2+b^2=c^2\), where a and b are legs of the triangle and c is the hypotenuse of the triangle. |
| Radical | The \(\sqrt\), or square root, sign. |
Additional Resources
Interactive Element
Video: Solving Special Right Triangles
Activities: 30-60-90 Right Triangles Discussion Questions
Study Aids: Special Right Triangles Study Guide
Practice: 30-60-90 Right Triangles
Real World: Fighting the War on Drugs Using Geometry and Special Triangles

